Sudan: Difference between revisions
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
{{TOC|right}} | {{TOC|right}} | ||
'''Sudan''' is a nation in [[East Africa]], which has the third-largest land area of any country in [[Africa]]. It gained independence from the [[United Kingdom]], and has had near-continuous civil wars and local conflicts since then. The [[Second Sudanese Civil War]] first established, with the [[Machakos Protocol]] of 2002, a framework for agreement, and then, with the [[Naivasha Comprehensive Peace Agreement]] (CPA) in 2005, led to a treaty. The treaty included provisions for a [[referendum]], in 2011, in which the then-[[South Sudan|southern region]] had the option to become an independent nation; the result was over 98% for independence.<ref>''BBC News'': '[http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-africa-12379431 South Sudan backs independence - results]'. February 7, 2011.</ref> The South become independent in July 2011. There is also an active struggle in the [[Darfur]] region in the west of the country, with the most important border being with [[Chad]]; elements of one of the rebel groups in Darfur attacked [[Omdurman]], the sister city/suburb of the national capital, [[Khartoum]], in May 2008. | |||
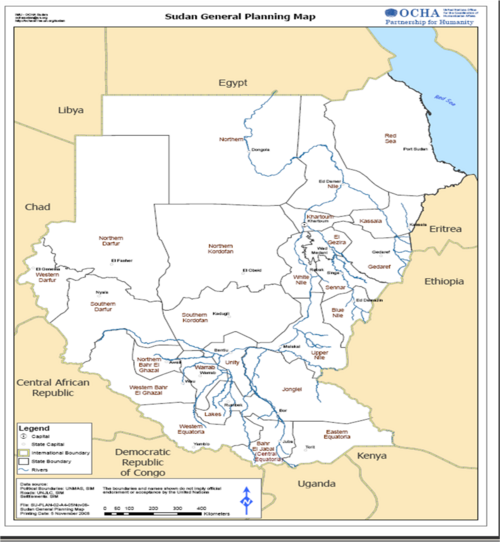
[[Image:Sudan General Planning.png|thumb|left|500px|UN General Planning Map]] | |||
Both the Darfur Conflict and the Civil Wars are complex, mixtures of power, ethnic and sometimes religious struggles. | Both the [[Darfur Conflict]] and the Civil Wars are complex, mixtures of power, ethnic and sometimes religious struggles. Northern Sudan, which has historically held the most power, is [[Arab people|Arab]] and [[Islam|Muslim]], with [[Egypt]]ian ancestry having the highest social status. The former southern region is much more mixed, with Nilotic and other sub-[[Sahara]]n ethnicities, and a mixture of [[Christianity|Christian]], indigenous [[animism|animist]], and Muslim religions. | ||
The main native groups of Darfur, while Muslim, are not Arab. As in the [[The Troubles]], at least for the North-South struggle, religion and ethnicity are surrogates for political and economic power. It is no accident that the peace treaty is called the [[Power-Sharing Agreement]]. | |||
==Government== | ==Government== | ||
Effectively, Sudan is a federation under a coalition government | Effectively, Sudan is a federation under a coalition government headed by the prior national president, [[Omar al-Bashir]], Al-Bashir is national president; [[Ali Osman Taha]], the former national vice-president in the northern-dominated government, is now vice-president. | ||
The major political parties are: | The major political parties are: | ||
*[[National Congress Party]] (NCP), headed by [[Omar al-Bashir]] | *[[National Congress Party]] (NCP), headed by [[Omar al-Bashir]]; | ||
*National Democratic Alliance (NDA); | |||
*National Democratic Alliance (NDA) | **[[Democratic Union Party]] (DUP) [[Muhammad Uthman al-Mirghani]]; | ||
**[[Democratic Union Party]] (DUP) [[Muhammad Uthman al-Mirghani]] | **[[Umma Party]] [[Siddiq al-Mahdi Sadiq]]; | ||
**[[Umma Party]] [[Siddiq al-Mahdi Sadiq]] | **Popular Congress Party (PCP) [[Hassan al-Turabi]]; | ||
**Popular Congress Party (PCP) [[Hassan al-Turabi]] | |||
In March 2009, the [[International Criminal Court]] issued a war crimes indictment against Bashir; a number of other officials previously had been indicted for crimes against humanity, primarily in the Darfur region. <ref name=ICC>{{citation | In March 2009, the [[International Criminal Court]] issued a war crimes indictment against Bashir; a number of other officials previously had been indicted for crimes against humanity, primarily in the Darfur region. <ref name=ICC>{{citation | ||
| date = March 4, 2009 | | date = March 4, 2009 | ||
| title = ICC issues a warrant of arrest for Omar Al Bashir, President of Sudan | | title = ICC issues a warrant of arrest for Omar Al Bashir, President of Sudan | ||
