Yukon: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) (adding an image) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
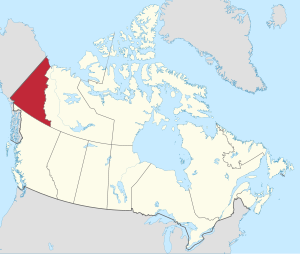
Yukon is a Canadian territory established in 1898 when the Yukon Territory Act was enacted. The Yukon was part of the Canadian Federation and governance of the territory was done through the federal government. James Walsh was appointed as the territories first commissioner in 1897. In 1898, land surveyor William Ogilvie took over as commissioner. | {{Image|Yukon in Canada 2.svg|right|300px|The Yukon territory in Canada.}} | ||
The '''Yukon''' is a [[Canada|Canadian]] territory (as opposed to a province), contiguous to [[Alaska (U.S. state)|Alaska]], established in 1898 when the [[Yukon Territory]] Act was enacted. The Yukon was part of the Canadian Federation and governance of the territory was done through the federal government. James Walsh was appointed as the territories first commissioner in 1897. In 1898, land surveyor William Ogilvie took over as commissioner. | |||
Whitehorse is the territorial capital and the majority of Yukon residents reside in Whitehorse. | Whitehorse is the territorial capital and the majority of Yukon residents reside in Whitehorse. | ||
Revision as of 12:03, 20 August 2024
The Yukon is a Canadian territory (as opposed to a province), contiguous to Alaska, established in 1898 when the Yukon Territory Act was enacted. The Yukon was part of the Canadian Federation and governance of the territory was done through the federal government. James Walsh was appointed as the territories first commissioner in 1897. In 1898, land surveyor William Ogilvie took over as commissioner.
Whitehorse is the territorial capital and the majority of Yukon residents reside in Whitehorse.
References
The Canadian Encyclopedia https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/yukon
Encyclopedia Britannica https://www.britannica.com/place/Yukon-territory