Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Difference between revisions
imported>Alex Lee |
imported>Alex Lee |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
==Cell structure and metabolism== | ==Cell structure and metabolism== | ||
Describe any interesting features and/or cell structures; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces. | Describe any interesting features and/or cell structures; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces. | ||
(Temporary General Outline) | |||
- Obligate Aerobe: Explains why it infects the upper lobes of the lungs | |||
- Slow rate of growth compared to other bacteria (about 15-20 hours) | |||
- Non-motile rod shaped | |||
- Size: ~2-4 um in length and 0.2-0.5 um in width | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
Revision as of 18:16, 28 March 2008
Articles that lack this notice, including many Eduzendium ones, welcome your collaboration! |
Classification
Higher order taxa
Domain: Bacteria
Phylum: Actinobacteria
Order: Actinomycetales
Suborder: Corynebacterineae
Family: Mycobacteriaceae
Species
Genus: Mycobacterium
Species: M. tuberculosis
Description and significance
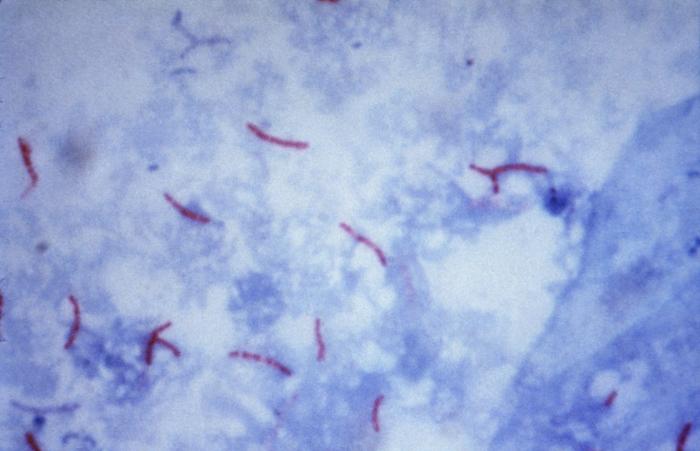 Describe the appearance, habitat, etc. of the organism, and why it is important enough to have its genome sequenced. Describe how and where it was isolated.
Include a picture or two (with sources) if you can find them.
Describe the appearance, habitat, etc. of the organism, and why it is important enough to have its genome sequenced. Describe how and where it was isolated.
Include a picture or two (with sources) if you can find them.
Genome structure
Describe the size and content of the genome. How many chromosomes? Circular or linear? Other interesting features? What is known about its sequence? Does it have any plasmids? Are they important to the organism's lifestyle?
Cell structure and metabolism
Describe any interesting features and/or cell structures; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces. (Temporary General Outline) - Obligate Aerobe: Explains why it infects the upper lobes of the lungs - Slow rate of growth compared to other bacteria (about 15-20 hours) - Non-motile rod shaped - Size: ~2-4 um in length and 0.2-0.5 um in width
Ecology
Describe any interactions with other organisms (included eukaryotes), contributions to the environment, effect on environment, etc.
Pathology
How does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
Application to Biotechnology
Does this organism produce any useful compounds or enzymes? What are they and how are they used?
Current Research
Enter summaries of the most recent research here--at least three required