| author = International Criminal Court | | author = [[International Criminal Court]] | ||
| url = http://www.icc-cpi.int/NR/exeres/0EF62173-05ED-403A-80C8-F15EE1D25BB3.htm}}</ref> This is the first warrant ever issued against a sitting | |url= http://www.icc-cpi.int/NR/exeres/0EF62173-05ED-403A-80C8-F15EE1D25BB3.htm}}</ref> This is the first warrant ever issued against a sitting Head of State and the entire matter is evolving. | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| Line 55: | Line 30: | ||
| contribution = Sudan | | contribution = Sudan | ||
| url = https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/print/su.html | | url = https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/print/su.html | ||
| publisher = Central Intelligence Agency}}</ref> | | publisher = [[Central Intelligence Agency]]}}</ref> | ||
*Central African Republic 1,165 km | *[[Central African Republic]] 1,165 km | ||
*Chad 1,360 km | *[[Chad]] 1,360 km | ||
* | *[[Egypt]] 1,273 km | ||
*[[Eritrea]] 605 km | |||
*Eritrea 605 km | *[[Ethiopia]] 1,606 km | ||
*Ethiopia 1,606 km | *[[South Sudan]] | ||
* | *[[Libya]] 383 km | ||
*Libya 383 km | |||
The Blue and White [[Nile]] rivers join to form the Nile at the Khartoum-Omdurman area. Sudan has significant internal river transport, and Port Sudan is on the Red Sea. | |||
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
Before the discovery of oil in 1974, not exploited until years later, the economy was primarily agricultural. Gum arabic, used in a variety of products, was probably its most important export. | Before the discovery of oil in 1974, not exploited until years later, the [[economy]] was primarily agricultural. Gum arabic, used in a variety of products, was probably its most important export. | ||
===Oil=== | ===Oil=== | ||
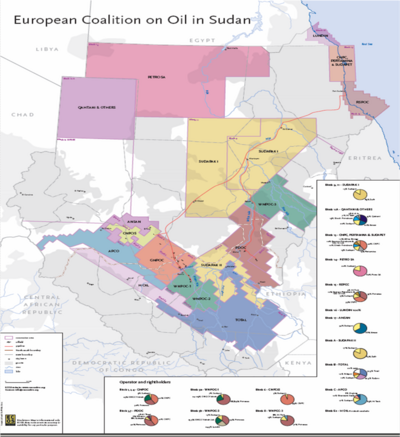
[[Image:Sudan Oil Concessions.png|thumb|left|400px|Foreign oil concessions, 2004 (United Nations)]] | [[Image:Sudan Oil Concessions.png|thumb|left|400px|Foreign oil concessions, 2004 (United Nations)]] | ||
One of the factors in the conflict is the increasing significance of oil; Sudan is self-sufficient and beginning to export. Economically viable oilfields were discovered in 1974 by Chevron Oil, who did not pursue their concession due to security concerns.<ref name=HRW-Chevron>{{citation | One of the factors in the conflict is the increasing significance of [[oil]]; Sudan is self-sufficient and beginning to export. Economically viable oilfields were discovered in 1974 by [[Chevron Oil]], who did not pursue their concession due to security concerns.<ref name=HRW-Chevron>{{citation | ||
| url = http://www.hrw.org/reports/2003/sudan1103/10.htm | | url = http://www.hrw.org/reports/2003/sudan1103/10.htm | ||
| author = Human Rights Watch | | author = Human Rights Watch | ||
| Line 77: | Line 51: | ||
| contribution = The Chevron Period: 1974-92 | | contribution = The Chevron Period: 1974-92 | ||
| title = Sudan, Oil, and Human Rights, HRW Report | | title = Sudan, Oil, and Human Rights, HRW Report | ||
}}</ref> Later, Western firms such as Talisman of Canada, established working fields in the South, centered around Bentiu, but eventually withdrew over shareholder human rights protest. The main oil consortium is the Greater Nile Petroleum Operating Company (GNPOC), | }}</ref> Later, Western firms such as Talisman of Canada, established working fields in the South, centered around Bentiu, but eventually withdrew over shareholder human rights protest. The main oil consortium is the [[Greater Nile Petroleum Operating Company]] (GNPOC), with ownership split among the [[People's Republic of China]], [[India]], and [[Malaysia]]; Sudan has a minor share. | ||
