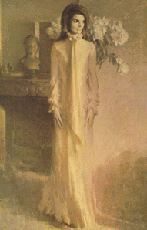Cosmetic surgery: Difference between revisions
imported>Nancy Sculerati MD |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (345 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | |||
{{TOC|right}} | |||
'''Cosmetic Surgery''' (Aesthetic Surgery) is surgery intended to improve appearance, rather than to cure disease. As one expert explains: "Aesthetic surgeons, in the normal practice of their specialty, routinely alter the otherwise acceptable physical form of the patient toward the arbitrary and stylized visages thought desirable either by the patient or by the community in general." <ref>{{cite journal |author=Isenberg J |title=The legacy of Narcissus |journal=Plast Reconstr Surg |volume=110 |pages=1815; author reply 1815-6 |year=2002 |pmid=12447085}}</ref> In other words, cosmetic surgery is surgery in the pursuit of human beauty, according to standards agreed upon by patient and surgeon. [[Plastic surgery]] encompasses ''both'' cosmetic and [[Reconstructive Surgery|reconstructive surgery]]. Currently, Cosmetic Surgery is an umbrella term for the professional knowledge that lies behind a gamut of medical techniques, like skin resurfacing ("peels") and laser ablation of facial capillaries, that are outside the traditional boundaries of operative surgery, ''along'' with the plastic surgery operations, like face lift and nose surgery, that have been used to enhance appearance. | |||
[[ | All surgery is accompanied by some risk of harm, even of death, but it is generally agreed (by patients, health care professionals, and society) that an operation is indicated when the likely benefits outweigh the potential harm. Cosmetic surgery presents a special situation in [[elective surgery]]. How can a surgical treatment ''ever'' be justified when ''no'' illness is present? Although cosmetic procedures do not remedy disease, they can improve the quality of life, and that benefit justifies their performance. In cosmetic surgery, however, the ceiling for acceptable risk of harm to the patient is low compared to operations designed to eradicate disease. Higher risk procedures to improve appearance are usually only contemplated when a person's appearance is so abnormal that it severely impairs his or her ability to interact normally with other people, or when the deformity is the result of a trauma or disease. In these cases, corrective surgery is considered to be [[Reconstructive Surgery|reconstructive]] rather than cosmetic. | ||
=Choosing cosmetic surgery= | |||
One important way that surgeons seek to ensure that the harm of cosmetic surgery does not outweigh its benefits is by patient selection; the ultimate success or failure of a given operation depends as much on proper patient selection as on the technical considerations of the operation. If the expectations of a patient seem reasonable, and if it seems probable that surgery will produce a satisfactory result at a reasonable risk, cosmetic surgery is said to be "indicated". If not, the patient might be suited for a different procedure, or may not be a candidate for any elective cosmetic surgery at all. When an individual has physical attributes that make a good technical result unlikely, or psychological attributes that make the result unlikely to satisfy the patient's wants, then surgery should not be offered. | |||
Well-trained ethical cosmetic surgeons are expected to consider ''why'' their patients want surgery, and to try to dissuade a patient with unreasonable expectations from having surgery, no matter what financial reward is offered. This is not entirely altruistic, as it has been said that “a plastic surgeon makes his money from operating and his reputation from refusing to operate.”<ref>Widgerow AD (2004) First signals. Plast Reconstr Surg 113:2206-10 PMID 15253216</ref>. Additionally, undertaking the surgical transformation of a patient who perceives this change as one of identity, or has demands that cannot be met by surgery because of such underlying disorders as [[Body Dysmorphism Syndrome]], can result in harm ''to the surgeon''. Apart from legal suits lodged as a punitive action, there have been cases of assault and even homicide of plastic surgeons by troubled patients after cosmetic surgery. <ref>Morain WD (1994) Up in arms. [Editorial] Ann Plast Surg 32:445-6 PMID 8210170</ref> <ref>Phillips KA ''et al.'' (2001) Surgical and nonpsychiatric medical treatment of patients with body dysmorphic disorder. Psychosomatics 42:504-10</ref> | |||
=Benefits and | ==Benefits of Cosmetic Surgery== | ||
Sometimes, cosmetic surgery is performed to help increase self-esteem. For example, removing gang-related tattoos, reducing scars, straightening nasal deviations and correcting physical mementoes of assaults can facilitate rehabilitation, ans some people have experienced a tremendous benefit by being freed of these stigmata. Such surgery has even been viewed as having social worth, and has sometimes been financed by charitable organizations and surgical training programs. Surgical modification of an unusual feature present since childhood, like a prominent nose, a receding chin, or a fat pad under the chin, can also sometimes give the patient greater self-confidence. Girls may be self-conscious about a perceived lack of breast development, or overdevelopment, and this may cause them to seek cosmetic surgery in adolescence or adulthood. There is evidence that most patients who undergo these procedures are satisfied with the results.<ref>Simis KJ ''et al.'' (2002) After plastic surgery: adolescent-reported appearance ratings and appearance-related burdens in patient and general population groups. Plast Reconstr Surg 109:9-17 PMID 11786785</ref> | |||
With aging, soft tissues tend to "droop", and a sense of rejuvenation can often be experienced when the appearance of this droop is reduced. The laxity of facial features that come with age also can create an appearance of fatigue or an unpleasant expression, which can be modifed with cosmetic surgery. In other words, pronounced frown lines or facial laxity can mimic the appearance of boredom, anger or otherwise create a misleading impression in social interactions, and change is sought on that basis rather than in pursuit of beauty, per se. When the patient's livelihood depends on personal appearance or photogenicity, the financial cost may be regarded as a business expense, and the time and discomfort as a career investment. | |||
==Risks of Cosmetic Surgery== | |||
''see also [[Surgery]], for risks of surgery'' | |||
All surgery carries some risk of harm, even of death, but there is general agreement (among patients, health care professionals, and society) that an operation is indicated when the likely benefits outweigh the potential harm. In cosmetic surgery, the ceiling for acceptable risk of harm to the patient is low compared to tumor surgery or other operations designed to eradicate disease. Higher risk procedures are usually only contemplated when a person's appearance is so abnormal that it severely impairs his or her ability to interact normally with other people, or when the deformity is the result of a trauma or disease. In these cases, corrective surgery is considered to be [[Reconstructive Surgery|reconstructive]] rather than cosmetic. | |||
If a patient is in poor health, cosmetic procedures ''as a whole'' may be contraindicated, but in most cases of ill health, only some procedures are contraindicated. Prolonged operations that need general anesthesia or injections of local anesthesia with vasoconstrictors (such as epinephrine), are of little risk to healthy individuals, but are of unacceptably high risk to people with severe cardiac disease, for example. Although a patient with such medical problems may not be a candidate for a full rhytidectomy (facelift), alternative procedures, such as dermatological treatments, may offer cosmetic improvement at lower risk. | |||
