imported>Milton Beychok |
|
| (636 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| '''Reconstruction''' was the attempt from 1865 to 1877 in American history to resolve the issues of the [[American Civil War]], when both the Confederacy and slavery were destroyed. Reconstruction addressed the return of the Southern states that had seceded, the status of ex-Confederate leaders, and the Constitutional and legal status of the African-American Freedmen (newly freed ex-slaves). Violent controversy arose over how to accomplish those tasks, and by the late 1870s Reconstruction had failed to equally integrate the Freedmen into the legal, political, economic and social system. "Reconstruction" is also the common name for the entire history of the era 1865 to 1877.
| | {{AccountNotLive}} |
| | __NOTOC__ |
| | [[File:Crude oil-fired power plant.jpg|thumb|right|225px|Industrial air pollution source]] |
| | Atmospheric dispersion modeling is the mathematical simulation of how air pollutants disperse in the ambient atmosphere. It is performed with computer programs that solve the mathematical equations and algorithms which simulate the pollutant dispersion. The dispersion models are used to estimate or to predict the downwind concentration of air pollutants emitted from sources such as industrial plants, vehicular traffic or accidental chemical releases. |
|
| |
|
| Reconstruction came in three phases. '''Presidential Reconstruction 1863-66''' was controlled by Presidents [[Abraham Lincoln]] and [[Andrew Johnson]], with the goal of speedily reuniting the country. Their moderate programs were opposed by the [[Radical Republicans]], a political faction that gained power after the 1866 elections and began '''Radical Reconstruction, 1866-1873''' emphasizing civil rights and voting rights for the Freedmen. A Republican coalition of Freedmen, [[Carpetbagger]]s and [[Scalawag]]s controlled most of the southern states. In the so-called '''Redemption, 1873-77''', white supremacist Southerners (calling themselves "[[Redeemers]]") defeated the Republicans and took control of each southern state, marking the end of '''Reconstruction'''.
| | Such models are important to governmental agencies tasked with protecting and managing the ambient air quality. The models are typically employed to determine whether existing or proposed new industrial facilities are or will be in compliance with the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) in the United States or similar regulations in other nations. The models also serve to assist in the design of effective control strategies to reduce emissions of harmful air pollutants. During the late 1960's, the Air Pollution Control Office of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA) initiated research projects to develop models for use by urban and transportation planners.<ref>J.C. Fensterstock et al, "Reduction of air pollution potential through environmental planning", ''JAPCA'', Vol. 21, No. 7, 1971.</ref> |
|
| |
|
| ==Policy Issues==
| | Air dispersion models are also used by emergency management personnel to develop emergency plans for accidental chemical releases. The results of dispersion modeling, using worst case accidental releases and meteorological conditions, can provide estimated locations of impacted areas and be used to determine appropriate protective actions. At industrial facilities in the United States, this type of consequence assessment or emergency planning is required under the Clean Air Act (CAA) codified in Part 68 of Title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations. |
|
| |
|
| There were conflicting theories of what the national government could and should do to restore the South to a normal status. The key constitutional provision was the national government must guarantee to every state a "republican form of government." Exactly what that meant was the issue. Radical Republican [[Charles Sumner]] argued that secession had destroyed statehood alone but the Constitution still extended its authority and its protection over individuals, as in the territories. [[Thaddeus Stevens]] and his followers viewed secession as having left the states in a status like newly conquered territory.
| | The dispersion models vary depending on the mathematics used to develop the model, but all require the input of data that may include: |
|
| |
|
| Congress rejected President Andrew Johnson's argument that he had the war power to decide what to do, since the war was now over. Congress decided it had the primary authority to decide because the Constitution said the Congress had to guarantee each state a republican form of government; the issue became how the core political values of [[Republicanism, U.S.|republicanism]] should operate in the South.
| | * Meteorological conditions such as wind speed and direction, the amount of atmospheric turbulence (as characterized by what is called the "stability class"), the ambient air temperature, the height to the bottom of any inversion aloft that may be present, cloud cover and solar radiation. |
| | * The emission parameters such the type of source (i.e., point, line or area), the mass flow rate, the source location and height, the source exit velocity, and the source exit temperature. |
| | * Terrain elevations at the source location and at receptor locations, such as nearby homes, schools, businesses and hospitals. |
| | * The location, height and width of any obstructions (such as buildings or other structures) in the path of the emitted gaseous plume as well as the terrain surface roughness (which may be characterized by the more generic parameters "rural" or "city" terrain). |
|
| |
|
| President [[Abraham Lincoln]] was the leader of the moderate Republicans and wanted to speed up Reconstruction and reunite the nation as soon as possible. Lincoln formally began Reconstruction in late 1863 with his [[Ten percent plan]], which went into operation in several states but which Radicals opposed. Lincoln vetoed the Radical plan, the [[Wade-Davis Bill]] of 1864. The opposing faction of [[Radical Republicans]] were much more skeptical of Southern intentions and demanded far more stringent federal action. Congressman [[Thaddeus Stevens]] and Senator [[Charles Sumner]] led the Radical Republicans. After [[Abraham Lincoln assassination|Lincoln's assassination]], President Andrew Johnson switched from the Radical to the moderate camp. He too favored voting rights for the 170,000 black veterans.
| | Many of the modern, advanced dispersion modeling programs include a pre-processor module for the input of meteorological and other data, and many also include a post-processor module for graphing the output data and/or plotting the area impacted by the air pollutants on maps. The plots of areas impacted usually include isopleths showing areas of pollutant concentrations that define areas of the highest health risk. The isopleths plots are useful in determining protective actions for the public and first responders. |
|
| |
|
| Republican leaders agreed that slavery and the [[Slave Power]] had to be permanently destroyed, and that all forms of Confederate nationalism had to be suppressed. Moderates said this could be easily accomplished as soon as Confederate armies surrendered and the Southern states repealed secession and ratified the 13th Amendment (which abolished slavery); all of which happened by September 1865, when Johnson felt Reconstruction was finished.
| | The atmospheric dispersion models are also known as atmospheric diffusion models, air dispersion models, air quality models, and air pollution dispersion models. |
|
| |
|
| By 1866, however, Johnson, with no party affiliation, broke with the moderate Republicans and aligned himself more with the Democrats who opposed equality and the Fourteenth Amendment. Radicals attacked the policies of Johnson, especially his veto of the Civil Rights Bill for the Freedmen.
| | ==Atmospheric layers== |
|
| |
|
| The House elections of 1866 decisively changed the balance of power, giving the Radicals control of Congress and enough votes to overcome Johnson's vetoes and even to impeach him. Johnson was acquitted by one vote, but he remained almost powerless regarding Reconstruction policy. Radicals used the Army to take over the South and give the vote to black men, and they took the vote away from an estimated 10,000 or 15,000 white men who had been Confederate officials or senior officers. The Radical stage lasted for varying lengths in the different states, where a Republican coalition of Freedmen, Scalawags, and Carpetbaggers took control and promoted modernization through railroads and public schools. They were charged with corruption by their opponents, the conservative–Democratic coalition, calling themselves "Redeemers" after 1870. Violence sponsored by the [[Ku Klux Klan]] was overcome by federal intervention.
| | Discussion of the layers in the Earth's atmosphere is needed to understand where airborne pollutants disperse in the atmosphere. The layer closest to the Earth's surface is known as the ''troposphere''. It extends from sea-level up to a height of about 18 km and contains about 80 percent of the mass of the overall atmosphere. The ''stratosphere'' is the next layer and extends from 18 km up to about 50 km. The third layer is the ''mesosphere'' which extends from 50 km up to about 80 km. There are other layers above 80 km, but they are insignificant with respect to atmospheric dispersion modeling. |
|
| |
|
| By 1877, however, Redeemers regained control of every state, and President [[Rutherford Hayes]] withdrew federal troops, causing the collapse of the remaining three Republican state governments. The 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments were permanent legacies. Bitterness from the heated partisanship of the era lasted well into the 20th century.
| | The lowest part of the troposphere is called the ''atmospheric boundary layer (ABL)'' or the ''planetary boundary layer (PBL)'' and extends from the Earth's surface up to about 1.5 to 2.0 km in height. The air temperature of the atmospheric boundary layer decreases with increasing altitude until it reaches what is called the ''inversion layer'' (where the temperature increases with increasing altitude) that caps the atmospheric boundary layer. The upper part of the troposphere (i.e., above the inversion layer) is called the ''free troposphere'' and it extends up to the 18 km height of the troposphere. |
|
| |
|
| ==Loyalty and Suffrage==
| | The ABL is the most important layer with respect to the emission, transport and dispersion of airborne pollutants. The part of the ABL between the Earth's surface and the bottom of the inversion layer is known as the ''mixing layer''. Almost all of the airborne pollutants emitted into the ambient atmosphere are transported and dispersed within the mixing layer. Some of the emissions penetrate the inversion layer and enter the free troposphere above the ABL. |
| ===Allow Rebels to vote?===
| |
|
| |
|
| Everyone agreed that only loyal Americans should be allowed to vote. Nearly all white southerners were willing to pledge future loyalty after the surrender; could they be trusted, and forgiven for their past support of the confederacy?
