Artificial neuron: Difference between revisions
imported>Felipe Ortega Gutiérrez No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (27 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | |||
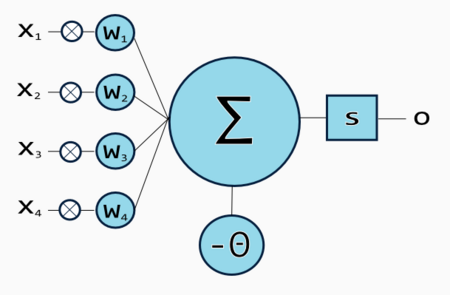
[[Image:artificialneuron.png]] | '''Artificial neurons''' are processing units based on a neural model, often inspired on the biological neurons. The first artificial neuron model was created by McCullough and Pitts, since when newer and more realistic models have appeared. | ||
Artificial neurons can be associated in order to create [[Artificial Neural Network|artificial neural networks]], which process the data carried through the neural connections. | |||
[[Image:artificialneuron.png|thumb|450px|Artificial neuron with 4 inputs.]] | |||
==Behavior== | ==Behavior== | ||
Neural processing involves the following operations: | |||
a) Synaptic operation. Processes incoming data, considering the strength of each connection (often represented as a value called ''weight''). | |||
b) Somatic operation. Provides operations such as thresholding, aggregation, non-linear activation and dynamic processing to the synaptic inputs. Most of these operations are used to implement a threshold effect. | |||
==Analogy to | ==Analogy to biological neurons== | ||
In biological neurons there is a similar behavior. Inputs are electrical pulses transmitted to the [[synapses]] (terminals in the dendrites). Electrical pulses produce a release of [[neurotransmitters]] which may alter the dendritic membrane potential ('' | In biological neurons there is a similar behavior. Inputs are electrical pulses transmitted to the [[synapses]] (terminals in the dendrites). Electrical pulses produce a release of [[neurotransmitter|neurotransmitters]] which may alter the dendritic membrane potential (''post-synaptic potential''). The post-synaptic potential travels over the axon, reaching another neuron, which will sum all the post-synaptic potentials received, and fire an output if the total sum of the post-synaptic potentials in the axon hillock received exceeds a threshold.[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:00, 13 July 2024
Artificial neurons are processing units based on a neural model, often inspired on the biological neurons. The first artificial neuron model was created by McCullough and Pitts, since when newer and more realistic models have appeared.
Artificial neurons can be associated in order to create artificial neural networks, which process the data carried through the neural connections.
Behavior
Neural processing involves the following operations:
a) Synaptic operation. Processes incoming data, considering the strength of each connection (often represented as a value called weight).
b) Somatic operation. Provides operations such as thresholding, aggregation, non-linear activation and dynamic processing to the synaptic inputs. Most of these operations are used to implement a threshold effect.
Analogy to biological neurons
In biological neurons there is a similar behavior. Inputs are electrical pulses transmitted to the synapses (terminals in the dendrites). Electrical pulses produce a release of neurotransmitters which may alter the dendritic membrane potential (post-synaptic potential). The post-synaptic potential travels over the axon, reaching another neuron, which will sum all the post-synaptic potentials received, and fire an output if the total sum of the post-synaptic potentials in the axon hillock received exceeds a threshold.