Sometimes, special care before, during, or after the procedure can reduce the risk of the surgery. For example, medications and plasma may be used to counteract an inherited tendency towards excessive bleeding. Still, in such situations, the patient must accept the greater risk of a problematic outcome, and not all patients wish to proceed. <ref>Borud LJ ''et al.'' (1999) Factor XI deficiency: implications for management of patients undergoing aesthetic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:1907-13 PMID 10541197</ref>. | |||
Cigarette smoking impairs the circulation in tissue flaps and interferes with wound healing. Many cosmetic surgeons insist that patients who desire procedures like facelift surgery ([[Rhytidectomy|rhytidectomy]]) that involve tissue flaps must stop smoking ''well'' before surgery is scheduled. Similarly, the use of aspirin or other drugs that can increase bleeding time is usually discouraged before, and for some time, after surgery. Patients who will not or cannot stop smoking or using medications that promote bleeding, may not be good candidates for soft tissue surgery. | |||
The chance of a poor outcome is higher in some patients because of specific aspects of skin quality or other physical characteristics. In patients with a history of keloid formation or hypertrophic scarring, skin incisions are less likely to heal unobtrusively. Although there are methods to decrease the chance of excessive scarring, the risk of a poor result may make such procedures as body contouring (that require long skin incisions), inappropriate. People with very fair, thin skin, on the other hand, have an increased risk of underlying implants or fracture lines (such as are made on either side of the nose in [[rhinoplasty]]) being evident through the skin after cosmetic surgery. The surgical technique or choice of implants should be tailored to the specific anatomical features of each person. | |||
==="Addiction" to cosmetic surgery=== | |||
= | <ref>Muhlbauer W ''et al.'' (2001) The thersites complex in plastic surgical patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 107:319-26 PMID 11214044</ref> | ||
==Paying for cosmetic surgery== | |||
Although the personal benefits of cosmetic procedures may justify them to the patients that choose to undergo them, and allow them to be accepted as legal and legitimate in most societies; the fact that illness is not present changes how the surgery is financed, as well as the general social support offered to the patient. Whereas private insurance and government health care plans are likely to partially or completely cover the cost of procedures required to treat disease, especially when they are life-threatening, the cost of cosmetic surgery is seldom subsidized by either. | |||
Although there are subcultures in which social networks provide abundant support to patients recovering from cosmetic surgery, generally, employer "sick time" and other institutional allowances are not automatically extended to patients when the surgery is cosmetic. | |||
==Surgeon selection== | |||
People who are contemplating cosmetic surgery are usually advised to take time to investigate the training and qualifications of any physician consulted. This is important, but difficult for a lay person to do successfully. That's because the credentialing of cosmetic surgeons is so variable, even within a single geographic region, and few practitioners are equally qualified in every aspect of each cosmetic procedure. The patient seeking consultation for a desired change in appearance does not necessarily know in advance which cosmetic procedure is best to effect that change, and therefore cannot be sure that the physician consulted has expertise in the procedure that is actually likely to best be of benefit. | |||
===Credentialing of the cosmetic surgeon=== | |||
Cosmetic surgeons come from a variety of backgrounds in surgical, and even dermatological, training. In most countries, a licensed physician can claim expertise in "cosmetics" without training or Board Certification in any of the specialties that are recognized by the medical profession as being part of plastic and cosmetic surgery. A physician can legally advertise cosmetic services even when he or she is not recognized as adequately qualified in cosmetic surgery by experts in the field. The fact that those experts have more than one possible Board Certified Specialty and course of training, complicates the patient's ability to recognize which physicians ''are'' adequately trained in cosmetic surgery. An understanding of which specialties are qualified to perform cosmetic procedures, and which procedures are performed by each is important in evaluating a potential provider of cosmetic surgery. | |||
====General Plastic Surgeons==== | |||
=====American Board of Plastic Surgery (US)===== | |||
The American Board of Plastic Surgery (ABPS) [http://www.abplsurg.org/] is recognized by the American Board of Medical Specialties to certify doctors in the specialty of plastic surgery. In addition to medical school education, requirements for board certification by the American Board of Plastic Surgery include residency or fellowship in Plastic Surgery followed by successful completion of a two-part oral and written examination. | |||
=====American Society of Plastic Surgeons (US)===== | |||
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) [http://www.plasticsurgery.org/], established in 1931, is the largest plastic surgery specialty organization in the world. Requirements to be a member of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons include being certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery. | |||
=====American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (US) [http://www.surgery.org/]===== | |||
=====International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (International) [http://www.isaps.org/]===== | |||
====Facial Plastic Surgeons==== | |||
"Most facial plastic surgeons do their residency training in Otolaryngology-Head-and-Neck Surgery". (US based, International Membership) [http://www.aafprs.org/] | |||
====Ophthalmologic Plastic Surgeons (Oculoplastic Surgery)==== | |||
Oculoplastic Surgery includes cosmetic surgery of the forehead, eyebrows, eyelids and mid-face. Surgeons are usually board-certified ophthalmologists with fellowship training in ophthalmologic plastic surgery. | |||
(Training in UK)[ http://www.oculo-plastics.org.uk/] | |||
====Dermatologists==== | |||
"Dermasurgeons (dermatologists) play an ever-expanding role in the management of cosmetic patient concerns. As a specialty, they have advanced and pioneered safe liposuction, noninvasive endovascular venous technologies, ablative and nonablative laser approaches, and minimally invasive suture-based lifting procedures".(Advanced Cosmetic Surgery Sadick NS - Dermatol Clin - 2005 Jul; 23(3); xi) | |||
(US)[http://www.asds-net.org/Patients/expert/skin_surgery_expert-overview.html] | |||
= | ====Oral and maxillofacial surgeons==== | ||
One group of professionals who are generally recognized as having expertise in cosmetic surgery are not physicians at all, but dentists. Graduates of Dental School who go on to post-graduate residency training in Oral Surgery with adequate experience in facial cosmetic surgery may practice cosmetic facial surgery. "Because of their surgical and dental background, oral and maxillofacial surgeons are uniquely qualified to perform cosmetic procedures that involve the functional and aesthetic aspects of the face, mouth, teeth and jaws." [http://www.aaoms.org/facial_cosmetic_surgery.php] | |||