| | In summary, the layers of the Earth's atmosphere from the surface of the ground upwards are: the ABL made up of the mixing layer capped by the inversion layer; the free troposphere; the stratosphere; the mesosphere and others. Many atmospheric dispersion models are referred to as ''boundary layer models'' because they mainly model air pollutant dispersion within the ABL. To avoid confusion, models referred to as ''mesoscale models'' have dispersion modeling capabilities that can extend horizontally as much as a few hundred kilometres. It does not mean that they model dispersion in the mesosphere. |
|
| |
|
| The loyalty issue emerged in the debates over the Wade-Davis Bill of 1864. Wade-Davis required voters to take the "Ironclad Oath," swearing that in the past they never had supported the Confederacy or been one of its soldiers. Lincoln ignored the past and asked voters to swear that in the future they would support the Union. The Radicals lost support following Lincoln's veto, but they regained strength in the mood of vengeance that followed Lincoln's assassination in April 1865.
| | ==Gaussian air pollutant dispersion equation== |
|
| |
|
| Suffrage (voting rights) for ex-Confederates was one of two main issues. First, both sides tried to keep the other from voting. It was a question of allowing some or all ex-Confederates to vote. The moderates wanted virtually all of them to vote, but the Radicals repeatedly tried to impose the Ironclad oath, which would allow none to vote. Thaddeus Stevens proposed, unsuccessfully, that all ex-Confederates lose the vote for five years. The compromise that was reached disenfranchised many ex-Confederate civil and military leaders; no one knew how many temporarily lost the vote, but one estimate was 10,000 to 15,000.<ref name=Foner1988>Foner, Eric (1988) ''Reconstruction: America's Unfinished Revolution, 1863-1877'' Pulitzer-prize winning synthesis from [[neoabolitionist]] perspective</ref>
| | The technical literature on air pollution dispersion is quite extensive and dates back to the 1930s and earlier. One of the early air pollutant plume dispersion equations was derived by Bosanquet and Pearson.<ref>C.H. Bosanquet and J.L. Pearson, "The spread of smoke and gases from chimneys", ''Trans. Faraday Soc.'', 32:1249, 1936.</ref> Their equation did not assume Gaussian distribution nor did it include the effect of ground reflection of the pollutant plume. |
|
| |
|
| ===Allow Freedmen to vote?===
| | Sir Graham Sutton derived an air pollutant plume dispersion equation in 1947<ref>O.G. Sutton, "The problem of diffusion in the lower atmosphere", ''QJRMS'', 73:257, 1947.</ref><ref>O.G. Sutton, "The theoretical distribution of airborne pollution from factory chimneys", ''QJRMS'', 73:426, 1947.</ref> which did include the assumption of Gaussian distribution for the vertical and crosswind dispersion of the plume and also included the effect of ground reflection of the plume. |
|
| |
|
| Second was the issue of whether blacks should vote. Northern states that had referenda on the subject rejected allowing their own small number of blacks to vote, but that was not the issue. More germane was the issue of creating a loyally pro-American electorate in the South. Radicals said that the ex-Confederates could not be trusted. Conservatives (including most white Southerners, Northern Democrats, and some Northern Republicans) opposed black voting. Lincoln and Johnson took a middle position that would allow some black men to vote, especially army veterans. Lincoln proposed giving the vote to "the very intelligent, and especially those who have fought gallantly in our ranks",<ref name=Gienapp>William Gienapp (2002) ''Abraham Lincoln and Civil War America''</ref> while, in 1864, Tennessee's Governor Andrew Johnson said, "The better class of them will go to work and sustain themselves, and that class ought to be allowed to vote, on the ground that a loyal negro is more worthy than a disloyal white man".<ref>Patton; James Welch (1934) ''Unionism and Reconstruction in Tennessee, 1860-1869'' [http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=94962448 online edition]</ref> As President in 1865, Johnson wrote to the man he appointed as governor of Mississippi, recommending, "If you could extend the elective franchise to all persons of color who can read the Constitution in English and write their names, and to all persons of color who own real estate valued at not less than two hundred and fifty dollars, and pay taxes thereon, you would completely disarm the adversary [Radicals in Congress], and set an example the other states will follow."<ref>Franklin, John Hope (1961) ''Reconstruction after the Civil War'', University of Chicago Press, 280 pages. Short survey by leading black scholar. Quotes a letter from President Andrew Johnson to Gov. William L. Sharkey, August 1865.</ref>
| | Under the stimulus provided by the advent of stringent environmental control regulations, there was an immense growth in the use of air pollutant plume dispersion calculations between the late 1960s and today. A great many computer programs for calculating the dispersion of air pollutant emissions were developed during that period of time and they were commonly called "air dispersion models". The basis for most of those models was the '''Complete Equation For Gaussian Dispersion Modeling Of Continuous, Buoyant Air Pollution Plumes''' shown below:<ref name=Beychok>{{cite book|author=M.R. Beychok|title=Fundamentals Of Stack Gas Dispersion|edition=4th Edition| publisher=author-published|year=2005|isbn=0-9644588-0-2}}.</ref><ref>{{cite book|author=D. B. Turner| title=Workbook of atmospheric dispersion estimates: an introduction to dispersion modeling| edition=2nd Edition |publisher=CRC Press|year=1994|isbn=1-56670-023-X}}.</ref> |
|
| |
|
| Senator Charles Sumner and Representative Thaddeus Stevens, leaders of the Radical Republicans, were initially hesitant to enfranchise the largely illiterate ex-slave population. [[Carl Schurz]] in his Radical phase said the ignorance of the freedmen did not matter because "practical liberty is a good school". Don't wait for the schools to be built said Schurz because the freedmen will need the ballot first in order to get schools.<ref>Carl Schurz (1865), "Considerations of Negro Suffrage" Arthur H. Clarke Company. [http://books.google.com/books?id=MOoLAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA97&lpg=PA97&dq=%22practical+liberty+is+a+good+school%22&source=web&ots=vGZVam70TI&sig=4-R1iq1Q51xsa2BuhXFC47Od7x0 Online version (see p 97)]</ref> Sumner and Stevens finally decided it was necessary for blacks to vote for three reasons:<ref> Randall, J. G. (1953. ''The Civil War and Reconstruction''. Long the standard survey. Updated by David Donald in 1961.</ref>
| |
|
| |
| # for their own protection;
| |
| # for the protection of white Unionists (scalawags);
| |
| # for the peace of the country.
| |
|
| |
| The Radicals said the only way to get experience was to get the vote first, and they passed laws allowing all male freedmen to vote. In 1867, black men voted for the first time and, over the course of Reconstruction, more than 1,500 African Americans held public office in the South. (The question of [[women's suffrage]] was also debated but was rejected, causing a split in the woman's movement.)
| |
|
| |
| The South's postwar white leaders renounced secession and slavery, but they were angered in 1867 when their state governments were ousted by federal military forces and replaced by Republican lawmakers elected by blacks, Scalawags and Carpetbaggers.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Presidential Reconstruction, 1863-66== | | <math>C = \frac{\;Q}{u}\cdot\frac{\;f}{\sigma_y\sqrt{2\pi}}\;\cdot\frac{\;g_1 + g_2 + g_3}{\sigma_z\sqrt{2\pi}}</math> |
| ===Lincoln's plan===
| |
|
| |
|
| Planning for Reconstruction began in 1861, at the onset of the war. The Radical Republicans, seeking strict policies, used as their base the Congressional Joint Committee on Reconstruction.
| | {| border="0" cellpadding="2" |
| | | |- |
| In 1863, Lincoln began the task of restoration. Motivated by a desire to build a strong Republican Party in the South and to end the bitterness engendered by war, on December 8, 1863, he issued a proclamation of amnesty and reconstruction for those areas of the Confederacy occupied by Union armies. It offered pardon, with certain exceptions, to any Confederate who would swear to support the Constitution and the Union. Once a group in any conquered state equal in number to one tenth of that state's total vote in the presidential election of 1860 took the prescribed oath and organized a government that abolished slavery, he would grant that government executive recognition. This was the ten percent plan.
| | |align=right|where: |
| | | | |
| Thus, Lincoln pursued a lenient plan for reconstruction, especially in Virginia, Louisiana, Tennessee, and Arkansas, which were partly occupied by Union forces. However, he was unable to get Congress to support his plans, leaving the situation unsettled at the time of his death.<ref>William C. Harris (1997), ''With Charity for All: Lincoln and the Restoration of the Union''</ref>
| | |- |
| | | !align=right|<math>f</math> |
| Lincoln's 1863 plan aroused the sharp opposition of the radicals in Congress, who believed it would simply restore to power the old planter aristocracy. In July 1864, they passed the Wade-Davis Bill, which required 50% of a state's male voters to take an “ironclad” oath that they had never voluntarily supported the Confederacy. Lincoln's veto kept the Wade-Davis Bill from becoming law, the Radicals lost momentum, and he implemented his own plan. By the end of the war it had been tried, not too successfully, in Louisiana, Arkansas, Tennessee, and Virginia. Congress, however, refused to seat the senators and representatives elected from those states, and by the time of Lincoln's assassination the President and Congress were at a stalemate.