Actual oil drilling | Actual oil drilling was centered around Bentiu in what is now South Sudan, but the only practical means of transporting it was a pipeline traveling north to a refinery outside Khartoum. Initially, the production of this refinery was devoted to domestic use, but export became possible by transport using road, rail, and possibly pipeline to Port Sudan on the Red Sea. Sudan's only seaport is equipped with an oil shipping terminal. | ||
A politically and economically significant, if difficult, alternative being explored is to develop rail service linking Bentiu to railroad facilities in northern Kenya, which would take crude oil as far as the head of a pipeline in Kenya, and thence to a refinery and port at Mombasa, Kenya. While an experienced German firm has been ready to build and fund the railroad, there has been slow progress in getting Kenyan approval for the project. The oil facilities in Mombasa are in need of renovation. | A politically and economically significant, if difficult, alternative being explored is to develop rail service linking Bentiu to [[railroad]] facilities in northern Kenya, which would take crude oil as far as the head of a pipeline in Kenya, and thence to a refinery and port at Mombasa, Kenya. While an experienced [[Germany|German]] firm has been ready to build and fund the railroad, there has been slow progress in getting Kenyan approval for the project. The oil facilities in Mombasa are in need of renovation. | ||
If the South Sudan to Kenya alternative became viable, it would be an immense political-economic lever on the | If the South Sudan to Kenya alternative became viable, it would be an immense political-economic lever on the Sudanese government, which saw the southern deposits as a source of foreign income. There are no likely oil fields in the main areas of the north, although there are in the disputed border provinces of North and South Kordofan. | ||
===Industry=== | ===Industry=== | ||
The country has been growing its industrial sector, much of it in well-designed facilities that make basic materials for infrastructure, such as concrete and steel, although there is some electrical and automotive production in a | The country has been growing its industrial sector, much of it in well-designed facilities that make basic materials for infrastructure, such as concrete and steel, although there is some electrical and automotive parts production in the purpose-built [[Giad Industrial City]]. The Giad facility also assembles vehicles including Accent passenger cars licensed by Korea’s Hyundai Motor Co. (005380.SE), $100,000 heavy-duty trucks licensed by Germany’s Man AG (MAN.XE) and France’s [[Renault]] SA (13190.FR) for sale in Sudan. | ||
Giad Automotive Co. had attempted to obtain capital by listing their stock on the [[Dubai Stock Exchange]], but brokers refused to list them, possibly due to [[United States of America|U.S.]] pressure. The company also makes military equipment, including a [[tank (military)|tank]] observed in Darfur.<ref name=ST2008-08-08>{{citation | |||
| title = Dubai Financial Market declines to list Sudan car firm over US sanctions | |||
| date = 8 August 2008 | journal = [[Sudan Tribune]] | |||
| url = http://www.sudantribune.com/spip.php?page=imprimable&id_article=28198}}</ref> | |||
==Foreign relations== | ==Foreign relations== | ||
Sudan is a member of the [[Arab League]]. Before the Power-Sharing Agreement, Sudan's foreign policy was oriented toward Arab cooperation. | Sudan is a member of the [[Arab League]]. Before the Power-Sharing Agreement, Sudan's foreign policy was oriented toward Arab cooperation. | ||
International economic policy, however, very much related to the participants in the Greater Nile Petroleum Operating Company, currently | International economic policy, however, very much related to the participants in the Greater Nile Petroleum Operating Company, currently China, [[India]], and [[Malaysia]]. Relations with [[France]] were complex, given both French oil concessions in Sudan, and that [[Chad]] is a French client. Since the oilfields are in South Sudan, the northern interests might be quite different if the South dealt with the oil operators. | ||