== | =====Interdisciplinary organizations===== | ||
Some professional organizations dedicated to Cosmetic Surgery now include members of various disciplines [http://www.cosmeticsurgery.org/] | |||
===Cosmetic procedures by other specialists (General Surgeons, Vascular Surgeons, and others)=== | |||
Certain types of procedures are usually performed by specialists whose training and practice is not typically in cosmetic or reconstructive surgery. Vascular surgeons have special expertise in removing varicose veins, and general surgeons, gynecologists, and urologists have expertise in cosmetic procedures of the genitals, anus, and perineum. | |||
==Meeting with the surgeon== | |||
The [[medical ethics|ethical surgeon]] uses techniques of [[Shared Decision-making]], which include undertaking a frank discussion of the risks and benefits of surgery with the patient, and then helping the patient to make a decision that is in the patient's best interests. However, every specialist is somewhat limited by his or her particular training and experience, and will not be equally familiar with all of the operations and procedures available. Patient advocates usually recommend that anyone who is considering elective surgery should find out about the background and reputation of a specialist, and if possible obtain a second opinion before going ahead with an operation. | |||
=Human beauty : universal attributes= | |||
[[Image:Michelangelos David.jpg|thumb|right|250 px|Michaelangelo's statue of David embodies an idealized form of masculine beauty.]] | |||
Symmetry, sexual dimorphism, skin | |||
=Cultural & ethnic considerations= | |||
Whereas certain attributes, like symmetry, seem to be valued by all peoples, there are many preferences that are not uniform - but held by certain people and not by others. The medical literature in cosmetic surgery analyses these preferences, because a good result depends on what the patient, and his peers, see as attractive, and that is not necessarily the same as what the surgeon sees as attractive. | |||
For example, what does the ideal female eyebrow look like? There were a series of ideal positions and shapes of the female eyebrow in European culture over the first three-quarters of the 20th century. A study by German plastic surgeons in 1976 indicated that the age of the patient was a primary determinant of which eyebrow shape and position was seen as more beautiful; older patients preferred the high, arched brow, popular in the earlier part of the era, and younger patients preferred a lower eyebrow without a definite arch. The surgeons concluded that, for beautiful eyebrows, "there is not one single choice, but at least three".<ref>Feser DK ''et al.'' Attractiveness of Eyebrow Position and Shape in Females Depends on the Age of the Beholder. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery.10.1007/s00266-006-0149-x.</ref> | |||
Below, many of the descriptions of cosmetic procedures include operations that are performed more often in certain cultures, and for variations of techniques that are tailored for skin and cartilage characteristics that are more common in some ethnic groups than others. | |||
=Hair transplant= | |||
=== | =Facial cosmetic surgery= | ||
==Forehead and brow== | |||
"The eyebrow is an integral aesthetic part of the upper facial anatomy. Its location and contour convey a degree of emotion and feeling in both men and women." <ref>Goldstein SM. Katowitz JA (2005) The male eyebrow: a topographic anatomic analysis. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 21:285-91 PMID 16052142</ref> | |||
==Cheekbones== | |||
In the west, high prominent cheekbones are generally thought to be beautiful, and many patients undergo the placement of various types of implants in [[Cheekbone augmentation|malar augmentation]] procedures. These procedures are all designed to make the cheekbones more pronounced. | |||
In the east, malar reduction procedure are described. "Young Korean women with prominent zygoma may experience stress in daily life because the Oriental physiognomy often associates prominent zygoma with bad luck. Moreover, prominent zygoma in a wide Oriental face has the effect of making a person appear older and stubborn. Zygomatic reduction is often necessary to relieve stress from self-consciousness about facial appearance and to obtain younger and softer features." <ref>Lee JG, Park YW (2003) Intraoral approach for reduction malarplasty: a simple method. Plast Reconstr Surg 111:453-60 PMID 12496618</ref> | |||
[[ | ==Eyelid surgery ([[Blepharoplasty]])== | ||
==Noses== | |||
===[[Rhinoplasty]]=== | |||
{{Image|Michael Jackson 1984.jpg|left|150px| Michael Jackson, 1984.}} | |||
The recognition of beauty can change over time, and some ethnic characteristics once seen as "ugly" have become widely appreciated as intolerance dissipates. For example, the actress Jennifer Grey experienced a ''set-back'' in her career when she had a cosmetic rhinoplasty that changed her distinctive natural nose (with a delicate downward hook) into a more generic nose with a diminutive button tip. | |||
Until surgical techniques advanced over the last few decades, cosmetic rhinoplasties tended to "overskeletonize" the nose, and such technical complications as pinched appearing nostrils, and collapse of the bridge of the nose ("saddle nose deformity") were fairly common. Especially in fair skinned patients whose skin was also thin, aggressive narrowing of the bony nose by the creation of fracture lines resulted in unsightly long-term results. Years after rhinoplasty, as these patients passed into and past middle age, additional age-related thinning of the skin exposed the irregular contour of these fracture lines. | |||
The initial use of silicone implants, and other materials used to raise the bridge of the nose, was complicated by a relatively high rate of infection, and erosion of the skin and soft tissues of the nasal tip. Poor results were especially frequent when oversize implants were used in an effort to raise the profiles of black and Asian noses, which naturally tend to have a bony pyramid of wider width and more diminutive height. | |||
===Changing ideals and improved techniques=== | |||
[[Rhinoplasty]] currently strives to enhance the appearance of the nose according to the individual face. <ref>Rohrich RJ ''et al.'' (2003) Male rhinoplasty. Ideal nasal proportions vary according to gender race and facial characteristics. Plast Reconstr Surg 112:1071-85 PMID 12973227)</ref> Straightness and refinement of the nasal tip are universal ideals, but modern cosmetic rhinoplasty aims to preserve ethnic and individual nasal characteristics rather than produce a uniform result. | |||
Less aggressive removal of cartilage and bone tends not only to give a more natural result, but to decrease the incidence of collapse from loss of supporting structure. | |||
==Lips== | |||
[[Image:Angelina_Jolie_2003.jpg|left|175 px| Angelina_Jolie, 2003.]] | |||
{{Image|Grace Kelly pressconf Expo67.jpg|right|200px| Grace Kelly, 1967.}} | |||
In the 21st century, very full lips are considered to be ''so'' attractive that procedures to "fill out" the lips are among the most popular procedures requested of aesthetic surgeons. Not only are various fillers injected into the lips, but traditional "cold knife' plastic surgery is used to give more lasting results than fillers can currently provide. <ref>{{cite journal |author=Mutaf M |title=V-Y in V-Y procedure: new technique for augmentation and protrusion of the upper lip |journal=Ann Plast Surg |volume=56 |pages=605-8 |year=2006 |pmid=16721070}}</ref>. | |||