| | |align=left|= crosswind dispersion parameter |
| | | |- |
| Observers at the time of the Wade-Davis bill—and historians since—agree that probably no state would have qualified, leaving them under military control indefinitely. By vetoing the bill, Lincoln blocked the Radicals from a dominant role in government. (They rose to power again in 1866.) Historian William Gienapp explains Lincoln's veto:<ref name=Gienapp/>
| | !align=right| |
| :Lincoln, in contrast, shrank from inaugurating a fundamental upheaval in southern society and mores, and by stressing future over past loyalty, he was willing to allow recanting Rebels to dominate the new southern governments. Moreover, Lincoln believed that the best strategy was to introduce black suffrage in the South by degrees in order to accustom southern whites to blacks voting. How far he was willing to go in extending rights to former slaves remained unclear, but his gradualist approach to social change remained intact, just as when he had tried to get the border states in 1862 to adopt gradual emancipation. Finally, the radicals and Lincoln held quite different views of the relationship of Reconstruction to the war effort. By erecting impossibly high standards that no Southern state could meet, the Wade–Davis bill sought to postpone Reconstruction until the war was over. For Lincoln, in contrast, a lenient program of Reconstruction would encourage Southern whites to abandon the Confederacy and thus was integral to his strategy for winning the war.
| | |align=left|= <math>\exp\;[-\,y^2/\,(2\;\sigma_y^2\;)\;]</math> |
| | | |- |
| On April 11, 1865, Lincoln delivered his last public address, in which he continued to uphold a generous and lenient reconstruction policy.
| | !align=right|<math>g</math> |
| | | |align=left|= vertical dispersion parameter = <math>\,g_1 + g_2 + g_3</math> |
| Lincoln thus wanted to bring the Southern states back into good standing as soon as possible and with a minimum of vengeance. Insisting, as well, that there be new rights for the Freedmen, he created the [[Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen and Abandoned Lands]] in January 1865, known as the Freedmen's Bureau. In one experiment in the Sea Islands of South Carolina, Freedmen were allowed to farm plantations seized by the Army; they never received ownership.<ref>Willie Lee Rose (1967), ''Rehearsal for Reconstruction: The Port Royal Experiment''</ref>
| | |- |
| | | !align=right|<math>g_1</math> |
| ==Johnson's presidential reconstruction: 1865–66== | | |align=left|= vertical dispersion with no reflections |
| | | |- |
| Northern anger over the assassination of Lincoln and the immense human cost of the war led to demands for harsh policies. Vice President Andrew Johnson had taken a hard line and spoke of hanging rebel Confederates, but when he succeeded Lincoln as President, Johnson took a much softer line, pardoning many Confederate leaders and allowing ex-Confederates to maintain their control of Southern state governments, Southern lands, and black people.<ref name=Trefousse1989> Trefousse, Hans L. (1989). ''Andrew Johnson: A Biography'' (1989) [http://www.questia.com/library/book/andrew-johnson-a-biography-by-hans-l-trefousse.jsp Online edition]</ref> [[Jefferson Davis]] was held in prison for two years, but not the other Confederate leaders; there were no treason trials. Only one person—Captain [[Henry Wirz]], the commandant of the Andersonville prison prison camp —was executed for war crimes.
| | !align=right| |
| | | |align=left|= <math>\; \exp\;[-\,(z - H)^2/\,(2\;\sigma_z^2\;)\;]</math> |
| ===Devastated region=== | | |- |
| | | !align=right|<math>g_2</math> |
| The economic calamity suffered by the South during the war affected every family. Except for land, most assets and investments had vanished with slavery, but debts were left behind. Worst of all were the human deaths and amputations. Most farms were intact but most had lost their horses, mules and cattle; fences and barns were in disrepair. Prices for cotton had plunged. The rebuilding would take years and require outside investment because the devastation was so thorough. One historian has summarized the collapse of the transportation infrastructure needed for economic recovery:<ref>John Samuel Ezell (1963), ''The South since 1865'' pp 27-28</ref>
| | |align=left|= vertical dispersion for reflection from the ground |
| :One of the greatest calamities which confronted Southerners was the havoc wrought on the transportation system. Roads were impassable or nonexistent, and bridges were destroyed or washed away. The important river traffic was at a standstill: levees were broken, channels were blocked, the few steamboats which had not been captured or destroyed were in a state of disrepair, wharves had decayed or were missing, and trained personnel were dead or dispersed. Horses, mules, oxen, carriages, wagons, and carts had nearly all fallen prey at one time or another to the contending armies. The railroads were paralyzed, with most of the companies bankrupt. These lines had been the special target of the enemy. On one stretch of 114 miles in Alabama, every bridge and trestle was destroyed, cross-ties rotten, buildings burned, water-tanks gone, ditches filled up, and tracks grown up in weeds and bushes. Sherman's men had destroyed all railroad equipment within reach -- 136 of 281 miles of the Central of Georgia, alone -- and added the novelty of twisting heated rails around trees. In Alabama nearly all of its 800 miles of railway was useless. One Mississippi line reported fit for use, though damaged, a total of one locomotive, two second-class passenger cars, one first-class passenger car, one baggage car, one provision car, two stock cars, and two flat cars. Communication centers like Columbia and Atlanta were in ruins; shops and foundries were wrecked or in disrepair. Even those areas bypassed by battle had been pirated for equipment needed on the battlefront, and the wear and tear of wartime usage without adequate repairs or replacements reduced all to a state of disintegration. Not for a generation were the railroads properly restored, and then largely by Northern capital.
| | |- |
| | | !align=right| |
| ===Black codes=== | | |align=left|= <math>\;\exp\;[-\,(z + H)^2/\,(2\;\sigma_z^2\;)\;]</math> |
| | | |- |
| [[Image:The Union as It Was.jpg|300px|thumb|right|a [[Harper's Magazine]] political cartoon denouncing Klan and White League opposition to Reconstruction]]
| | !align=right|<math>g_3</math> |
| The Johnson governments quickly enacted the restrictive "black codes". They gave freedmen more rights than free blacks had before the war, but they still had only a limited set of third-class civil rights, and no voting rights. The freed slaves were not considered citizens. Southern plantation owners feared extensive black vagrancy would mean loss of the essential labor force. Many Southern whites feared equality with Southern blacks. Two states, Mississippi and South Carolina, had full fledged Black Codes. Among other provisions, they stringently limited blacks' ability to control their own employment. <ref>Oberholtzer 1:128–9</ref> The Black codes outraged northern opinion, but in practive they had limited effect because the Freedman's Bureau protected the blacks legally. <ref> Donald (2001) p. 527</ref> The Black Codes were abolished by the Civil Rights Act of 1866.
| | |align=left|= vertical dispersion for reflection from an inversion aloft |
| | | |- |
| ===Moderate responses=== | | !align=right| |
| | | |align=left|= <math>\sum_{m=1}^\infty\;\big\{\exp\;[-\,(z - H - 2mL)^2/\,(2\;\sigma_z^2\;)\;]</math> |
| Moderates feared that the South was trying to create a form of semi-slavery, and that Confederate nationalism was not dead but simmered under the surface. Therefore Republicans blocked the readmission of the 11 states to the Congress in fall 1865. Congress also tried to renew the Freedman's Bureau, but Johnson vetoed the legislation in February 1866. Senator [[Lyman Trumbull]] of Illinois, leader of the moderate Republicans, took affront at the black codes. He proposed the first Civil Rights Law, because the abolition of slavery was empty if "laws are to be enacted and enforced depriving persons of African descent of privileges which are essential to freemen.... A law that does not allow a colored person to go from one county to another, and one that does not allow him to hold property, to teach, to preach, are certainly laws in violation of the rights of a freeman....The purpose of this bill is to destroy all these discriminations."<ref name=Rhodes>Rhodes, James G. (1920) ''History of the United States from the Compromise of 1850 to the McKinley-Bryan Campaign of 1896'' Highly detailed narrative by Pulitzer prize winner; argues was a political disaster because it violated the rights of white Southerners </ref>
| | |- |
| | | !align=right| |
| The key to the bill was the opening section:
| | |align=left| <math>+\, \exp\;[-\,(z + H + 2mL)^2/\,(2\;\sigma_z^2\;)\;]</math> |
| | | |- |
| : "All persons born in the United States ... are hereby declared to be citizens of the United States; and such citizens of every race and color, without regard to any previous condition of slavery ... shall have the same right in every State ...to make and enforce contracts, to sue, be parties, and give evidence, to inherit, purchase, lease, sell, hold, and convey real and personal property, and to full and equal benefit of all laws and proceedings for the security of person and property, as is enjoyed by white citizens, and shall be subject to like punishment, pains, and penalties and to none other, any law, statute, ordinance, regulation, or custom to the Contrary notwithstanding."
| | !align=right| |
| | | |align=left| <math>+\, \exp\;[-\,(z + H - 2mL)^2/\,(2\;\sigma_z^2\;)\;]</math> |
| Congress quickly passed the Civil Rights bill; the Senate on February 2 voted 33–12; the House on March 13 voted 111–38.
| | |- |
| | | !align=right| |
| ===Johnson vetoes; Republicans rally against him=== | | |align=left| <math>+\, \exp\;[-\,(z - H + 2mL)^2/\,(2\;\sigma_z^2\;)\;]\big\}</math> |
| | | |- |
| Although strongly urged by moderates in Congress to sign the Civil Rights bill, Johnson broke decisively with them by vetoing it on March 27. His veto message objected to the measure because it conferred citizenship on the Freedmen at a time when eleven out of thirty-six states were unrepresented and attempted to fix by Federal law "a perfect equality of the white and black races in every State of the Union." Johnson said it was an invasion by Federal authority of the rights of the States; it had no warrant in the Constitution and was contrary to all precedents. It was a "stride toward centralization and the concentration of all legislative power in the national government."<ref name=Rhodes/>
| | !align=right|<math>C</math> |
| | | |align=left|= concentration of emissions, in g/m³, at any receptor located: |
| [[Image:Free-bur.jpg|thumb|450px|The debate over reconstruction and the Freedman's Bureau was nationwide, as seen in this 1866 Pennsylvania election poster. It shows Bureau money lavished on lazy freedmen at the expense of white workers. ]]
| | |- |
| | | !align=right| |
| The Democratic Party, proclaiming itself the party of white men, north and south, supported Johnson.<ref name=Trefousse1989/> However the Republicans in Congress overrode his veto (the Senate by the close vote of 33:15, the House by 122:41) and the Civil Rights bill became law. Congress also passed the Freedmen's Bureau Bill over Johnson's veto.