Since the Agreement, however | Since the Agreement, however, the Southern interactions emphasize [[Uganda]] and [[Kenya]], and has a good deal of interaction with the West as well as China and India. External Christian groups, at a final conference in [[Washington, D.C.]], helped resolve the internal conflict between Dinka and Nuer. There are mutual interests with [[Ethiopia]]. | ||
==Internal conflicts== | ==Internal and border conflicts== | ||
===North-South=== | ===North-South=== | ||
===Dinka-Nuer=== | ===Dinka-Nuer=== | ||
===South Sudan=== | |||
{{main|South Sudan}} | |||
While the [[Darfur Conflict]] has drawn the most world attention, there were more deaths in 2008 in South Sudan than in Darfur, along with more than 350,000 [[Internally Displaced Persons]]. These are primarily local and tribal conflicts, although there is a possibility of limited destabilization from Sudan. It was feared that the Government of Southern Sudan (GoSS) would cease to be viable before the self-determination referendum in January 2011. The International Crisis Group considered Sudanese destabilization possible but not probable.<ref name=ICG-Africa-154>{{citation | |||
| title=Jonglei's Tribal Conflicts: Countering Insecurity in Southern Sudan | |||
| publisher = International Crisis Group | |||
| id = Africa Report N°154 | date = 23 December 2009 | |||
| url = http://www.crisisgroup.org/home/index.cfm?id=6452&l=1}}</ref> The ''New York Times'' reported it as being more likely, mentioning a flow of weapons into the South.<ref name=NYT2009-12-12>{{citation | |||
|date = 12 December 2009 | |||
| title = Violence Grips South Sudan as Vote Nears | |||
| author = Jeffrey Gettleman | journal = [[New York Times]] | |||
| url = http://www.nytimes.com/2009/12/12/world/africa/12sudan.html?_r=1&hpw=&pagewanted=print}}</ref> Before the Power-Sharing Agreement, Sudan assisted the [[Uganda]]n-based [[Lord's Resistance Army]] against the South. | |||
The worst violence is in the state of [[Jonglei]], with an area of 120,000 km<sup>2</sup> and a population of 1.3 million engaged primarily in pastoralism with seasonal migration. Roads and other infrastructure are largely absent, as is a secure food supply and access to justice. "The escalating conflict cycles witnessed in and around Jonglei in 2009 have sown deep mistrust, and movement during the dry season could reignite large-scale conflict".<ref name=ICG-Africa-154 /> An attack in September, against Dinka-majority Duk Padiet in Jonglei, was conducted by [[Nuer]], who said "Dinka-led local government was blockading a road into Nuer areas and not allowing the Nuer access to the river. 'The Nuer felt the government was ignoring them,' said Solomon Pur, a Nuer youth leader."<ref name=NYT2009-12-12 /> | |||
===Darfur=== | ===Darfur=== | ||
{{main|Darfur Conflict}} | |||
{{seealso|Darfur}} | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:01, 23 October 2024
Sudan is a nation in East Africa, which has the third-largest land area of any country in Africa. It gained independence from the United Kingdom, and has had near-continuous civil wars and local conflicts since then. The Second Sudanese Civil War first established, with the Machakos Protocol of 2002, a framework for agreement, and then, with the Naivasha Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA) in 2005, led to a treaty. The treaty included provisions for a referendum, in 2011, in which the then-southern region had the option to become an independent nation; the result was over 98% for independence.[1] The South become independent in July 2011. There is also an active struggle in the Darfur region in the west of the country, with the most important border being with Chad; elements of one of the rebel groups in Darfur attacked Omdurman, the sister city/suburb of the national capital, Khartoum, in May 2008.