Interestingly, there was little demand for lip augmentation a generation ago, because the fashionable face was different then. Whereas the actress Angelina Jolie (left) is thought by many to have nearly perfect feminine lips in 2007, the actress Grace Kelly was much closer to that ideal in 1967 (right). Both women are generally considered to be great beauties, yet each of them, as pictured in these photographs, might also be considered as candidates for cosmetic surgery. Forty years ago, what are now considered beautifully full lips were then viewed as excessively thick. Rather than lip augmentations, surgeons concentrated on "lip thinning" operations to make the mouth appear smaller and more delicate. Lip reduction operations were a standard part of the facial plastic surgeons repertoire in the 1960's and 1970's, and were featured in the plastic surgery textbooks of those times. Currently, as demand has changed, such procedures receive scant mention in the medical literature. | |||
One could speculate that if Angelina Jolie could be brought back in time to be examined by a cosmetic surgeon in Grace Kelly's era, she might be offered a lip reduction to improve her appearance. On the other hand, Grace Kelly, at the peak of her beauty, might be seen as a candidate for lip augmentation by a contemporary cosmetic surgeon. An awareness of how opinions change over time about what constitutes beauty is important for both the surgeons and the patients involved in cosmetic surgery, as permanent changes in the face and body made to accommodate a preference that is temporary is liable to eventually be regretted by each. | |||
==Jaw== | |||
{{Image|Jacqueline_Lee_Bouvier_Kennedy.gif|left|175px|caption:Part of Jacqueline Kennedy's classic beauty was in the square angle of her jaw.}} | |||
= | Whereas a square angle of the jaw is a mark of great beauty in both men and women of all races in the West, in Asia, in women, the opposite is true. A strong jaw, with a square angle, is traditionally viewed as unsightly. <ref>{{cite journal |author=Satoh K |title=Mandibular contouring surgery by angular contouring combined with genioplasty in orientals |journal=Plast Reconstr Surg |volume=113 |pages=425-30 |year=2004 |pmid=14707669}}</ref> | ||
<ref>{{cite journal |author=Lee D ''et al.'' |title=A simple technique for reduction gonioplasty |journal=Plast Reconstr Surg |volume=111 |issue=2 |pages=951-2 |year=2003 |pmid=12560737}}</ref> | |||
==Rejuvenation of the aging face== | =="Rejuvenation" of the aging face== | ||
Removing lax [[skin]], resurfacing of sun-damaged skin, and tightening of [[subcutaneous tissues]] and facial [[muscles]] can reduce some of the superficial signs of aging, especially when due to sun damage. This type of surgery is often combined with various types of skin resurfacing or dermal fillers. Reversal of some of the signs of ageingin the face can raise self-esteem. <ref>{{cite journal |author=Charles Finn J ''et al.'' |title=Social implications of hyperfunctional facial lines |journal=Dermatol Surg |volume=29 |pages=450-5 |year=2003 |pmid=12752510}}</ref>. Some patients also benefit from the modification of lowered brows, hooded eyes, or frown lines that give the appearance of a negative expression to the face. <ref>{{cite journal |author=Khan JA |title=Aesthetic surgery: diagnosing and healing the miscues of human facial expression |journal=Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg |volume=17 |pages=4-6 |year=200& |pmid=1120674}}</ref> | |||
===Botulinum toxin=== | ===Botulinum toxin=== | ||
"What is so different about the injection of cosmetic botulinum toxin from other injections? Simply stated, neurotoxin injections are a surgical procedure—because the results depend entirely on the injector's knowledge of the underlying muscular anatomy and pharmacology as well as the principles of aesthetics." | "What is so different about the injection of cosmetic botulinum toxin from other injections? Simply stated, neurotoxin injections are a surgical procedure—because the results depend entirely on the injector's knowledge of the underlying muscular anatomy and pharmacology as well as the principles of [[aesthetics]]." <ref>{{cite journal |author=Carruthers J |title=Caveat emptor (buyer beware) |journal=Arch Dermatol |volume=138 |pages=1243-4 |year=2002 |pmid=12224991}}</ref> | ||
===Skin=== | |||
Beauty is only skin deep, or so it is said. From a cosmetic point of view, human skin consists of three layers: epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous fat. | |||
===Dermal fillers=== | ===Dermal fillers=== | ||
The natural matrix of skin lies below the epidermis in the dermis. The main fiber filling the bulk of the dermis is collagen, and the main types of collagen in human skin are I, and III. With aging there is collagen loss, and a change in the abundance of the types of collagen, a relative loss of I and gain of III. | |||
====Bovine collagen==== | |||
====Human collagen==== | |||
=====Human fibroblast cell-culture lines===== | |||
=====Cultured from own skin===== | |||
====Hyaluronic acid==== | |||
Hyaluronic acid is non-allergic, but in pure form, lasts only for a couple of days. | |||
===Laser resurfacing=== | ===Laser resurfacing=== | ||
| Line 95: | Line 165: | ||
===Chemical peels=== | ===Chemical peels=== | ||
=The Neck= | |||
Cosmetic operations on the neck are usually focused either on removing a fat pad, or in rejuvenation surgery. The appearance of the aged neck is primarily due to excess skin as well as laxity of the thin sheet of muscle called the platysma. Various surgical methods of removing the excess skin and "tightening" the underlying muscle are employed. <ref>Rohrich RJ ''et al.'' (2006) Neck rejuvenation revisited. Plast Reconstr Surg 118:1251-63, PMID 17016198</ref> | |||
=Body Recontouring= | |||
{{Image|Rubens - Judgement of Paris.jpg|right|250px|Jean Paul Ruben's painting of the "Judgement of Paris" shows three of the most beautiful mythologic goddesses. This is an example of the idealized female form in 17th century European culture.}} | |||
There are multiple procedures to change the contour of the body for cosmetic enhancement. Generally, the contours sought have at least two ideal forms: male and female, and so the goal of a given procedure, and even the type of procedure, are often different for men and women. | |||
All body recontouring procedures require a skin incision, and every incision leaves a scar. Plastic techniques can minimize the appearance of a scar, but except when surgery is performed in a fetus (which, to date, has never been done for purely cosmetic reasons) no surgical technique, including the use of the laser, can part the full thickness of the skin and not result in a scar. | |||
In liposuction procedures, a long thin cannula is placed through a small skin incision, allowing the contour of large areas of the body to be modified by the suction removal of fat. Placing a small incision in natural skin creases tend to help camoflauge them. However, when the skin is left intact, but the underlying contour is reduced, the appearance may be compromised by lax, hanging skin. | |||
In traditional body contouring surgery, relatively long skin incisions are made, and, not only is underlying fat removed, but closure of the skin and subcutaneous tissue is done in a manner that shapes the body part. Sometimes, for example after massive weight loss, the aim of this surgery is to remove excess skin and effect a "redraping". In other cases, such as breast lift, the emphasis on recontouring is mainly on the underlying tissues, rather than the skin, although skin may be trimmed as part of the procedure. | |||
