Vertebra: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
imported>Robert Badgett No edit summary |
imported>Robert Badgett No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
In [[anatomy]], a '''vertebra''' is a bone in the spinal column.<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref> | In [[anatomy]], a '''vertebra''' is a bone in the spinal column.<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref> The zygapophyseal joint (facet joint) is "the joint that occurs between facets of the interior and superior articular processes of adjacent vertebra."<ref>{{MeSH|Zygapophyseal Joint}}</ref> | ||
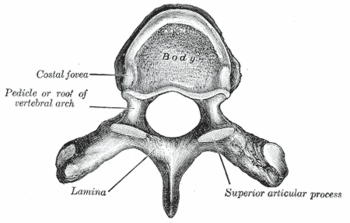
{{Image|Grays 82.gif|right|350px|A typical thoracic vertebra, viewed from above.}} | {{Image|Grays 82.gif|right|350px|A typical thoracic vertebra, viewed from above.}} | ||
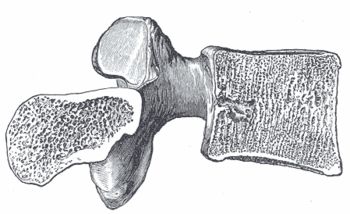
{{Image|Gray - image83.gif|right|350px|Sagittal section of a lumbar vertebra.}} | {{Image|Gray - image83.gif|right|350px|Sagittal section of a lumbar vertebra.}} | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
* [[Spondylolisthesis]] | * [[Spondylolisthesis]] | ||
* Facet joint osteoarthritis. An underpowered [[randomized controlled trial]] found one of 10 patients benefited from [[corticosteroid]] injection of the facet joint.<ref name="pmid1832209">{{cite journal| author=Carette S, Marcoux S, Truchon R, Grondin C, Gagnon J, Allard Y et al.| title=A controlled trial of corticosteroid injections into facet joints for chronic low back pain. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 1991 | volume= 325 | issue= 14 | pages= 1002-7 | pmid=1832209 | * Facet joint osteoarthritis. An underpowered [[randomized controlled trial]] found one of 10 patients benefited from [[corticosteroid]] injection of the facet joint.<ref name="pmid1832209">{{cite journal| author=Carette S, Marcoux S, Truchon R, Grondin C, Gagnon J, Allard Y et al.| title=A controlled trial of corticosteroid injections into facet joints for chronic low back pain. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 1991 | volume= 325 | issue= 14 | pages= 1002-7 | pmid=1832209 | ||
| url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=1832209 }} <!--Formatted by http://sumsearch.uthscsa.edu/cite/--></ref> However, possibly due to the small size of the trial, this result did not reach [[statistical significance]]. | | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=1832209 }} <!--Formatted by http://sumsearch.uthscsa.edu/cite/--></ref> However, possibly due to the small size of the trial, this result did not reach [[statistical significance]]. Radiofrequency denervation or ablation may be able to reduce pain.<ref name="pmid12535508">{{cite journal| author=Niemisto L, Kalso E, Malmivaara A, Seitsalo S, Hurri H| title=Radiofrequency denervation for neck and back pain. A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. | journal=Cochrane Database Syst Rev | year= 2003 | volume= | issue= 1 | pages= CD004058 | pmid=12535508 | ||
| url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=12535508 | doi=10.1002/14651858.CD004058 }} <!--Formatted by http://sumsearch.uthscsa.edu/cite/--></ref> Hypertrophy of the facet joint may lead to [[sciatica]].<ref name="pmid18789864">{{cite journal| author=Kulcu DG, Naderi S| title=Differential diagnosis of intraspinal and extraspinal non-discogenic sciatica. | journal=J Clin Neurosci | year= 2008 | volume= 15 | issue= 11 | pages= 1246-52 | pmid=18789864 | |||
| url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=18789864 | doi=10.1016/j.jocn.2008.01.017 }} <!--Formatted by http://sumsearch.uthscsa.edu/cite/--></ref> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 06:37, 4 November 2009
In anatomy, a vertebra is a bone in the spinal column.[1] The zygapophyseal joint (facet joint) is "the joint that occurs between facets of the interior and superior articular processes of adjacent vertebra."[2]
Disorders
Various disorders may lead to lumbalgia (low back pain).
- Spondylosis
- Spondylolysis
- Spondylolisthesis
- Facet joint osteoarthritis. An underpowered randomized controlled trial found one of 10 patients benefited from corticosteroid injection of the facet joint.[3] However, possibly due to the small size of the trial, this result did not reach statistical significance. Radiofrequency denervation or ablation may be able to reduce pain.[4] Hypertrophy of the facet joint may lead to sciatica.[5]
References
- ↑ Anonymous (2025), Vertebra (English). Medical Subject Headings. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Anonymous (2025), Zygapophyseal Joint (English). Medical Subject Headings. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Carette S, Marcoux S, Truchon R, Grondin C, Gagnon J, Allard Y et al. (1991). "A controlled trial of corticosteroid injections into facet joints for chronic low back pain.". N Engl J Med 325 (14): 1002-7. PMID 1832209.
- ↑ Niemisto L, Kalso E, Malmivaara A, Seitsalo S, Hurri H (2003). "Radiofrequency denervation for neck and back pain. A systematic review of randomized controlled trials.". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1): CD004058. DOI:10.1002/14651858.CD004058. PMID 12535508. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Kulcu DG, Naderi S (2008). "Differential diagnosis of intraspinal and extraspinal non-discogenic sciatica.". J Clin Neurosci 15 (11): 1246-52. DOI:10.1016/j.jocn.2008.01.017. PMID 18789864. Research Blogging.