Both the Darfur Conflict and the Civil Wars are complex, mixtures of power, ethnic and sometimes religious struggles. Northern Sudan, which has historically held the most power, is Arab and Muslim, with Egyptian ancestry having the highest social status. The former southern region is much more mixed, with Nilotic and other sub-Saharan ethnicities, and a mixture of Christian, indigenous animist, and Muslim religions.
The main native groups of Darfur, while Muslim, are not Arab. As in the The Troubles, at least for the North-South struggle, religion and ethnicity are surrogates for political and economic power. It is no accident that the peace treaty is called the Power-Sharing Agreement.
Government
Effectively, Sudan is a federation under a coalition government headed by the prior national president, Omar al-Bashir, Al-Bashir is national president; Ali Osman Taha, the former national vice-president in the northern-dominated government, is now vice-president.
The major political parties are:
- National Congress Party (NCP), headed by Omar al-Bashir;
- National Democratic Alliance (NDA);
- Democratic Union Party (DUP) Muhammad Uthman al-Mirghani;
- Umma Party Siddiq al-Mahdi Sadiq;
- Popular Congress Party (PCP) Hassan al-Turabi;
In March 2009, the International Criminal Court issued a war crimes indictment against Bashir; a number of other officials previously had been indicted for crimes against humanity, primarily in the Darfur region. [2] This is the first warrant ever issued against a sitting Head of State and the entire matter is evolving.
Geography
Sudan shares boundaries with:[3]
- Central African Republic 1,165 km
- Chad 1,360 km
- Egypt 1,273 km
- Eritrea 605 km
- Ethiopia 1,606 km
- South Sudan
- Libya 383 km
The Blue and White Nile rivers join to form the Nile at the Khartoum-Omdurman area. Sudan has significant internal river transport, and Port Sudan is on the Red Sea.
Economy
Before the discovery of oil in 1974, not exploited until years later, the economy was primarily agricultural. Gum arabic, used in a variety of products, was probably its most important export.
Oil
One of the factors in the conflict is the increasing significance of oil; Sudan is self-sufficient and beginning to export. Economically viable oilfields were discovered in 1974 by Chevron Oil, who did not pursue their concession due to security concerns.[4] Later, Western firms such as Talisman of Canada, established working fields in the South, centered around Bentiu, but eventually withdrew over shareholder human rights protest. The main oil consortium is the Greater Nile Petroleum Operating Company (GNPOC), with ownership split among the People's Republic of China, India, and Malaysia; Sudan has a minor share.
Actual oil drilling was centered around Bentiu in what is now South Sudan, but the only practical means of transporting it was a pipeline traveling north to a refinery outside Khartoum. Initially, the production of this refinery was devoted to domestic use, but export became possible by transport using road, rail, and possibly pipeline to Port Sudan on the Red Sea. Sudan's only seaport is equipped with an oil shipping terminal.
A politically and economically significant, if difficult, alternative being explored is to develop rail service linking Bentiu to railroad facilities in northern Kenya, which would take crude oil as far as the head of a pipeline in Kenya, and thence to a refinery and port at Mombasa, Kenya. While an experienced German firm has been ready to build and fund the railroad, there has been slow progress in getting Kenyan approval for the project. The oil facilities in Mombasa are in need of renovation.