Because body recontouring by open surgery leaves relatively long scars, cosmetic surgeons try to get the most improvement with the least apparent scarring, so procedures are sometimes combined to allow access to more than one area through the same opening. For example, women who seek abdominal surgery to disguise the effects of childbearing, weight loss, or aging, often also want breast augmentation or mastopexy. Performing the breast augmentation through the abdominoplasty incision means that both results can be achieved in one operation, avoiding incisions on the breasts. (<ref>Rinker B, Jack JM(2007) Subpectoral Breast Augmentation Through the Abdominoplasty Incision. Ann Plast Surg 58:</ref> | |||
==Breast augmentation and mammapexy ("lift")== | |||
Schwarzman E. Goldan S. Wilflingseder P. (1977) The classic reprint. Die Technik der Mammaplastik (the technique of mammaplasty). Plast Reconstr Surg 59:107-12, PMID 318746 | |||
Breast augmentation techniques and resultant shapes have been revised since the invention of the procedure in the 1960s. <ref>{{cite journal |author=Hsia H, Thomson J |title=Differences in breast shape preferences between plastic surgeons and patients seeking breast augmentation |journal=Plast Reconstr Surg |volume=112 |pages=312-20; discussion 321-2 |year=2003 |pmid=12832909}}</ref> | |||
== | ===Medical consequences of breast augmentation=== | ||
=="Belly tuck"== | =="Belly tuck"== | ||
| Line 110: | Line 195: | ||
A 2003 study of abdominoplasty patients indicated significant improvements in body image, as measured by several different outcomes. There were no changes reported in self-esteem or other psychological components. <ref>{{cite journal |author=Bolton M ''et al.'' |title=Measuring outcomes in plastic surgery: body image and quality of life in abdominoplasty patients |journal=Plast Reconstr Surg |volume=112 |pages=619-25; discussion 626-7 |year=2003 |pmid=12900625}}</ref> | |||
=Liposuction= | =Liposuction= | ||
Since 1980, suction-assisted lipoplasty has today become the most commonly performed aesthetic surgical procedure.<ref>Prado A ''et al.'' (2006) A prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial comparing laser-assisted lipoplasty with suction-assisted lipoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 118:1032-45 PMID 16980867.</ref> Liposuction has become so popular that even the FDA, a US government health agency, maintains information on the web as a public service. [http://www.fda.gov/cdrh/liposuction/]. In the US, any licensed physician can perform liposuction. | |||
=Sclerotherapy= | |||
[[Category: | =References= | ||
<references/>[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:00, 2 August 2024
Cosmetic Surgery (Aesthetic Surgery) is surgery intended to improve appearance, rather than to cure disease. As one expert explains: "Aesthetic surgeons, in the normal practice of their specialty, routinely alter the otherwise acceptable physical form of the patient toward the arbitrary and stylized visages thought desirable either by the patient or by the community in general." [1] In other words, cosmetic surgery is surgery in the pursuit of human beauty, according to standards agreed upon by patient and surgeon. Plastic surgery encompasses both cosmetic and reconstructive surgery. Currently, Cosmetic Surgery is an umbrella term for the professional knowledge that lies behind a gamut of medical techniques, like skin resurfacing ("peels") and laser ablation of facial capillaries, that are outside the traditional boundaries of operative surgery, along with the plastic surgery operations, like face lift and nose surgery, that have been used to enhance appearance.
All surgery is accompanied by some risk of harm, even of death, but it is generally agreed (by patients, health care professionals, and society) that an operation is indicated when the likely benefits outweigh the potential harm. Cosmetic surgery presents a special situation in elective surgery. How can a surgical treatment ever be justified when no illness is present? Although cosmetic procedures do not remedy disease, they can improve the quality of life, and that benefit justifies their performance. In cosmetic surgery, however, the ceiling for acceptable risk of harm to the patient is low compared to operations designed to eradicate disease. Higher risk procedures to improve appearance are usually only contemplated when a person's appearance is so abnormal that it severely impairs his or her ability to interact normally with other people, or when the deformity is the result of a trauma or disease. In these cases, corrective surgery is considered to be reconstructive rather than cosmetic.
Choosing cosmetic surgery
One important way that surgeons seek to ensure that the harm of cosmetic surgery does not outweigh its benefits is by patient selection; the ultimate success or failure of a given operation depends as much on proper patient selection as on the technical considerations of the operation. If the expectations of a patient seem reasonable, and if it seems probable that surgery will produce a satisfactory result at a reasonable risk, cosmetic surgery is said to be "indicated". If not, the patient might be suited for a different procedure, or may not be a candidate for any elective cosmetic surgery at all. When an individual has physical attributes that make a good technical result unlikely, or psychological attributes that make the result unlikely to satisfy the patient's wants, then surgery should not be offered.
Well-trained ethical cosmetic surgeons are expected to consider why their patients want surgery, and to try to dissuade a patient with unreasonable expectations from having surgery, no matter what financial reward is offered. This is not entirely altruistic, as it has been said that “a plastic surgeon makes his money from operating and his reputation from refusing to operate.”[2]. Additionally, undertaking the surgical transformation of a patient who perceives this change as one of identity, or has demands that cannot be met by surgery because of such underlying disorders as Body Dysmorphism Syndrome, can result in harm to the surgeon. Apart from legal suits lodged as a punitive action, there have been cases of assault and even homicide of plastic surgeons by troubled patients after cosmetic surgery. [3] [4]
Benefits of Cosmetic Surgery
Sometimes, cosmetic surgery is performed to help increase self-esteem. For example, removing gang-related tattoos, reducing scars, straightening nasal deviations and correcting physical mementoes of assaults can facilitate rehabilitation, ans some people have experienced a tremendous benefit by being freed of these stigmata. Such surgery has even been viewed as having social worth, and has sometimes been financed by charitable organizations and surgical training programs. Surgical modification of an unusual feature present since childhood, like a prominent nose, a receding chin, or a fat pad under the chin, can also sometimes give the patient greater self-confidence. Girls may be self-conscious about a perceived lack of breast development, or overdevelopment, and this may cause them to seek cosmetic surgery in adolescence or adulthood. There is evidence that most patients who undergo these procedures are satisfied with the results.[5]
With aging, soft tissues tend to "droop", and a sense of rejuvenation can often be experienced when the appearance of this droop is reduced. The laxity of facial features that come with age also can create an appearance of fatigue or an unpleasant expression, which can be modifed with cosmetic surgery. In other words, pronounced frown lines or facial laxity can mimic the appearance of boredom, anger or otherwise create a misleading impression in social interactions, and change is sought on that basis rather than in pursuit of beauty, per se. When the patient's livelihood depends on personal appearance or photogenicity, the financial cost may be regarded as a business expense, and the time and discomfort as a career investment.
