User:Milton Beychok/Sandbox: Difference between revisions
imported>Milton Beychok |
imported>Milton Beychok |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
{{Image|UBA Organization.png|center|600px|Organization chart of the UBA.<ref name=Umwelt/><ref>[http://www.umweltbundesamt.de/uba-info-e/uba-organisation-druckversion.pdf Umweltbundesamt for our environment, Organizational Chart] As of November 26, 2010]</ref>}} | {{Image|UBA Organization.png|center|600px|Organization chart of the UBA.<ref name=Umwelt/><ref>[http://www.umweltbundesamt.de/uba-info-e/uba-organisation-druckversion.pdf Umweltbundesamt for our environment, Organizational Chart] As of November 26, 2010]</ref>}} | ||
==Major | ==Major tasks and issues== | ||
The | The major tasks and issues for which the UBA is responsible may be summarized as: | ||
{{col-begin}} | {{col-begin}} | ||
{{col-break|width= | {{col-break|width=40%}} | ||
* | * Agriculture and foodstuffs industry | ||
* | * Air and air pollution control | ||
* | * Chemicals policy and pollutants | ||
* | * Climate change | ||
* | * Energy | ||
{{col-break|width= | * Environmental awareness and sustainable consumption | ||
* | * Environmental data | ||
* | * Environmental economics and management | ||
* | * Environmental laws and associational claims | ||
* | * Environmental monitoring | ||
* | * Environmental and spatial planning | ||
{{col-break|width=60%}} | |||
* German Emissions Trading Authority | |||
* Health and environmental hygiene | |||
* International and Antarctic environmental protection | |||
* Noise | |||
* Products | |||
* Resource conservation | |||
* Soil and contaminated sites | |||
* Technology processes and safety | |||
* Transport | |||
* Waste management | |||
* Water, drinking water and water protection | |||
{{col-end}} | {{col-end}} | ||
Revision as of 18:54, 11 December 2010
The Federal Environment Agency of Germany was founded in 1974 and is the central federal authority for environmental matters in Germany. The agency is commonly referred to as the UBA, an acronym for its German language name of Umweltbundesamt.
The UBA is part of Germany's Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety and is responsible for protecting the environment as well as human health and well-being from adverse environmental impacts. Its key mandates are:[1]
- To provide scientific support to the: Federal Ministries of Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety; Health; Education and Research; and Transport, Building and Urban Affairs.
- Implementation of environmental laws such as emissions trading, authorization (approval) of chemicals, pharmaceuticals and pesticides.
- To provide public information about environmental protection issues.
Organization and staffing
The UBA is headquartered in the city of Dessau and also has offices in the cities of Berlin, Langen, and Bad Elster as well as monitoring stations at seven other locations nationwide. As of 2009, the agency had a total staff of about 1,400 working at 13 locations and an annual budget of about €100,000,000. About 800 of the total staff work in the Dessau headquarters.[2][3]
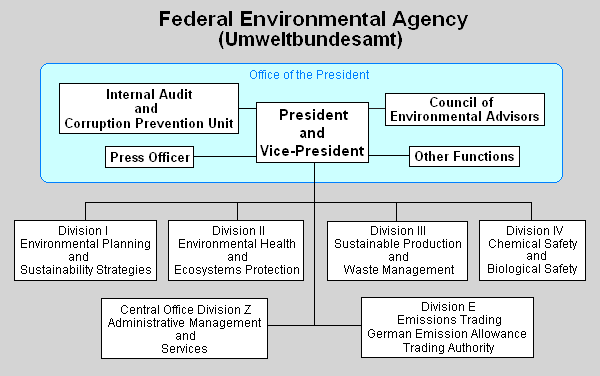
The UBA's organization chart is summarized below. The agency is governed by the Office of the President consisting of a President and a Vice-President, assisted by a Council of Environmental Advisors, an Internal Audit and Corruption Prevention Unit, a Press Officer and other functional entities.
As shown in the chart below, there are four operational groups (Division I, II, III and IV), an administrative management and services group (Division Z) and a special group for air pollution emissions trading (Division E). Most of the functions depicted in the chart are located in the headquarters site in Dessau, but some are in Berlin and the other locations (Langen and Bad Elster).
Major tasks and issues
The major tasks and issues for which the UBA is responsible may be summarized as:
|
|
Air quality and air pollution control
References
- ↑ Get to know us: Mandate and Organization From the English version website of the Umweltbundesamt (UBA)
- ↑ Network of the Heads of Environmental Protection Agencies: Germany
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Umweltbundesamt Federal Environment Agency for People and the Environment
- ↑ Umweltbundesamt for our environment, Organizational Chart As of November 26, 2010]