Carbodiimide: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
imported>David E. Volk No edit summary |
imported>David E. Volk (→EDAC) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== EDAC == | == EDAC == | ||
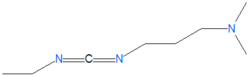
{{Image|EDAC.png|left|250px|EDAC chemical structure.}} | {{Image|EDAC.png|left|250px|EDAC chemical structure.}} | ||
The reagent [[1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide]], abbreviated as EDAC, EDC or EDCI, is a widely used reagent for coupling water soluble carboxylic acids with water soluble primary amides under aqueous conditions and within a [[pH]] range of 4-6. | The reagent [[1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide]], abbreviated as EDAC, EDC or EDCI, is a widely used reagent for coupling water soluble carboxylic acids with water soluble primary amides under aqueous conditions and within a [[pH]] range of 4-6. | ||
Revision as of 11:00, 3 October 2009
EDAC
The reagent 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide, abbreviated as EDAC, EDC or EDCI, is a widely used reagent for coupling water soluble carboxylic acids with water soluble primary amides under aqueous conditions and within a pH range of 4-6.