Risks of Cosmetic Surgery
see also Surgery, for risks of surgery
All surgery carries some risk of harm, even of death, but there is general agreement (among patients, health care professionals, and society) that an operation is indicated when the likely benefits outweigh the potential harm. In cosmetic surgery, the ceiling for acceptable risk of harm to the patient is low compared to tumor surgery or other operations designed to eradicate disease. Higher risk procedures are usually only contemplated when a person's appearance is so abnormal that it severely impairs his or her ability to interact normally with other people, or when the deformity is the result of a trauma or disease. In these cases, corrective surgery is considered to be reconstructive rather than cosmetic.
If a patient is in poor health, cosmetic procedures as a whole may be contraindicated, but in most cases of ill health, only some procedures are contraindicated. Prolonged operations that need general anesthesia or injections of local anesthesia with vasoconstrictors (such as epinephrine), are of little risk to healthy individuals, but are of unacceptably high risk to people with severe cardiac disease, for example. Although a patient with such medical problems may not be a candidate for a full rhytidectomy (facelift), alternative procedures, such as dermatological treatments, may offer cosmetic improvement at lower risk.
Sometimes, special care before, during, or after the procedure can reduce the risk of the surgery. For example, medications and plasma may be used to counteract an inherited tendency towards excessive bleeding. Still, in such situations, the patient must accept the greater risk of a problematic outcome, and not all patients wish to proceed. [6].
Cigarette smoking impairs the circulation in tissue flaps and interferes with wound healing. Many cosmetic surgeons insist that patients who desire procedures like facelift surgery (rhytidectomy) that involve tissue flaps must stop smoking well before surgery is scheduled. Similarly, the use of aspirin or other drugs that can increase bleeding time is usually discouraged before, and for some time, after surgery. Patients who will not or cannot stop smoking or using medications that promote bleeding, may not be good candidates for soft tissue surgery.
The chance of a poor outcome is higher in some patients because of specific aspects of skin quality or other physical characteristics. In patients with a history of keloid formation or hypertrophic scarring, skin incisions are less likely to heal unobtrusively. Although there are methods to decrease the chance of excessive scarring, the risk of a poor result may make such procedures as body contouring (that require long skin incisions), inappropriate. People with very fair, thin skin, on the other hand, have an increased risk of underlying implants or fracture lines (such as are made on either side of the nose in rhinoplasty) being evident through the skin after cosmetic surgery. The surgical technique or choice of implants should be tailored to the specific anatomical features of each person.
"Addiction" to cosmetic surgery
Paying for cosmetic surgery
Although the personal benefits of cosmetic procedures may justify them to the patients that choose to undergo them, and allow them to be accepted as legal and legitimate in most societies; the fact that illness is not present changes how the surgery is financed, as well as the general social support offered to the patient. Whereas private insurance and government health care plans are likely to partially or completely cover the cost of procedures required to treat disease, especially when they are life-threatening, the cost of cosmetic surgery is seldom subsidized by either.
Although there are subcultures in which social networks provide abundant support to patients recovering from cosmetic surgery, generally, employer "sick time" and other institutional allowances are not automatically extended to patients when the surgery is cosmetic.
Surgeon selection
People who are contemplating cosmetic surgery are usually advised to take time to investigate the training and qualifications of any physician consulted. This is important, but difficult for a lay person to do successfully. That's because the credentialing of cosmetic surgeons is so variable, even within a single geographic region, and few practitioners are equally qualified in every aspect of each cosmetic procedure. The patient seeking consultation for a desired change in appearance does not necessarily know in advance which cosmetic procedure is best to effect that change, and therefore cannot be sure that the physician consulted has expertise in the procedure that is actually likely to best be of benefit.
Credentialing of the cosmetic surgeon
Cosmetic surgeons come from a variety of backgrounds in surgical, and even dermatological, training. In most countries, a licensed physician can claim expertise in "cosmetics" without training or Board Certification in any of the specialties that are recognized by the medical profession as being part of plastic and cosmetic surgery. A physician can legally advertise cosmetic services even when he or she is not recognized as adequately qualified in cosmetic surgery by experts in the field. The fact that those experts have more than one possible Board Certified Specialty and course of training, complicates the patient's ability to recognize which physicians are adequately trained in cosmetic surgery. An understanding of which specialties are qualified to perform cosmetic procedures, and which procedures are performed by each is important in evaluating a potential provider of cosmetic surgery.
General Plastic Surgeons
American Board of Plastic Surgery (US)
The American Board of Plastic Surgery (ABPS) [1] is recognized by the American Board of Medical Specialties to certify doctors in the specialty of plastic surgery. In addition to medical school education, requirements for board certification by the American Board of Plastic Surgery include residency or fellowship in Plastic Surgery followed by successful completion of a two-part oral and written examination.
American Society of Plastic Surgeons (US)
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) [2], established in 1931, is the largest plastic surgery specialty organization in the world. Requirements to be a member of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons include being certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery.
American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (US) [3]
International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (International) [4]
Facial Plastic Surgeons
"Most facial plastic surgeons do their residency training in Otolaryngology-Head-and-Neck Surgery". (US based, International Membership) [5]
Ophthalmologic Plastic Surgeons (Oculoplastic Surgery)
Oculoplastic Surgery includes cosmetic surgery of the forehead, eyebrows, eyelids and mid-face. Surgeons are usually board-certified ophthalmologists with fellowship training in ophthalmologic plastic surgery. (Training in UK)[ http://www.oculo-plastics.org.uk/]
Dermatologists
"Dermasurgeons (dermatologists) play an ever-expanding role in the management of cosmetic patient concerns. As a specialty, they have advanced and pioneered safe liposuction, noninvasive endovascular venous technologies, ablative and nonablative laser approaches, and minimally invasive suture-based lifting procedures".(Advanced Cosmetic Surgery Sadick NS - Dermatol Clin - 2005 Jul; 23(3); xi)
(US)[6]
Oral and maxillofacial surgeons
One group of professionals who are generally recognized as having expertise in cosmetic surgery are not physicians at all, but dentists. Graduates of Dental School who go on to post-graduate residency training in Oral Surgery with adequate experience in facial cosmetic surgery may practice cosmetic facial surgery. "Because of their surgical and dental background, oral and maxillofacial surgeons are uniquely qualified to perform cosmetic procedures that involve the functional and aesthetic aspects of the face, mouth, teeth and jaws." [7]
Interdisciplinary organizations
Some professional organizations dedicated to Cosmetic Surgery now include members of various disciplines [8]
Cosmetic procedures by other specialists (General Surgeons, Vascular Surgeons, and others)
Certain types of procedures are usually performed by specialists whose training and practice is not typically in cosmetic or reconstructive surgery. Vascular surgeons have special expertise in removing varicose veins, and general surgeons, gynecologists, and urologists have expertise in cosmetic procedures of the genitals, anus, and perineum.