| | |align=left| x meters downwind from the emission source point |
| | |
| The last moderate proposal was the Fourteenth Amendment, also authored by moderate Trumbull. It was designed to put the key provisions of the Civil Rights Act into the Constitution, but it went much further. It extended citizenship to everyone born in the United States (except visitors and Indians on reservations), penalized states that did not give the vote to Freedmen, and most importantly, created new federal civil rights that could be protected by federal courts. It guaranteed the Federal war debt (and promised the Confederate debt would never be paid). Johnson used his influence to block the amendment in the states since three-fourths of the states were required for ratification. (The amendment was later ratified.) The moderate effort to compromise with Johnson had failed, and a political fight broke out between the Republicans (both Radical and moderate) on one side, and on the other side, Johnson and his allies in the Democratic party in the North, and the conservative groupings (which used different names) in each southern state.
| |
| | |
| ==Radical Reconstruction: 1866–73== | |
| ===Constitutional amendments===
| |
| | |
| Three new Constitutional amendments were adopted. The 13th Amendment abolished slavery and was ratified in 1865. The 14th Amendment was rejected in 1866 but ratified in 1868, guaranteeing citizenship to all persons born or naturalized in the United States, except Native Americans, and granting them federal civil rights. The 15th Amendment passed in 1870, decreeing that the right to vote could not be denied because of race, color, or previous condition of servitude. The amendment did not declare the vote an unconditional right and only prohibited these specific types of discrimination while specific electoral policies were determined within each state. Notably, the 15th Amendment did not mention the right of women to vote.
| |
| | |
| === Re-admission to Congress === | |
| | |
| *Tennessee - July 24, 1866
| |
| *Arkansas - June 22, 1868
| |
| *Florida - June 25, 1868
| |
| *North Carolina - July 4, 1868
| |
| *South Carolina - July 9, 1868
| |
| *Louisiana - July 9, 1868
| |
| *Alabama - July 13, 1868
| |
| *Virginia - January 26, 1870
| |
| *Mississippi - February 23, 1870
| |
| *Texas - March 30, 1870
| |
| *Georgia - July 15, 1870
| |
| | |
| ===Military reconstruction=== | |
| | |
| The first Reconstruction Act placed ten Confederate states under military control, grouping them into five military districts:<ref name=Foner1988/>
| |
| | |
| * First Military District: Virginia, under General [[John Schofield]]
| |
| * Second Military District: North and South Carolina, under General [[Daniel Sickles]]
| |
| * Third Military District: Georgia, Alabama and Florida, under General [[John Pope]]
| |
| * Fourth Military District: Arkansas and Mississippi, under General [[Edward Ord]]
| |
| * Fifth Military District: Texas and Louisiana, under Generals [[Philip Sheridan]] and [[Winfield Scott Hancock]]
| |
| | |
| Tennessee and the border states were not controlled by Congress.
| |
| | |
| The ten Southern state governments were re-constituted under the direct control of the U.S. Army. There was little or no fighting, but rather a state of martial law in which the military closely supervised local government, supervised elections, and protected office holders from violence. Blacks were enrolled as voters; former Confederate leaders were excluded.<ref name=Foner1988/> Every state was somewhat different; here is what happened in Texas:<ref> Randolph Campbell, ''Gone to Texas'' 2003 p. 276.</ref>
| |
| | |
| : The first critical step … was the registration of voters according to guidelines established by Congress and interpreted by Generals Sheridan and Griffin. The Reconstruction Acts called for registering all adult males, white and black, except those who had ever sworn an oath to uphold the Constitution of the United States and then engaged in rebellion.… Sheridan interpreted these restrictions stringently, barring from registration not only all pre-1861 officials of state and local governments who had supported the Confederacy but also all city officeholders and even minor functionaries such as sextons of cemeteries. In May Griffin … appointed a three-man board of registrars for each county, making his choices on the advice of known Unionists and local Freedman's Bureau agents. In every county where practicable a freedman served as one of the three registrars.… Final registration amounted to approximately 59,633 whites and 49,479 blacks. It is impossible to say how many whites were rejected or refused to register (estimates vary from 7,500 to 12,000), but blacks, who constituted only about 30 percent of the state's population, were significantly overrepresented at 45 percent of all voters. </blockquote>
| |
|
| |
| All Southern states were readmitted to the Union by the end of 1870, the last being Georgia. All but 500 top Confederate leaders were pardoned when President Grant signed the Amnesty Act of 1872.
| |
| | |
| ===Black officeholders=== | |
| | |
| Republicans took control of all Southern state governorships and state legislatures, leading to the election of numerous African-Americans to state and national offices, as well as local offices. About 137 black officeholders lived outside the South before the Civil War.<ref name=Foner1988/>
| |
| | |
| {| class=wikitable border=1
| |
| |+ Race of delegates to 1867<br>state constitutional conventions<ref name=Rhodes/> | |
| ! State !! White !! Black !! % White
| |
| |- | | |- |
| | Virginia ||align=center |80 ||align=center |25 ||align=center |76%
| | !align=right| |
| | |align=left| y meters crosswind from the emission plume centerline |
| |- | | |- |
| | North Carolina ||align=center |107 ||align=center |13 ||align=center |89%
| | !align=right| |
| | |align=left| z meters above ground level |
| |- | | |- |
| | South Carolina ||align=center |48 ||align=center |76 ||align=center |39%
| | !align=right|<math>Q</math> |
| | |align=left|= source pollutant emission rate, in g/s |
| |- | | |- |
| | Georgia ||align=center |133 ||align=center |33 ||align=center |80%
| | !align=right|<math>u</math> |
| | |align=left|= horizontal wind velocity along the plume centerline, m/s |
| |- | | |- |
| | Florida ||align=center |28 ||align=center |18 ||align=center |61%
| | !align=right|<math>H</math> |
| | |align=left|= height of emission plume centerline above ground level, in m |
| |- | | |- |
| | Alabama ||align=center |92 ||align=center |16 ||align=center |85%
| | !align=right|<math>\sigma_z</math> |
| | |align=left|= vertical standard deviation of the emission distribution, in m |
| |- | | |- |
| | Mississippi ||align=center |68 ||align=center |17 ||align=center |80%
| | !align=right|<math>\sigma_y</math> |
| | |align=left|= horizontal standard deviation of the emission distribution, in m |
| |- | | |- |
| | Louisiana ||align=center |25 ||align=center |44 ||align=center |36%
| | !align=right|<math>L</math> |
| | |align=left|= height from ground level to bottom of the inversion aloft, in m |
| |- | | |- |
| | Texas ||align=center |81 ||align=center |9 ||align=center |90%
| | !align=right|<math>\exp</math> |
| | |align=left|= the exponential function |
| |} | | |} |
|
| |
|
| ===Public schools ===
| | The above equation not only includes upward reflection from the ground, it also includes downward reflection from the bottom of any inversion lid present in the atmosphere. |
| | |
| As modernizers, the Republicans believed that education was a long-term solution to the economic poverty and ignorance of the South. They created a system of public schools, which were segregated by race everywhere except [[New Orleans]]. Most blacks approved the segregated schools because they provided jobs for black teachers. In general, elementary and a few secondary schools were built in the cities. But the South had few cities, and in the rural areas the public school was a one-room affair that attracted about half the younger children. The teachers were poorly paid, and their pay was often in arrears.<ref name=Foner1988/> Conservatives contended the rural schools were too expensive and unnecessary for a region where the vast majority of people were cotton or tobacco farmers. One historian found that the schools were not very effective because of "poverty, the inability of the states to collect taxes, and inefficiency and corruption in many places prevented successful operation of the schools."<ref>Franklin 139</ref>
| |
| [[Image:~KKK.JPG|thumb|left|300px|1868 Republican cartoon identifies Democratic candidate [[Horatio Seymour]] (right panel) with KKK violence and with Confederate soldiers (left panel)]]
| |
| | |
| Numerous private academies and colleges for Freedmen were established by northern missionaries. Every state created state colleges for Freedmen, such as [[Alcorn State University]] in Mississippi; in 1890, the black state colleges started receiving federal funds as land grant schools.<ref>McAfee 1998</ref> They received state funds after Reconstruction ended because, as Lynch explains, "there are very many liberal, fair-minded and influential Democrats in the State who are strongly in favor of having the State provide for the liberal education of both races."<ref>Lynch 1913</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===Railroad subsidies and payoffs===
| |
| | |
| Every Southern state subsidized railroads, which modernizers felt could haul the South out of isolation and poverty. Millions of dollars in bonds and subsidies were fraudulently pocketed. One ring in North Carolina spent $200,000 in bribing the legislature and obtained millions in state money for its railroads. Instead of building new track, however, it used the funds to speculate in bonds, reward friends with extravagant fees, and enjoy lavish trips to Europe.<ref name=Foner1988/> Taxes were quadrupled across the South to pay off the railroad bonds and the school costs, leading to intense complaints among taxpayers.<ref>Franklin p 141-48; Summers 1984</ref> Nevertheless thousands of miles of lines were built as the Southern system expanded from 11,000 miles (17,700 km) in 1870 to 29,000 miles (46,700 km) in 1890. The lines were owned and directed overwhelmingly by Northerners. Railroads helped create a mechanically skilled group of craftsmen and indeed broke the isolation of much of the region. Passengers were few, however, and apart from hauling the cotton crop when it was harvested, there was little freight traffic.<ref>Stover 1955</ref> As Franklin explains, "numerous railroads fed at the public trough by bribing legislators...and through the use and misuse of state funds." The effect, according to one businessman, "was to drive capital from the State, paralyze industry, and demoralize labor."<ref>Franklin p147–8</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===Taxpayer revolt===
