Navicular bone: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Bruce M. Tindall mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
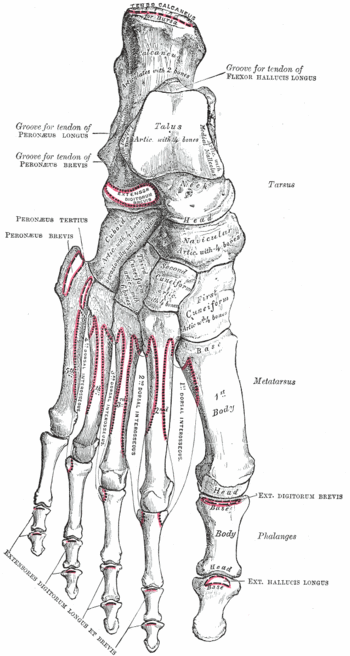
{{Image|Grays-image268.gif|right|350px|Bones of the right foot. Dorsal surface.}} | {{Image|Grays-image268.gif|right|350px|Bones of the right foot. Dorsal surface.}} | ||
In | In [[human anatomy]], the '''navicular bone''', also called '''scaphoid bone''', is one of the tarsal bones of the mid-foot.<ref name="isbn1-58734-102-6chapt6d">{{cite book |author=Gray, Henry David |title=Anatomy of the human body |edition=20th edition|publisher=Bartleby.com |location= |year=1918|chapter=6d. The Foot. 1. The Tarsus|chapterurl=http://www.bartleby.com/107/63.html |pages= |isbn=1-58734-102-6 |oclc= |doi=}}</ref> | ||
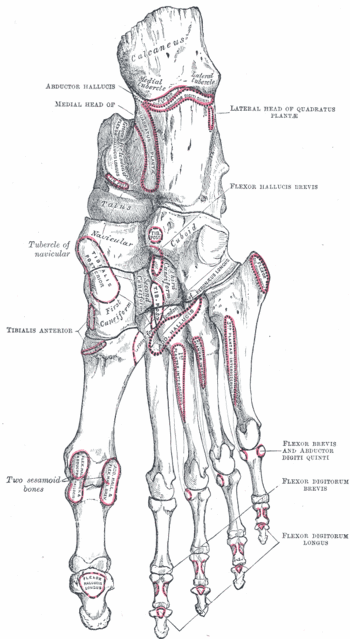
{{Image|Grays-image269.gif|right|350px|Bones of the right foot. Plantar surface.}} | {{Image|Grays-image269.gif|right|350px|Bones of the right foot. Plantar surface.}} | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/>[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:00, 24 September 2024
In human anatomy, the navicular bone, also called scaphoid bone, is one of the tarsal bones of the mid-foot.[1]
The posterior tibial tendon inserts onto the plantar surface of the navicular bone. Rupture or dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon may cause adult flatfoot.[2]
References
- ↑ Gray, Henry David (1918). “6d. The Foot. 1. The Tarsus”, Anatomy of the human body, 20th edition. Bartleby.com. ISBN 1-58734-102-6.
- ↑ Bluman EM, Myerson MS (June 2007). "Stage IV posterior tibial tendon rupture". Foot Ankle Clin 12 (2): 341–62, viii. DOI:10.1016/j.fcl.2007.03.004. PMID 17561206. Research Blogging.