Atorvastatin: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk (drug interactions) |
imported>David E. Volk m (class II --> type II) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
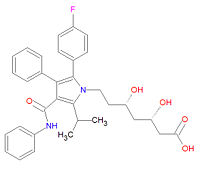
[[Image:Atorvastatin structure.jpg|right|thumb|200px|{{#ifexist:Template:Atorvastatin structure.jpg/credit|{{Atorvastatin structure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}Atorvastatin, a | [[Image:Atorvastatin structure.jpg|right|thumb|200px|{{#ifexist:Template:Atorvastatin structure.jpg/credit|{{Atorvastatin structure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}Atorvastatin, a type II statin.]] | ||
'''Atorvastatin''', commonly called '''Lipitor''', is a | '''Atorvastatin''', commonly called '''Lipitor''', is a type II statin used to treat high cholesterol ([[hypercholesterolemia]]), prevent [[mycardial infarction|heart attacks]] and [[stroke]]s, and to lessen the formation of [[atherlosclerosis|artial plaque]]. It is a [[Hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitor|HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor]] that decreases the synthesis of [[mevalonate]], a key chemical precursor of [[cholesterol]]. Although the structure is based on an indole ring, as are the other type II statins [[fluvastatin]] and [[rosuvastatin]], its longer half-life and specificity for the liver makes atorvastatin a better drug for lowering LDL-cholesterol levels. The metabolites of atorvastatin, ortho- and parahydroxylated derivatives and various beta-oxidation products, are equivalent HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. The drug should be taken with a low fat meal and alcohol and grapefruit juice should be avoided. Atorvastatin can be toxic, leading to liver problems, rhabdomyolysis and eye hemorrhages. | ||
Its official IUPAC chemical name is (3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-propan-2-ylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid and it has chemical formula C<sub>33</sub>H<sub>35</sub>FN<sub>2</sub>O<sub>5</sub>. | Its official IUPAC chemical name is (3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-propan-2-ylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid and it has chemical formula C<sub>33</sub>H<sub>35</sub>FN<sub>2</sub>O<sub>5</sub>. | ||
Revision as of 11:52, 24 January 2008
Atorvastatin, commonly called Lipitor, is a type II statin used to treat high cholesterol (hypercholesterolemia), prevent heart attacks and strokes, and to lessen the formation of artial plaque. It is a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor that decreases the synthesis of mevalonate, a key chemical precursor of cholesterol. Although the structure is based on an indole ring, as are the other type II statins fluvastatin and rosuvastatin, its longer half-life and specificity for the liver makes atorvastatin a better drug for lowering LDL-cholesterol levels. The metabolites of atorvastatin, ortho- and parahydroxylated derivatives and various beta-oxidation products, are equivalent HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. The drug should be taken with a low fat meal and alcohol and grapefruit juice should be avoided. Atorvastatin can be toxic, leading to liver problems, rhabdomyolysis and eye hemorrhages.
Its official IUPAC chemical name is (3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-propan-2-ylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid and it has chemical formula C33H35FN2O5.
brand names
- Cardyl
- Lipitor
- Sotis
- Torvast
- Tozalip
- Xavator
- Sortis
- Torvacard
- Totalip
- Tulip
- Xarator
- Atorpic
- Liprimar
Drug interactions
- Amprenavir can possibly increase the statin
- Atazanavir increases the effect and toxicity of the statin
- Bezafibrate increases the risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis
- Bosentan could decrease atorvastatin
- Carbamazepine decreases the effect of the statin
- Colchicine increases the risk of rhadbomyolysis with this combination
- Clarithromycin possibly increases the statin toxicity
- Cyclosporine may cause myopathy and rhabdomyolysis
- Delavirdine an NNRT inhibitor increases the effect and toxicity of the statin
- Diltiazem increases the effect and toxicity of atorvastatin
- Efavirenz, an NNRT inhibitor, increases the effect and toxicity of the statin
- Erythromycin possibly increases the statin toxicity
- Fenofibrate Increasing risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis
- Fluconazole Increases the risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis
- Fosamprenavir Amprenavir can possibly increase the statin toxicity
- Gemfibrozil Increases the risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis
- Imatinib increases the effect and toxicity of atorvastatin
- Indinavir increases the effect and toxicity of atorvastatin
- Itraconazole Increases the risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis
- Josamycin, a macrolide, possibly increases the statin toxicity
- Ketoconazole increases the risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis
- Nefazodone increases the effect and toxicity of the statin drug
- Nelfinavir increases the effect and toxicity of the statin
- Nevirapine, an NNRT inhibitor, increases the effect and toxicity of the statin
- Quinupristin presents an increased risk of toxicity
- Rifabutin, a rifamycin, decreases the effect of the statin drug
- Rifampin, a rifamycin, decreases the effect of the statin drug
- Ritonavir increases the effect and toxicity of the statin
- Saquinavir increases the effect and toxicity of atorvastatin
- Tacrolimus increases the effect and toxicity of the statin
- Telithromycin may possibly increase statin toxicity
- Verapamil increases the effect and toxicity of the statin