Meeting with the surgeon
The ethical surgeon uses techniques of Shared Decision-making, which include undertaking a frank discussion of the risks and benefits of surgery with the patient, and then helping the patient to make a decision that is in the patient's best interests. However, every specialist is somewhat limited by his or her particular training and experience, and will not be equally familiar with all of the operations and procedures available. Patient advocates usually recommend that anyone who is considering elective surgery should find out about the background and reputation of a specialist, and if possible obtain a second opinion before going ahead with an operation.
Human beauty : universal attributes
Symmetry, sexual dimorphism, skin
Cultural & ethnic considerations
Whereas certain attributes, like symmetry, seem to be valued by all peoples, there are many preferences that are not uniform - but held by certain people and not by others. The medical literature in cosmetic surgery analyses these preferences, because a good result depends on what the patient, and his peers, see as attractive, and that is not necessarily the same as what the surgeon sees as attractive.
For example, what does the ideal female eyebrow look like? There were a series of ideal positions and shapes of the female eyebrow in European culture over the first three-quarters of the 20th century. A study by German plastic surgeons in 1976 indicated that the age of the patient was a primary determinant of which eyebrow shape and position was seen as more beautiful; older patients preferred the high, arched brow, popular in the earlier part of the era, and younger patients preferred a lower eyebrow without a definite arch. The surgeons concluded that, for beautiful eyebrows, "there is not one single choice, but at least three".[8]
Below, many of the descriptions of cosmetic procedures include operations that are performed more often in certain cultures, and for variations of techniques that are tailored for skin and cartilage characteristics that are more common in some ethnic groups than others.
Hair transplant
Facial cosmetic surgery
Forehead and brow
"The eyebrow is an integral aesthetic part of the upper facial anatomy. Its location and contour convey a degree of emotion and feeling in both men and women." [9]
Cheekbones
In the west, high prominent cheekbones are generally thought to be beautiful, and many patients undergo the placement of various types of implants in malar augmentation procedures. These procedures are all designed to make the cheekbones more pronounced.
In the east, malar reduction procedure are described. "Young Korean women with prominent zygoma may experience stress in daily life because the Oriental physiognomy often associates prominent zygoma with bad luck. Moreover, prominent zygoma in a wide Oriental face has the effect of making a person appear older and stubborn. Zygomatic reduction is often necessary to relieve stress from self-consciousness about facial appearance and to obtain younger and softer features." [10]
Eyelid surgery (Blepharoplasty)
Noses
Rhinoplasty
The recognition of beauty can change over time, and some ethnic characteristics once seen as "ugly" have become widely appreciated as intolerance dissipates. For example, the actress Jennifer Grey experienced a set-back in her career when she had a cosmetic rhinoplasty that changed her distinctive natural nose (with a delicate downward hook) into a more generic nose with a diminutive button tip.
Until surgical techniques advanced over the last few decades, cosmetic rhinoplasties tended to "overskeletonize" the nose, and such technical complications as pinched appearing nostrils, and collapse of the bridge of the nose ("saddle nose deformity") were fairly common. Especially in fair skinned patients whose skin was also thin, aggressive narrowing of the bony nose by the creation of fracture lines resulted in unsightly long-term results. Years after rhinoplasty, as these patients passed into and past middle age, additional age-related thinning of the skin exposed the irregular contour of these fracture lines.
The initial use of silicone implants, and other materials used to raise the bridge of the nose, was complicated by a relatively high rate of infection, and erosion of the skin and soft tissues of the nasal tip. Poor results were especially frequent when oversize implants were used in an effort to raise the profiles of black and Asian noses, which naturally tend to have a bony pyramid of wider width and more diminutive height.
Changing ideals and improved techniques
Rhinoplasty currently strives to enhance the appearance of the nose according to the individual face. [11] Straightness and refinement of the nasal tip are universal ideals, but modern cosmetic rhinoplasty aims to preserve ethnic and individual nasal characteristics rather than produce a uniform result.
Less aggressive removal of cartilage and bone tends not only to give a more natural result, but to decrease the incidence of collapse from loss of supporting structure.
Lips
In the 21st century, very full lips are considered to be so attractive that procedures to "fill out" the lips are among the most popular procedures requested of aesthetic surgeons. Not only are various fillers injected into the lips, but traditional "cold knife' plastic surgery is used to give more lasting results than fillers can currently provide. [12].
Interestingly, there was little demand for lip augmentation a generation ago, because the fashionable face was different then. Whereas the actress Angelina Jolie (left) is thought by many to have nearly perfect feminine lips in 2007, the actress Grace Kelly was much closer to that ideal in 1967 (right). Both women are generally considered to be great beauties, yet each of them, as pictured in these photographs, might also be considered as candidates for cosmetic surgery. Forty years ago, what are now considered beautifully full lips were then viewed as excessively thick. Rather than lip augmentations, surgeons concentrated on "lip thinning" operations to make the mouth appear smaller and more delicate. Lip reduction operations were a standard part of the facial plastic surgeons repertoire in the 1960's and 1970's, and were featured in the plastic surgery textbooks of those times. Currently, as demand has changed, such procedures receive scant mention in the medical literature.
One could speculate that if Angelina Jolie could be brought back in time to be examined by a cosmetic surgeon in Grace Kelly's era, she might be offered a lip reduction to improve her appearance. On the other hand, Grace Kelly, at the peak of her beauty, might be seen as a candidate for lip augmentation by a contemporary cosmetic surgeon. An awareness of how opinions change over time about what constitutes beauty is important for both the surgeons and the patients involved in cosmetic surgery, as permanent changes in the face and body made to accommodate a preference that is temporary is liable to eventually be regretted by each.
Jaw
Whereas a square angle of the jaw is a mark of great beauty in both men and women of all races in the West, in Asia, in women, the opposite is true. A strong jaw, with a square angle, is traditionally viewed as unsightly. [13] [14]
"Rejuvenation" of the aging face
Removing lax skin, resurfacing of sun-damaged skin, and tightening of subcutaneous tissues and facial muscles can reduce some of the superficial signs of aging, especially when due to sun damage. This type of surgery is often combined with various types of skin resurfacing or dermal fillers. Reversal of some of the signs of ageingin the face can raise self-esteem. [15]. Some patients also benefit from the modification of lowered brows, hooded eyes, or frown lines that give the appearance of a negative expression to the face. [16]
Botulinum toxin
"What is so different about the injection of cosmetic botulinum toxin from other injections? Simply stated, neurotoxin injections are a surgical procedure—because the results depend entirely on the injector's knowledge of the underlying muscular anatomy and pharmacology as well as the principles of aesthetics." [17]
Skin
Beauty is only skin deep, or so it is said. From a cosmetic point of view, human skin consists of three layers: epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous fat.
Dermal fillers
The natural matrix of skin lies below the epidermis in the dermis. The main fiber filling the bulk of the dermis is collagen, and the main types of collagen in human skin are I, and III. With aging there is collagen loss, and a change in the abundance of the types of collagen, a relative loss of I and gain of III.