| |
| | |
| The new spending on schools and especially on railroad subsidies, combined with fraudulent spending and a collapse in state credit because of huge deficits, forced the states to dramatically increase tax rates—up to ten times higher—despite the poverty of the region. Angry taxpayers revolted, and the conservatives shifted their focus away from race to taxes.<ref name=Foner1988/> Former Congressman John Lynch, a black Republican leader from Mississippi, concluded, "The argument made by the taxpayers, however, was plausible and it may be conceded that, upon the whole, they were about right; for no doubt it would have been much easier upon the taxpayers to have increased at that time the interest-bearing debt of the State than to have increased the tax rate. The latter course, however, had been adopted and could not then be changed."<ref>Lynch 1913</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===Views of conservatives in the South===
| |
| | |
| The white Southerners who lost power reformed themselves into "Conservative" parties that battled the Republicans throughout the South. The party names varied, but by the late 1870s, they simply called themselves "Democrats." Historian [[Walter Lynwood Fleming]] describes mounting anger of Southern whites: "The Negro troops, even at their best, were everywhere considered offensive by the native whites.... The Negro soldier, impudent by reason of his new freedom, his new uniform, and his new gun, was more than Southern temper could tranquilly bear, and race conflicts were frequent." <ref> Fleming online at [http://www.blackmask.com/books11c/sequelap.htm#ax]</ref>
| |
| | |
| Fleming described the first results of the [[Ku Klux Klan]] movement as "good" and the later ones as "both good and bad." According to Fleming (1907) the KKK "quieted the Negroes, made life and property safer, gave protection to women, stopped burnings, forced the Radical leaders to be more moderate, made the Negroes work better, drove the worst of the Radical leaders from the country and started the whites on the way to gain political supremacy." The evil results, Fleming said, was that lawless elements "made use of the organization as a cloak to cover their misdeeds....the lynching habits of today [1907] are due largely to conditions, social and legal, growing out of Reconstruction."<ref>Walter Lynwood Fleming, ed. ''Documentary History of the Reconstruction (1907), II, p. 328-9 </ref>
| |
| | |
| [[Ellis Oberholtzer]] (a northern scholar) in 1917 explained:<ref>Oberholtzer, vol 1 p 485</ref>
| |
| : Outrages upon the ex-slaves in the South there were in plenty. Their sufferings were many. But white men, too, were victims of lawless violence, and in all portions of the North as well as in the late "rebel" states. Not a political campaign passed without the exchange of bullets, the breaking of skulls with sticks and stones, the firing of rival club-houses. Republican clubs marched the streets of [[Philadelphia]], amid revolver shots and brickbats, to save the negroes from the "rebel" savages in Alabama.... The project to make voters out of black men was not so much for their social elevation as for the further punishment of the Southern white people—for the capture of offices for Radical scamps and the entrenchment of the Radical party in power for a long time to come in the South and in the country at large."
| |
| | |
| Reaction by conservatives included the formation of violent secret societies, especially the [[Ku Klux Klan]]. Violence occurred in cities and in the countryside between white former Confederates, Republicans, African-Americans, representatives of the federal government, and Republican-organized armed [[Loyal Leagues]].
| |
| | |
| ==Redemption 1873-77==
| |
| ===Republicans split nationally: Election of 1872===
| |
| | |
| As early as 1868 Supreme Court Chief Justice [[Salmon P. Chase]], a leading Radical during the war, concluded that:
| |
| :"Congress was right in not limiting, by its reconstruction acts, the right of suffrage to whites; but wrong in the exclusion from suffrage of certain classes of citizens and all unable to take its prescribed retrospective oath, and wrong also in the establishment of despotic military governments for the States and in authorizing military commissions for the trial of civilians in time of peace. There should have been as little military government as possible; no military commissions; no classes excluded from suffrage; and no oath except one of faithful obedience and support to the Constitution and laws, and of sincere attachment to the constitutional Government of the United States."<ref>J. W. Schuckers, ''The Life and Public Services of Salmon Portland Chase,'' (1874). p. 585; letter of May 30, 1868 to August Belmont </ref>
| |
| | |
| By 1872, President Grant had alienated large numbers of leading Republicans, including many Radicals by the wanton corruption of his administration and his use of federal soldiers to prop up Radical state regimes in the South. The opponents, called [[Liberal Republican Party (United States)|"Liberal Republicans"]], included founders of the party who expressed dismay that the party had succumbed to corruption. Leaders included editors of some of the nation's most powerful newspapers. [[Charles Sumner]], embittered by the corruption of the Grant administration, joined the new party, which nominated editor [[Horace Greeley]]. The badly disorganized Democratic party also supported Greeley.
| |
| | |
| Grant made up for the defections by new gains among Union veterans, as well as strong support from the "Stalwart" faction of his party (which depended on his patronage), and the Southern Republican parties. Grant won a smashing landslide, as the Liberal Republican party vanished and many former supporters—even ex-abolitionists—abandoned the cause of Reconstruction.<ref>McPherson 1975</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===Republican coalition splinters in South===
| |
| | |
| In the South, political–racial tensions built up inside the Republican party. In 1868, Georgia Democrats, with support from some Republicans, expelled all 28 black Republican members (arguing blacks were eligible to vote but not to hold office.) In several states the more conservative scalawags fought for control with the more radical carpetbaggers and usually lost. Thus, in Mississippi, the conservative faction led by scalawag [[James Lusk Alcorn]] was decisively defeated by the radical faction led by carpetbagger [[Adelbert Ames]]. The party lost support steadily as many scalawags left it; few new recruits were acquired. Meanwhile, the Freedmen were demanding a much bigger share of the offices and patronage, thus squeezing out their carpetbagger allies.<ref name=Foner1988/> Finally some of the more prosperous Freedmen were joining the Democrats, angered at the failure of the Republicans to help them acquire land.<ref name=Foner1988/>
| |
| Although some Marxist historians, especially [[W.E.B. Du Bois]], looked for and celebrated a cross-racial coalition of poor whites and poor blacks, such coalition rarely formed. Congressman Lynch explains that,
| |
| | |
| :"While the colored men did not look with favor upon a political alliance with the poor whites, it must be admitted that, with very few exceptions, that class of whites did not seek, and did not seem to desire such an alliance."
| |
| | |
| Lynch explains that poor whites resented the job competition from Freedmen. Furthermore, the poor whites: "with a few exceptions, were less efficient, less capable, and knew less about matters of state and governmental administration than many of the ex-slaves.… As a rule, therefore, the whites that came into the leadership of the Republican party between 1872 and 1875 were representatives of the most substantial families of the land."<ref>Lynch 1915</ref>
| |
| | |
| Thus, the poor whites became Democrats and bitterly opposed the black Republicans. Snay (2004) erxplores the failure of the Republican Party to appeal to the white yeomanry of the South--a recurring puzzle in the historiography of Reconstruction. Acknowledging the important role of white resistance, racism, and economic depression, Snay instead locates the roots of its failure in its ideology. The Southern Republican appeal to the yeomanry was inherently weakened by yoking together Whiggish appeals of economic development (which appealed to the middle class) with the yeoman-class appeals of Jacksonian democracy. The coupling of these clashing tendencies brought to the surface the latent conflicts of Jacksonian politics in the South, driving still another wedge into the Southern Republican coalition.
| |
| | |
| <ref> Mitchell Snay, "Freedom and Progress: the Dilemma of Southern Republican Thought During Radical Reconstruction." ''American Nineteenth Century History''2004 5(1): 100-114. Issn: 1466-4658 Fulltext: [[Ebsco]]</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===Democrats try a "New Departure"===
| |
| | |
| By 1870, the Democratic–Conservative leadership across the South decided it had to end its opposition to Reconstruction as well as to black suffrage in order to survive and move on to new issues. The Grant administration had proven by its crackdown on the Ku Klux Klan that it would use as much federal power as necessary to suppress open anti-black violence. The Democrats in the North concurred. They wanted to fight the GOP on economic grounds rather than race. The [[New Departure (Democrats)|New Departure]] offered the chance for a clean slate without having to refight the Civil War every election. Furthermore, many wealthy landowners thought they could control part of the newly enfranchised black electorate to their own advantage.
| |
| | |
| Not all Democrats agreed; a hard core element wanted to resist Reconstruction no matter what. Eventually, a group called "Redeemers" took control of the party in the states.<ref>Perman 1984, ch 3</ref> They formed coalitions with conservative Republicans, including scalawags and carpetbaggers, emphasizing the need for economic modernization. Railroad building was seen as a panacea since northern capital was needed. The new tactics were a success in [[History of Virginia|Virginia]] where [[William Mahone]] built a winning coalition. In Tennessee, the Redeemers formed a coalition with Republican governor DeWitt Senter. Across the South Democrats switched from the race issue to taxes and corruption, charging that Republican governments were corrupt and inefficient, as taxes began squeezing cash-poor farmers who rarely saw $20 in currency a year but had to pay taxes in currency or lose their farm.
