Diatom: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Pat Palmer (adding an image) |
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) (linking to Google's slideshow of Diatoms of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
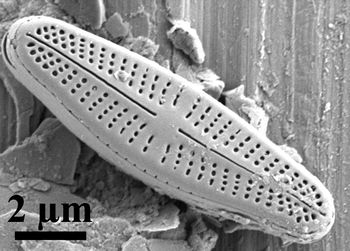
'''Diatom'''s are single-celled [[Algae|algae]] living in water, encased in tiny glass shells. They are the bottom of the food chain. The mix of their populations serves as a good indicator of the health of a body of water. Algae, including diatoms, account for nearly a quarter of the world's oxygen. | '''Diatom'''s are single-celled [[Algae|algae]] living in water, encased in tiny glass shells. They are the bottom of the food chain. The mix of their populations serves as a good indicator of the health of a body of water. Algae, including diatoms, account for nearly a quarter of the world's oxygen. | ||
The intricacy and symmetry of diatom fossils are renowned for their beauty<ref>[https://artsandculture.google.com/story/diatoms-of-the-academy-of-natural-sciences-of-drexel-university-academy-of-natural-sciences-of-drexel-university/BwWh7EaVlShRLw?hl=en Diatoms of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University] slideshow published online by Google. Last access 4/17/2022.</ref>. | |||
Revision as of 10:30, 17 April 2022
- See also: Algae
Diatoms are single-celled algae living in water, encased in tiny glass shells. They are the bottom of the food chain. The mix of their populations serves as a good indicator of the health of a body of water. Algae, including diatoms, account for nearly a quarter of the world's oxygen.
The intricacy and symmetry of diatom fossils are renowned for their beauty[1].
- ↑ Diatoms of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University slideshow published online by Google. Last access 4/17/2022.