Lake Superior: Difference between revisions
George Swan (talk | contribs) ({{subpages}}) |
George Swan (talk | contribs) (add references) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
[[File:Lake Superior NASA.jpg | thumb]] | [[File:Lake Superior NASA.jpg | thumb]] | ||
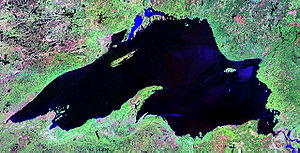
'''Lake Superior''' is the uppermost, deepest and largest of the [[North American Great Lakes]]. It is the largest both by volume and by surface area. The only freshwater lake that has a greater volume is [[Lake Baikal]], in [[Siberia]]. | '''Lake Superior''' is the uppermost, deepest and largest of the [[North American Great Lakes]].<ref name=umkcLakeSuperior/> It is the largest both by volume and by surface area. The only freshwater lake that has a greater volume is [[Lake Baikal]], in [[Siberia]]. | ||
It takes water | It takes water approximately 200 years to transit the lake.<ref name=umkcLakeSuperior/> | ||
The name "Superior" is said to be due to a mistranslation. It is said that early French maps didn't actually name the lake, they merely described it as "superior", meaning uppermost, but English | The name "Superior" is said to be due to a mistranslation. It is said that early French maps didn't actually name the lake, they merely described it as "superior", meaning uppermost, but English travelers, using the French maps, assumed that was its name.<ref name=SuperiorName/> | ||
The lake forms part of the boundary between [[Canada]] and the [[United States of America|United States]]. Over 100 [[Lake freighter]]s, and many "salties" use the lake to transport ore, grain, and construction materials like sand, gravel, limestone, and raw cement. | The lake forms part of the boundary between [[Canada]] and the [[United States of America|United States]]. Over 100 [[Lake freighter]]s, and many "salties" use the lake to transport ore, grain, and construction materials like sand, gravel, limestone, and raw cement. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
[[Duluth, Minnesota]], at the very western tip of the lake, is the most important port on the United States' side. | [[Duluth, Minnesota]], at the very western tip of the lake, is the most important port on the United States' side. | ||
==References== | |||
{{reflist|refs= | |||
<ref name=umkcLakeSuperior> | |||
[http://law2.umkc.edu/faculty/projects/ftrials/superior/superiorfacts.html Lake Superior Facts] | |||
</ref> | |||
<ref name=SuperiorName> | |||
[https://www.eekwi.org/great-lakes/humans-and-great-lakes/great-lakes-name-meanings#:~:text=The%20first%20French%20explorers%20approaching,the%20name%20became%20Lake%20Superior. Great Lakes name meanings] | |||
</ref> | |||
}} | |||
Revision as of 23:36, 13 February 2024
Lake Superior is the uppermost, deepest and largest of the North American Great Lakes.[1] It is the largest both by volume and by surface area. The only freshwater lake that has a greater volume is Lake Baikal, in Siberia.
It takes water approximately 200 years to transit the lake.[1]
The name "Superior" is said to be due to a mistranslation. It is said that early French maps didn't actually name the lake, they merely described it as "superior", meaning uppermost, but English travelers, using the French maps, assumed that was its name.[2]
The lake forms part of the boundary between Canada and the United States. Over 100 Lake freighters, and many "salties" use the lake to transport ore, grain, and construction materials like sand, gravel, limestone, and raw cement.
Thunder Bay, Ontario, on the northeast shore, is the railhead for Canadian railways.
Duluth, Minnesota, at the very western tip of the lake, is the most important port on the United States' side.