Isoleucine: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk (stub and structure) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
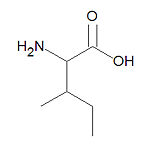
{{Image|Isoleucine stick figure.jpg|right|150px|'''Isoleucine''', one of the common amino acids.}} | |||
'''Isoleucine''', abbreviated '''Ile''' or '''I''', is one of the twenty common [[amino acid]]s used by living organisms to build [[protein]]s. It is a nonpolar, uncharged, aliphatic and [[hydrophobic]] amino acid. In [[protein structure]]s it is normally found in hydrophobic patches sequestered away from the protein surface. It is similar in structure and properties to the amino acids [[leucine]] and [[valine]]. | '''Isoleucine''', abbreviated '''Ile''' or '''I''', is one of the twenty common [[amino acid]]s used by living organisms to build [[protein]]s. It is a nonpolar, uncharged, aliphatic and [[hydrophobic]] amino acid. In [[protein structure]]s it is normally found in hydrophobic patches sequestered away from the protein surface. It is similar in structure and properties to the amino acids [[leucine]] and [[valine]].[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:01, 3 September 2024
Isoleucine, abbreviated Ile or I, is one of the twenty common amino acids used by living organisms to build proteins. It is a nonpolar, uncharged, aliphatic and hydrophobic amino acid. In protein structures it is normally found in hydrophobic patches sequestered away from the protein surface. It is similar in structure and properties to the amino acids leucine and valine.