| |
| | |
| In North Carolina, Republican Governor [[William Woods Holden]] used state troops against the Klan, but the prisoners were released by federal judges. Holden became the first governor in American history to be impeached and removed from office. Republican political disputes in Georgia split the party and enabled the Redeemers to take over.<ref name=Foner1988/> Violence was a factor in neutralizing Republican leaders in the [[Deep South]], with its larger black Republican population. In the North, a live-and-let-live attitude made elections more like a sporting contest. But in the Deep South, it affected the lives of the citizens. As an Alabama scalawag explained, "Our contest here is for life, for the right to earn our bread...for a decent and respectful consideration as human beings and members of society."<ref name=Foner1988/>
| |
| | |
| ===Panic of 1873 weakens GOP===
| |
| | |
| The [[Panic of 1873]] hit the Southern economy hard and disillusioned many Republicans who had gambled that railroads would pull the South out of its poverty. The price of cotton fell by half; many small landowners, local merchants and cotton factors (wholesalers) went bankrupt. [[Sharecropping]], for both black and white farmers, became more common as a way to spread the risk of owning land. The old abolitionist element in the North was aging away, or had lost interest, and was not replenished. Many carpetbaggers returned to the North or joined the Redeemers. Blacks had an increased voice in the Republican Party, but across the South it was divided by internal bickering and was rapidly losing its cohesion. Many local black leaders started emphasizing individual economic progress in cooperation with white elites, rather than racial political progress in opposition to them, a conservative attitude that foreshadowed [[Booker T. Washington]].<ref name=Foner1988/>
| |
| | |
| Nationally, President Grant took the blame for the depression; the Republican Party lost 96 seats in all parts of the country in the [[United States House election, 1874|1874 elections]]. The [[Bourbon Democrats]] took control of the House and were confident of electing [[Samuel J. Tilden]] president in 1876. President Grant was not running for re-election and seemed to be losing interest in the South. States fell to the Redeemers, with only four in Republican hands in 1873, Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi and South Carolina; Arkansas then fell after the [[Brooks-Baxter War]] in 1874. Political violence was endemic in Louisiana, but efforts to seize the state government were repulsed by federal troops who entered the state legislature and hauled away several Democratic legislators. The violation of tradition embarrassed Grant, and some of his cabinet recommended against further intervention.<ref name=Foner1988/> By now, all Democrats and most northern Republicans agreed that Confederate nationalism and slavery were dead—the war goals were achieved—and further federal military interference was an undemocratic violation of historic Republican values. The victory of [[Rutherford Hayes]] in the hotly contested Ohio gubernatorial election of 1875 indicated his "let alone" policy toward the South would become Republican policy, as indeed happened when he won the 1876 GOP nomination for president. The last explosion of violence came in [[Mississippi gubernatorial election, 1875|Mississippi's 1875 election]], in which Democratic rifle clubs, operating in the open and without disguise, threatened or shot enough Republicans to decide the election for the Redeemers. Republican Governor Adelbert Ames asked Grant for federal troops to fight back; Grant refused, saying public opinion was "tired out" of the perpetual troubles in the South. Ames fled the state as the Democrats took over Mississippi.<ref name=Foner1988/>
| |
| | |
| ===1876 election===
| |
| | |
| Reconstruction continued in South Carolina, Louisiana and Florida until 1877. After Republican Rutherford Hayes won the disputed [[U.S. presidential election, 1876|U.S. Presidential election of 1876]], the [[Compromise of 1877]] was reached whereby the white South agreed to accept Hayes's victory if he withdrew the last Federal troops. By this point, everyone had agreed that Reconstruction was finished. However, the African-Americans who wanted their legal rights guaranteed by the Federal government were repeatedly frustrated for another 75 years; they considered Reconstruction a failure.<ref name=Foner1988/>
| |
| | |
| ===Redeemers in the South===
| |
| | |
| The end of Reconstruction marked the beginning of a period, 1877–1900, that saw the steady reduction of many civil and political rights for African-Americans, and ushered in the nadir of American race relations. The process varied by states and towns. In Virginia, the [[Redeemers]] gerrymandered cities to minimize Republican seats; reduced the number of polling places in black precincts; made local officials appointees of the state legislature; and did not allow the vote to felons or to people who failed to pay their annual poll tax.
| |
|
| |
|
| Much of the Reconstruction civil rights legislation was overturned by the United States Supreme Court. Most notably, the court held in the ''[[Civil Rights Cases]]'' (1883), that the 14th amendment only gave Congress the power to outlaw public, rather than private, discrimination. In ''[[Plessy v. Ferguson]]'' (1896) the court went even further, announcing that state-mandated segregation was legal as long as the law provided for "separate but equal" facilities.
| | The sum of the four exponential terms in <math>g_3</math> converges to a final value quite rapidly. For most cases, the summation of the series with '''''m''''' = 1, '''''m''''' = 2 and '''''m''''' = 3 will provide an adequate solution. |
|
| |
|
| == Legacy and historiography ==
| | <math>\sigma_z</math> and <math>\sigma_y</math> are functions of the atmospheric stability class (i.e., a measure of the turbulence in the ambient atmosphere) and of the downwind distance to the receptor. The two most important variables affecting the degree of pollutant emission dispersion obtained are the height of the emission source point and the degree of atmospheric turbulence. The more turbulence, the better the degree of dispersion. |
|
| |
|
| The interpretation of Reconstruction has swung back and forth several times. Nearly all historians, however, have concluded it was a failure. <ref>McPherson 1965</ref> In the 1865-75 period, most writers took the view that the ex-Confederates were traitors and Johnson was their ally who threatened to undo the Union's Constitutional achievements. In the 1870s and 1880s many writers argued that Johnson and his allies were not traitors but blundered badly in rejecting the 14th Amendment and setting the stage for Radical Reconstruction. <ref> Fletcher M. Green, "Walter Lynwood Fleming: Historian of Reconstruction," ''The Journal of Southern History,'' Vol. 2, No. 4. (Nov., 1936), pp. 497-521.</ref>
| | Whereas older models rely on stability classes for the determination of <math>\sigma_y</math> and <math>\sigma_z</math>, more recent models increasingly rely on Monin-Obukhov similarity theory to derive these parameters. |
|
| |
|
| Among black scholars [[Booker T. Washington]], who grew up in West Virginia during Reconstruction, concluded that, "the Reconstruction experiment in racial democracy failed because it began at the wrong end, emphasizing political means and civil rights acts rather than economic means and self-determination."<ref>Louis R. Harlan, ''Booker T. Washington in Perspective'' (1988) p. 164; A. A. Taylor, "Historians of the Reconstruction," ''The Journal of Negro History'' Vol. 23, No. 1. (Jan., 1938), pp. 16-34. </ref> His solution was to concentrate on building the economic infrastructure of the black community.
| | ==Briggs plume rise equations== |
|
| |
|
| In popular literature two novels by Thomas Dixon—''The Clansman'' and ''The Leopard's Spots: A Romance of the White Man's Burden — 1865–1900''—romanticized white resistance to Northern/black coercion, hailing vigilante action by the Ku Klux Klan. Other authors romanticized the benevolence of slavery and the happy world of the antebellum plantation. These sentiments were expressed on the screen in [[D.W. Griffith]]'s anti-Republican 1915 movie ''[[The Birth of a Nation]]''.
