Indinavir: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk (drug interactions partly finished) |
imported>David E. Volk (drug interactions done) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Drug interactions == | == Drug interactions == | ||
The absorption of indinavir is decreased by St. John's Wort, antacids, such as [[aluminum]], [[bismuth]], [[calcium]], [[magnesium]] and [[magnesium oxide]], by [[omeprazole]] and related compounds ([[esomeprazole]], [[lansoprazole]], [[pantoprazole]] and [[rabeprazole]]) and by [[Rifampin]] and its derivitive [[Rifabutin]]. | The absorption of indinavir is decreased by [[St. John's Wort]], [[Vitamin C]], antacids, such as [[aluminum]], [[bismuth]], [[calcium]], [[magnesium]] and [[magnesium oxide]], by [[efavirenz]], [[omeprazole]] and related compounds ([[esomeprazole]], [[lansoprazole]], [[pantoprazole]] and [[rabeprazole]]) and by [[Rifampin]] and its derivitive [[Rifabutin]]. The effects of indinavir are increased when taken with [[clarithromycine]], [[delavirdine]] or [[ketoconazole]]. [[Saquinavir]], also a protease inhibitor, may be an agonist of indinavir. | ||
Indinavir increases the anticoagulant effect of [[anisindione]], [[acenocoumarol]], [[dicumarol]], and [[warfarin]] and also increases the effect of [[benzodiazepine]]. Benzodiazepine related drugs include [[Alprazolam]], [[Chlordiazepoxide]], [[Clonazepam]], [[Clorazepate]], [[Diazepam]], [[Estazolam]], [[Flurazepam]], [[Halazepam]], [[Midazolam]], [[Prazepam]], [[Quazepam]] and [[Triazolam]]. | Indinavir increases the anticoagulant effect of [[anisindione]], [[acenocoumarol]], [[dicumarol]], and [[warfarin]] and also increases the effect of [[benzodiazepine]]. Benzodiazepine related drugs include [[Alprazolam]], [[Chlordiazepoxide]], [[Clonazepam]], [[Clorazepate]], [[Diazepam]], [[Estazolam]], [[Flurazepam]], [[Halazepam]], [[Midazolam]], [[Prazepam]], [[Quazepam]] and [[Triazolam]]. | ||
An increased risk of cariotoxicity and [[arrhythmia]]s occurs when taken with [[astemizole]], [[cisapride]] or [[terfenadine]]. The effects and toxicity of [[amiodarone]], [[atorvastatin]], [[carbamazepine]], [[cyclosporine]], [[fentanyl]], [[fusidic acid]], [[pimozide]], [[sildenafil]], [[tacrolimus]] and [[Vardenafil]] are increased when taken with indinavir. The effect and toxicity of ergot derivatives, such as [[ergotamine]] and [[dihydroergotamine]], and [[erlotinib]], [[quinupristin]], [[ranolazine]] and [[trazodone]] are also increased. An increase in extrapyramidal symptoms may occur with [[risperidone]] and increased risks of [[hyperbilirubinemia]] are associated with [[atazanavir]] use. | |||
== External Links == | == External Links == | ||
{{DailyMed}} | {{DailyMed}} | ||
Drug Bank at http://www.drugbank.ca/cgi-bin/getCard.cgi?CARD=DB00224.txt | Drug Bank at http://www.drugbank.ca/cgi-bin/getCard.cgi?CARD=DB00224.txt | ||
Revision as of 11:04, 29 January 2008
Indinavir, also called indinavir sulfate or Compound J and sold under the trade name Crixivan®, is a protease inhibitor used to treat HIV/AIDS. The HIV-1 protease in required to cleave the viral gag-pol polyprotein into individual functional proteins to make an infectious mature viral particle. Indinavir binds to the HIV-1 protease, inhibiting its function and stopping the production of infectious viral particles. Protease inhibitors are usually used with two or more other anti-HIV medications. Symptoms of overdose include heart attack and chest pain.
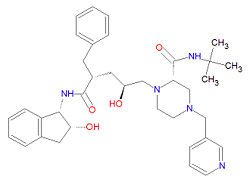
Its IUPAC chemical name is (2S)-N-tert-butyl-1-[(2S,4R)-2-hydroxy-5-[[(1S,2R)-2-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-yl]amino]-5-oxo-4-(phenylmethyl)pentyl]-4-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)piperazine-2-carboxamide and it has chemical formula C36H47N5O4.
Drug interactions
The absorption of indinavir is decreased by St. John's Wort, Vitamin C, antacids, such as aluminum, bismuth, calcium, magnesium and magnesium oxide, by efavirenz, omeprazole and related compounds (esomeprazole, lansoprazole, pantoprazole and rabeprazole) and by Rifampin and its derivitive Rifabutin. The effects of indinavir are increased when taken with clarithromycine, delavirdine or ketoconazole. Saquinavir, also a protease inhibitor, may be an agonist of indinavir.
Indinavir increases the anticoagulant effect of anisindione, acenocoumarol, dicumarol, and warfarin and also increases the effect of benzodiazepine. Benzodiazepine related drugs include Alprazolam, Chlordiazepoxide, Clonazepam, Clorazepate, Diazepam, Estazolam, Flurazepam, Halazepam, Midazolam, Prazepam, Quazepam and Triazolam.
An increased risk of cariotoxicity and arrhythmias occurs when taken with astemizole, cisapride or terfenadine. The effects and toxicity of amiodarone, atorvastatin, carbamazepine, cyclosporine, fentanyl, fusidic acid, pimozide, sildenafil, tacrolimus and Vardenafil are increased when taken with indinavir. The effect and toxicity of ergot derivatives, such as ergotamine and dihydroergotamine, and erlotinib, quinupristin, ranolazine and trazodone are also increased. An increase in extrapyramidal symptoms may occur with risperidone and increased risks of hyperbilirubinemia are associated with atazanavir use.
External Links
Indinavir - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine). Drug Bank at http://www.drugbank.ca/cgi-bin/getCard.cgi?CARD=DB00224.txt