If the South Sudan to Kenya alternative became viable, it would be an immense political-economic lever on the Sudanese government, which saw the southern deposits as a source of foreign income. There are no likely oil fields in the main areas of the north, although there are in the disputed border provinces of North and South Kordofan.
Industry
The country has been growing its industrial sector, much of it in well-designed facilities that make basic materials for infrastructure, such as concrete and steel, although there is some electrical and automotive parts production in the purpose-built Giad Industrial City. The Giad facility also assembles vehicles including Accent passenger cars licensed by Korea’s Hyundai Motor Co. (005380.SE), $100,000 heavy-duty trucks licensed by Germany’s Man AG (MAN.XE) and France’s Renault SA (13190.FR) for sale in Sudan.
Giad Automotive Co. had attempted to obtain capital by listing their stock on the Dubai Stock Exchange, but brokers refused to list them, possibly due to U.S. pressure. The company also makes military equipment, including a tank observed in Darfur.[5]
Foreign relations
Sudan is a member of the Arab League. Before the Power-Sharing Agreement, Sudan's foreign policy was oriented toward Arab cooperation.
International economic policy, however, very much related to the participants in the Greater Nile Petroleum Operating Company, currently China, India, and Malaysia. Relations with France were complex, given both French oil concessions in Sudan, and that Chad is a French client. Since the oilfields are in South Sudan, the northern interests might be quite different if the South dealt with the oil operators.
Since the Agreement, however, the Southern interactions emphasize Uganda and Kenya, and has a good deal of interaction with the West as well as China and India. External Christian groups, at a final conference in Washington, D.C., helped resolve the internal conflict between Dinka and Nuer. There are mutual interests with Ethiopia.
Internal and border conflicts
North-South
Dinka-Nuer
South Sudan
While the Darfur Conflict has drawn the most world attention, there were more deaths in 2008 in South Sudan than in Darfur, along with more than 350,000 Internally Displaced Persons. These are primarily local and tribal conflicts, although there is a possibility of limited destabilization from Sudan. It was feared that the Government of Southern Sudan (GoSS) would cease to be viable before the self-determination referendum in January 2011. The International Crisis Group considered Sudanese destabilization possible but not probable.[6] The New York Times reported it as being more likely, mentioning a flow of weapons into the South.[7] Before the Power-Sharing Agreement, Sudan assisted the Ugandan-based Lord's Resistance Army against the South.
The worst violence is in the state of Jonglei, with an area of 120,000 km2 and a population of 1.3 million engaged primarily in pastoralism with seasonal migration. Roads and other infrastructure are largely absent, as is a secure food supply and access to justice. "The escalating conflict cycles witnessed in and around Jonglei in 2009 have sown deep mistrust, and movement during the dry season could reignite large-scale conflict".[6] An attack in September, against Dinka-majority Duk Padiet in Jonglei, was conducted by Nuer, who said "Dinka-led local government was blockading a road into Nuer areas and not allowing the Nuer access to the river. 'The Nuer felt the government was ignoring them,' said Solomon Pur, a Nuer youth leader."[7]
Darfur
- See also: Darfur
References
- ↑ BBC News: 'South Sudan backs independence - results'. February 7, 2011.
- ↑ International Criminal Court (March 4, 2009), ICC issues a warrant of arrest for Omar Al Bashir, President of Sudan
- ↑ , Sudan, World Factbook, Central Intelligence Agency
- ↑ Human Rights Watch (November 2003), The Chevron Period: 1974-92, Sudan, Oil, and Human Rights, HRW Report
- ↑ "Dubai Financial Market declines to list Sudan car firm over US sanctions", Sudan Tribune, 8 August 2008
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Jonglei's Tribal Conflicts: Countering Insecurity in Southern Sudan, International Crisis Group, 23 December 2009, Africa Report N°154
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Jeffrey Gettleman (12 December 2009), "Violence Grips South Sudan as Vote Nears", New York Times