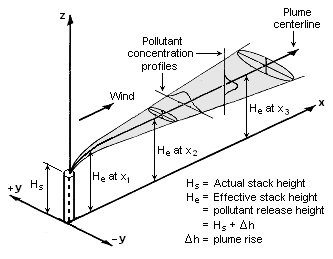
| | The Gaussian air pollutant dispersion equation (discussed above) requires the input of ''H'' which is the pollutant plume's centerline height above ground level. ''H'' is the sum of ''H''<sub>s</sub> (the actual physical height of the pollutant plume's emission source point) plus Δ''H'' (the plume rise due the plume's buoyancy). |
|
| |
|
| The [[Dunning School]] of scholars based at the history department of Columbia University analyzed Reconstruction as a failure, at least after 1866, for quite different reasons. They claimed that it took freedoms and rights from qualified whites and gave them to unqualified blacks who were being duped by corrupt carpetbaggers and scalawags. As one scholar notes, "Reconstruction was a battle between two extremes: the Democrats, as the group which included the vast majority of the whites, standing for decent government and racial supremacy, versus the Republicans, the Negroes, alien carpetbaggers, and renegade scalawags, standing for dishonest government and alien ideals. These historians wrote literally in terms of white and black."<ref> Williams 1946 p. 473; Green (1936).</ref>
| | [[File:Gaussian Plume.png|thumb|right|333px|Visualization of a buoyant Gaussian air pollutant dispersion plume]] |
|
| |
|
| In the 1930s, "revisionism" became popular among scholars. As disciples of [[Charles A. Beard]], revisionists focused on economics, downplaying politics and constitutional issues. They argued that the Radical rhetoric of equal rights was mostly a smokescreen hiding the true motivation of Reconstruction's real backers. While conceding that a few men like Stevens and Sumner were thoroughly idealistic, Howard Beale argued Reconstruction was primarily a successful attempt by financiers, railroad builders and industrialists in the Northeast, using the Republican Party, to control the national government for its own selfish economic ends. Those ends were to continue the wartime high protective tariff, the new network of national banks, and to guarantee a "sound" currency. To succeed the business class had to remove the old ruling [[agrarian]] class of Southern planters and Midwestern farmers. This it did by inaugurating Reconstruction, which made the South Republican, and by selling its policies to the voters wrapped up in such attractive vote-getting packages as northern patriotism or the bloody shirt. Historian William Hesseltine added the point that the Northeastern businessmen wanted to control the South economically, which they did through ownership of the railroads.<ref>Williams 1946 p470</ref> However, historians in the 1950s and 1960s refuted Beale's economic causation by demonstrating that Northern businessmen were widely divergent on monetary or tariff policy, and seldom paid attention to Reconstruction issues.<ref name=Foner1982>Foner, Eric (1982) "Reconstruction Revisited" in ''Reviews in American History'', Vol. 10, No. 4, ''The Promise of American History: Progress and Prospects'' (Dec., 1982), pp. 82-100, review of the historiography, online in Project MUSE</ref>
| | To determine Δ''H'', many if not most of the air dispersion models developed between the late 1960s and the early 2000s used what are known as "the Briggs equations." G.A. Briggs first published his plume rise observations and comparisons in 1965.<ref>G.A. Briggs, "A plume rise model compared with observations", ''JAPCA'', 15:433–438, 1965.</ref> In 1968, at a symposium sponsored by CONCAWE (a Dutch organization), he compared many of the plume rise models then available in the literature.<ref>G.A. Briggs, "CONCAWE meeting: discussion of the comparative consequences of different plume rise formulas", ''Atmos. Envir.'', 2:228–232, 1968.</ref> In that same year, Briggs also wrote the section of the publication edited by Slade<ref>D.H. Slade (editor), "Meteorology and atomic energy 1968", Air Resources Laboratory, U.S. Dept. of Commerce, 1968.</ref> dealing with the comparative analyses of plume rise models. That was followed in 1969 by his classical critical review of the entire plume rise literature,<ref>G.A. Briggs, "Plume Rise", ''USAEC Critical Review Series'', 1969.</ref> in which he proposed a set of plume rise equations which have become widely known as "the Briggs equations". Subsequently, Briggs modified his 1969 plume rise equations in 1971 and in 1972.<ref>G.A. Briggs, "Some recent analyses of plume rise observation", ''Proc. Second Internat'l. Clean Air Congress'', Academic Press, New York, 1971.</ref><ref>G.A. Briggs, "Discussion: chimney plumes in neutral and stable surroundings", ''Atmos. Envir.'', 6:507–510, 1972.</ref> |
|
| |
|
| In the 1960s, [[neoabolitionist]] historians emerged, led by [[John Hope Franklin]], [[Kenneth Stampp]] and [[Eric Foner]]. Strongly aligned with the [[American Civil Rights Movement (1955-1968)|Civil Rights Movement]], they rejected the Dunning school and found a great deal to praise in Radical Reconstruction. Foner, the primary advocate of this view, argued that it was never truly completed, and that a Second Reconstruction was needed in the late 20th century to complete the goal of full equality for African-Americans. The neo-abolitionists followed the revisionists in minimizing the corruption and waste created by Republican state governments, saying it was no worse than Boss Tweed's ring in New York City.<ref>Williams, 469</ref> Instead they emphasized that poor treatment of Freedmen was a worse scandal and a grave corruption of America's republican ideals. They argued that the real tragedy of Reconstruction was not that it failed because blacks were incapable of governing, but that it failed because the civil rights and equalities granted during this period were but a passing, temporary development. These rights were suspended in the South from the 1880s through 1964, but were restored by the Civil Rights Movement that is sometimes referred to as the "Second Reconstruction."
| | Briggs divided air pollution plumes into these four general categories: |
| | * Cold jet plumes in calm ambient air conditions |
| | * Cold jet plumes in windy ambient air conditions |
| | * Hot, buoyant plumes in calm ambient air conditions |
| | * Hot, buoyant plumes in windy ambient air conditions |
|
| |
|
| More recent work by Nina Silber, David Blight, Cecelia O'Leary, Laura Edwards, LeeAnn Whites, and Edward J. Blum, has encouraged greater attention to race, religion, and issues of gender while at the same time pushing the "end" of Reconstruction to the end of the nineteenth century, while monographs by Charles Reagan Wilson, Gaines Foster, W. Scott Poole have offered new views of the southern "Lost Cause."
| | Briggs considered the trajectory of cold jet plumes to be dominated by their initial velocity momentum, and the trajectory of hot, buoyant plumes to be dominated by their buoyant momentum to the extent that their initial velocity momentum was relatively unimportant. Although Briggs proposed plume rise equations for each of the above plume categories, '''''it is important to emphasize that "the Briggs equations" which become widely used are those that he proposed for bent-over, hot buoyant plumes'''''. |
|
| |
|
| == Significant dates ==
| | In general, Briggs's equations for bent-over, hot buoyant plumes are based on observations and data involving plumes from typical combustion sources such as the flue gas stacks from steam-generating boilers burning fossil fuels in large power plants. Therefore the stack exit velocities were probably in the range of 20 to 100 ft/s (6 to 30 m/s) with exit temperatures ranging from 250 to 500 °F (120 to 260 °C). |
|
| |
|
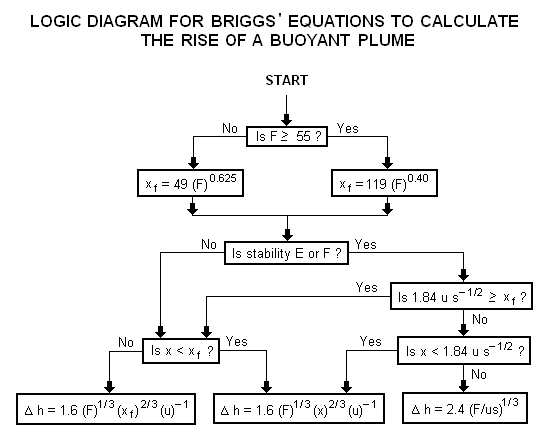
| {| class="wikitable" | | A logic diagram for using the Briggs equations<ref name=Beychok/> to obtain the plume rise trajectory of bent-over buoyant plumes is presented below: |
| ! State !! Seceded from Union !! Joined Confederacy !! Readmitted into Union !! Democratic Party Establishes Control
| | [[Image:BriggsLogic.png|none]] |
| | :{| border="0" cellpadding="2" |
| |- | | |- |
| |[[South Carolina]] || [[December 20]], 1860 || [[February 4]], 1861 ||[[July 9]], 1868 || [[April 11]], 1877 | | |align=right|where: |
| | | |
| |- | | |- |
| |[[Mississippi]] || [[January 9]], 1861 || [[February 4]], 1861 || [[February 23]], 1870 || [[January 4]], 1876 | | !align=right| Δh |
| | |align=left|= plume rise, in m |
| |- | | |- |
| |[[Florida]] || [[January 10]], 1861||[[February 4]], 1861 || [[June 25]], 1868 || [[January 2]], 1877 | | !align=right| F<sup> </sup> <!-- The HTML is needed to line up characters. Do not remove.--> |
| | |align=left|= buoyancy factor, in m<sup>4</sup>s<sup>−3</sup> |
| |- | | |- |
| |[[Alabama]] || [[January 11]], 1861 || [[February 4]], 1861 || [[July 14]], 1868 || [[November 16]], 1874 | | !align=right| x |
| | |align=left|= downwind distance from plume source, in m |
| |- | | |- |
| |[[Georgia (U.S. state)|Georgia]] || [[January 19]], 1861 || [[February 4]], 1861 || [[July 15]], 1870 || [[November 1]], 1871 | | !align=right| x<sub>f</sub> |
| | |align=left|= downwind distance from plume source to point of maximum plume rise, in m |
| |- | | |- |
| |[[Louisiana]] || [[January 26]], 1861 || [[February 4]], 1861 || [[June 25]] or [[July 9]], 1868 || [[January 2]], 1877 | | !align=right| u |
| | |align=left|= windspeed at actual stack height, in m/s |
| |- | | |- |
| |[[Texas]] || [[February 1]], 1861 || [[March 2]], 1861 || [[March 30]], 1870 || [[January 14]], 1873 | | !align=right| s<sup> </sup> <!-- The HTML is needed to line up characters. Do not remove.--> |
| |-
| | |align=left|= stability parameter, in s<sup>−2</sup> |
| |[[Virginia]] || [[April 17]], 1861 || [[May 7]], 1861 || [[January 26]], 1870 || [[October 5]], 1869
| |
| |-
| |
| |[[Arkansas]] || [[May 6]], 1861 || [[May 18]], 1861 || [[June 22]], 1868 || [[November 10]], 1874
| |
| |-
| |
| |[[North Carolina]] || [[May 21]], 1861 || [[May 16]], 1861 || [[July 4]], 1868 || [[November 28]], 1876
| |
| |-
| |
| |[[Tennessee]] || [[June 8]], 1861 || [[May 16]], 1861 || [[July 24]], 1866 ||[[October 4]], 1869 | |
| |} | | |} |
| | The above parameters used in the Briggs' equations are discussed in Beychok's book.<ref name=Beychok/> |
| | |
| | ==References== |
| | {{reflist}} |
| | |
| | == Further reading== |
| | |
| | *{{cite book | author=M.R. Beychok| title=Fundamentals Of Stack Gas Dispersion | edition=4th Edition | publisher=author-published | year=2005 | isbn=0-9644588-0-2}} |
|
| |
|
| ==Bibliography== | | *{{cite book | author=K.B. Schnelle and P.R. Dey| title=Atmospheric Dispersion Modeling Compliance Guide | edition=1st Edition| publisher=McGraw-Hill Professional | year=1999 | isbn=0-07-058059-6}} |
|
| |
|
| See [[Reconstruction: Bibliography]] for a much longer guide
| | *{{cite book | author=D.B. Turner| title=Workbook of Atmospheric Dispersion Estimates: An Introduction to Dispersion Modeling | edition=2nd Edition | publisher=CRC Press | year=1994 | isbn=1-56670-023-X}} |
|
| |
|
| * Donald, David H. et al., ''Civil War and Reconstruction'' (2001) textbook | | *{{cite book | author= S.P. Arya| title=Air Pollution Meteorology and Dispersion | edition=1st Edition | publisher=Oxford University Press | year=1998 | isbn=0-19-507398-3}} |
| * Du Bois, W.E.B. "Reconstruction and its Benefits," ''American Historical Review'', 15 (July, 1910), 781—99 [http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0002-8762%28191007%2915%3A4%3C781%3ARAIB%3E2.0.CO%3B2-T JSTOR]
| |
| * Donald, David Herbert. ''Charles Sumner and the Rights of Man'' (1970), Pulitzer prize winning biography
| |
| * Dunning, William Archibald. ''Reconstruction: Political & Economic, 1865-1877'' (1905). Blames Carpetbaggers for failure of Reconstruction. [http://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=XgIOAAAAIAAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR13&dq=Dunning,+William+Archibald.+%27%27Reconstruction:+Political+%26+&ots=hfgL3IVGbC&sig=hJEGx4hCEmMeJr0FqSVkvr9ECPg online edition]
| |
| * Fitzgerald, Michael W. ''Splendid Failure: Postwar Reconstruction in the American South.'' (2007. xiv, 234 pp. isbn 978-1-56663-734-3.)