Bovine collagen
Human collagen
Human fibroblast cell-culture lines
Cultured from own skin
Hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid is non-allergic, but in pure form, lasts only for a couple of days.
Laser resurfacing
Chemical peels
The Neck
Cosmetic operations on the neck are usually focused either on removing a fat pad, or in rejuvenation surgery. The appearance of the aged neck is primarily due to excess skin as well as laxity of the thin sheet of muscle called the platysma. Various surgical methods of removing the excess skin and "tightening" the underlying muscle are employed. [18]
Body Recontouring
There are multiple procedures to change the contour of the body for cosmetic enhancement. Generally, the contours sought have at least two ideal forms: male and female, and so the goal of a given procedure, and even the type of procedure, are often different for men and women.
All body recontouring procedures require a skin incision, and every incision leaves a scar. Plastic techniques can minimize the appearance of a scar, but except when surgery is performed in a fetus (which, to date, has never been done for purely cosmetic reasons) no surgical technique, including the use of the laser, can part the full thickness of the skin and not result in a scar.
In liposuction procedures, a long thin cannula is placed through a small skin incision, allowing the contour of large areas of the body to be modified by the suction removal of fat. Placing a small incision in natural skin creases tend to help camoflauge them. However, when the skin is left intact, but the underlying contour is reduced, the appearance may be compromised by lax, hanging skin.
In traditional body contouring surgery, relatively long skin incisions are made, and, not only is underlying fat removed, but closure of the skin and subcutaneous tissue is done in a manner that shapes the body part. Sometimes, for example after massive weight loss, the aim of this surgery is to remove excess skin and effect a "redraping". In other cases, such as breast lift, the emphasis on recontouring is mainly on the underlying tissues, rather than the skin, although skin may be trimmed as part of the procedure.
Because body recontouring by open surgery leaves relatively long scars, cosmetic surgeons try to get the most improvement with the least apparent scarring, so procedures are sometimes combined to allow access to more than one area through the same opening. For example, women who seek abdominal surgery to disguise the effects of childbearing, weight loss, or aging, often also want breast augmentation or mastopexy. Performing the breast augmentation through the abdominoplasty incision means that both results can be achieved in one operation, avoiding incisions on the breasts. ([19]
Breast augmentation and mammapexy ("lift")
Schwarzman E. Goldan S. Wilflingseder P. (1977) The classic reprint. Die Technik der Mammaplastik (the technique of mammaplasty). Plast Reconstr Surg 59:107-12, PMID 318746
Breast augmentation techniques and resultant shapes have been revised since the invention of the procedure in the 1960s. [20]
Medical consequences of breast augmentation
"Belly tuck"
Abdominoplasty
A 2003 study of abdominoplasty patients indicated significant improvements in body image, as measured by several different outcomes. There were no changes reported in self-esteem or other psychological components. [21]
Liposuction
Since 1980, suction-assisted lipoplasty has today become the most commonly performed aesthetic surgical procedure.[22] Liposuction has become so popular that even the FDA, a US government health agency, maintains information on the web as a public service. [9]. In the US, any licensed physician can perform liposuction.
Sclerotherapy
References
- ↑ Isenberg J (2002). "The legacy of Narcissus". Plast Reconstr Surg 110: 1815; author reply 1815-6. PMID 12447085.
- ↑ Widgerow AD (2004) First signals. Plast Reconstr Surg 113:2206-10 PMID 15253216
- ↑ Morain WD (1994) Up in arms. [Editorial] Ann Plast Surg 32:445-6 PMID 8210170
- ↑ Phillips KA et al. (2001) Surgical and nonpsychiatric medical treatment of patients with body dysmorphic disorder. Psychosomatics 42:504-10
- ↑ Simis KJ et al. (2002) After plastic surgery: adolescent-reported appearance ratings and appearance-related burdens in patient and general population groups. Plast Reconstr Surg 109:9-17 PMID 11786785
- ↑ Borud LJ et al. (1999) Factor XI deficiency: implications for management of patients undergoing aesthetic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:1907-13 PMID 10541197
- ↑ Muhlbauer W et al. (2001) The thersites complex in plastic surgical patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 107:319-26 PMID 11214044
- ↑ Feser DK et al. Attractiveness of Eyebrow Position and Shape in Females Depends on the Age of the Beholder. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery.10.1007/s00266-006-0149-x.
- ↑ Goldstein SM. Katowitz JA (2005) The male eyebrow: a topographic anatomic analysis. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 21:285-91 PMID 16052142
- ↑ Lee JG, Park YW (2003) Intraoral approach for reduction malarplasty: a simple method. Plast Reconstr Surg 111:453-60 PMID 12496618
- ↑ Rohrich RJ et al. (2003) Male rhinoplasty. Ideal nasal proportions vary according to gender race and facial characteristics. Plast Reconstr Surg 112:1071-85 PMID 12973227)
- ↑ Mutaf M (2006). "V-Y in V-Y procedure: new technique for augmentation and protrusion of the upper lip". Ann Plast Surg 56: 605-8. PMID 16721070.
- ↑ Satoh K (2004). "Mandibular contouring surgery by angular contouring combined with genioplasty in orientals". Plast Reconstr Surg 113: 425-30. PMID 14707669.
- ↑ Lee D et al. (2003). "A simple technique for reduction gonioplasty". Plast Reconstr Surg 111 (2): 951-2. PMID 12560737.
- ↑ Charles Finn J et al. (2003). "Social implications of hyperfunctional facial lines". Dermatol Surg 29: 450-5. PMID 12752510.
- ↑ Khan JA (200&). "Aesthetic surgery: diagnosing and healing the miscues of human facial expression". Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 17: 4-6. PMID 1120674.
- ↑ Carruthers J (2002). "Caveat emptor (buyer beware)". Arch Dermatol 138: 1243-4. PMID 12224991.
- ↑ Rohrich RJ et al. (2006) Neck rejuvenation revisited. Plast Reconstr Surg 118:1251-63, PMID 17016198
- ↑ Rinker B, Jack JM(2007) Subpectoral Breast Augmentation Through the Abdominoplasty Incision. Ann Plast Surg 58:
- ↑ Hsia H, Thomson J (2003). "Differences in breast shape preferences between plastic surgeons and patients seeking breast augmentation". Plast Reconstr Surg 112: 312-20; discussion 321-2. PMID 12832909.
- ↑ Bolton M et al. (2003). "Measuring outcomes in plastic surgery: body image and quality of life in abdominoplasty patients". Plast Reconstr Surg 112: 619-25; discussion 626-7. PMID 12900625.
- ↑ Prado A et al. (2006) A prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial comparing laser-assisted lipoplasty with suction-assisted lipoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 118:1032-45 PMID 16980867.