| |
| * [[Walter Lynwood Fleming]] [http://www.blackmask.com/books11c/sequelapdex.htm ''The Sequel of Appomattox, A Chronicle of the Reunion of the States''(1918)]. [[Dunning School]][http://www.historians.org/info/AHA_History/jhfranklin.htm].
| |
| * Foner, Eric and Mahoney, Olivia. ''America's Reconstruction: People and Politics After the Civil War.'' short well-illustrated survey from [[neoabolitionist]] perspective
| |
| * Foner, Eric. ''Reconstruction: America's Unfinished Revolution, 1863-1877'' (1988) Pulitzer-prize winning synthesis from [[neoabolitionist]] perspective
| |
| * Foner, Eric. ''Forever Free: The Story of Emancipation and Reconstruction.'' 2005. 268 pp. popular version from [[neoabolitionist]] perspective
| |
| * Ford, Lacy K., ed. ''A Companion to the Civil War and Reconstruction.'' Blackwell, 2005. 518 pp.
| |
| * Franklin, John Hope. ''Reconstruction after the Civil War'' (1961), University of Chicago Press, 280 pages. Short survey by leading black scholar
| |
| * Jenkins, Wilbert L. ''Climbing up to Glory: A Short History of African Americans during the Civil War and Reconstruction.'' SR Books, 2002. 285 pp.
| |
| * Litwack, Leon. ''Been in the Storm So Long'' (1979). Pulitzer Prize; focus on the African Americans from [[neoabolitionist]] perspective
| |
| * Milton, George Fort. ''The Age of Hate: Andrew Johnson and the Radicals.'' (1930). [http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=14804076 online edition] Based on [[Dunning School]]
| |
| * Oberholtzer, Ellis Paxson. ''A History of the United States since the Civil War''. Vol 1 and vol 2 (1917). Based on [[Dunning School]] [http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=55407034 vol 1 online, 1865-68]
| |
| * Perman, Michael. ''Emancipation and Reconstruction'' (2003). 144 pp.
| |
| * Randall, J. G. ''The Civil War and Reconstruction'' (1953). Long the standard survey, with elaborate bibliography; updated by David Donald in 1961
| |
| * Rhodes, James G. ''History of the United States from the Compromise of 1850 to the McKinley-Bryan Campaign of 1896. Volume: 6.'' (1920). 1865-72; Highly detailed narrative by Pulitzer prize winner; argues was a political disaster because it violated the rights of white Southerners.
| |
| * Stampp, Kenneth M. ''The Era of Reconstruction, 1865-1877'' (1967); survey from [[neoabolitionist]] perspective
| |
| * Trefousse, Hans L. ''Historical Dictionary of Reconstruction'' Greenwood (1991), 250 entries
| |
| * Trefousse, Hans L. ''Andrew Johnson: A Biography'' (1989) [http://www.questia.com/library/book/andrew-johnson-a-biography-by-hans-l-trefousse.jsp online edition]
| |
| * Trefousse, Hans L. ''Thaddeus Stevens: Nineteenth-Century Egalitarian'' (1997)
| |
| * Williams, T. Harry. "An Analysis of Some Reconstruction Attitudes" ''The Journal of Southern History,'' Vol. 12, No. 4. (Nov., 1946), pp. 469-486. [http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0022-4642%28194611%2912%3A4%3C469%3AAAOSRA%3E2.0.CO%3B2-N JSTOR]
| |
|
| |
|
| ===Primary sources=== | | *{{cite book | author=R. Barrat| title=Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling | edition=1st Edition | publisher=Earthscan Publications | year=2001 | isbn=1-85383-642-7}} |
|
| |
|
| * Fleming, Walter L. ''Documentary History of Reconstruction: Political, Military, Social, Religious, Educational, and Industrial'' 2 vol (1906). Uses broad collection of primary sources; vol 1 on national politics; vol 2 on states; [http://books.google.com/books?vid=0OnNK8pM92WrjQK2ijCaciu&id=yukLAAAAIAAJ&printsec=toc&dq=%22Documentary+History+of+Reconstruction%22&sig=KbFxeYrtnbJAFZRBvK_rApDguQg#PPR11,M1 volume 1 online 493 pp ] and [http://books.google.com/books?vid=0lH-_oan672uKoftngo_tzc&id=beoLAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA305&lpg=PA305&dq=documentary+plantation&as_brr=1#PPR7,M1 vol 2 online 480 pp ] | | *{{cite book | author=S.R. Hanna and R.E. Britter| title=Wind Flow and Vapor Cloud Dispersion at Industrial and Urban Sites | edition=1st Edition | publisher=Wiley-American Institute of Chemical Engineers | year=2002 | isbn=0-8169-0863-X}} |
| * Lynch, John R. ''The Facts of Reconstruction.'' (1913)[http://www.gutenberg.org/files/16158/16158-h/16158-h.htm Full text online]. Memoir by black congressmen from Mississippi during Reconstruction.
| |
| * McPherson, Edward, ed. [http://books.google.com/books?vid=LCCN04007498&id=kaG2Am68tuAC&pg=PP3&dq=mcpherson+period+of+reconstruction '' The Political History of the United States of America During the Period of Reconstruction'' (1875)], large collection of speeches and primary documents, 1865-1870, complete text online.
| |
| * Stalcup, Brenda. ed. ''Reconstruction: Opposing Viewpoints'' (Greenhaven Press: 1995). Primary documents from opposing viewpoints.
| |
|
| |
|
| ====Notes==== | | *{{cite book | author=P. Zannetti| title=Air pollution modeling : theories, computational methods, and available software | edition= | publisher= Van Nostrand Reinhold | year=1990 | isbn=0-442-30805-1 }} |
| <references/>
| |



![{\displaystyle \exp \;[-\,y^{2}/\,(2\;\sigma _{y}^{2}\;)\;]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e8925630e3b8de6be025fb258aa809189a852082)



![{\displaystyle \;\exp \;[-\,(z-H)^{2}/\,(2\;\sigma _{z}^{2}\;)\;]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/32be81e17b8659fb72ef85e886a95c57401160bd)

![{\displaystyle \;\exp \;[-\,(z+H)^{2}/\,(2\;\sigma _{z}^{2}\;)\;]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b8359e355bf985dc7714abecb7a250155e07b62f)

![{\displaystyle \sum _{m=1}^{\infty }\;{\big \{}\exp \;[-\,(z-H-2mL)^{2}/\,(2\;\sigma _{z}^{2}\;)\;]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/37cb296347f56a0618c59d247cbf00125fc3de8c)
![{\displaystyle +\,\exp \;[-\,(z+H+2mL)^{2}/\,(2\;\sigma _{z}^{2}\;)\;]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8546ac2627ada5bfebad51a692c902206a5efa2c)
![{\displaystyle +\,\exp \;[-\,(z+H-2mL)^{2}/\,(2\;\sigma _{z}^{2}\;)\;]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1fe6a89e17f16835d86e8d9a8971a74db46d1e4b)
![{\displaystyle +\,\exp \;[-\,(z-H+2mL)^{2}/\,(2\;\sigma _{z}^{2}\;)\;]{\big \}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6ff94c96673914895d6e0a6d2643dca0e9e4bc77)