Brown hyaena: Difference between revisions
imported>Meg Taylor m (spelling: Univeristy -> University) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:00, 21 July 2024
| brown hyaena | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Brown hyaena (Parahyaena brunnea), Namibia.
| ||||||||||||||||
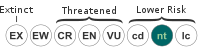
| Conservation status | ||||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Binomial name | ||||||||||||||||
| Parahyaena brunnea Thunberg, 1820 |
The brown hyaena (also known as brown hyena) Parahyaena brunnea is the only species within the genus Parahyaena. It has the most restricted range of the members of the family Hyaenidae. Current research is showing that the behaviour of this hyaena is extremely variable.
Description
The brown hyaena Hyaenidae is 1.3-1.6 m in length, with the tail being between 17 and 30 cm, and stands approximately 80 cm at the shoulder. Adult males weight 47 kg and females 42 kg. [2] [3] Sexual dimorphism favours the males of the species. Brown hyaenas share the typical ‘hyaena’ stature, that being high at the shoulders and lower in the hindquarters. The brown hyaena has very shaggy coat of light to dark brown, with mane area typically lighter in colour and the ears are very large and pointed.. The legs are striped, which has recently been found to be diagnostic for distinguishing individuals. [4]
Behaviour
The brown hyaena was previously believed to be strictly nocturnal. [2] [3]. Current research on the south west coast of Namibia shows that brown hyaenas are active all hours of the day and night. [4] Females give birth to 2-3 cubs at any time of the year [2]. They live in loose clan systems, which share a fixed home range, but forage alone.
Diet
Not an efficient hunter, in most of its range the brown hyaena is primarily a scavenger and forages a wide range of food from vegetables and fruit to reptiles, birds and mammals. The lone exception to this is the populations living on the Namibian coast where they have been observed killing seal pups. They are capable of scavenging from the largest available prey in the region [5] They are known to collect vast quantities of faunal remains in their dens, said collections of bone are a direct reflection of the other species found in the region at the time of collection [5].
Geographical distribution
The range of brown hyaena is limited to areas of Namibia, Botswana, South Africa, Zimbabwe and south west Angola. At one time their range extended all the way to Table Bay in the Western Cape of South Africa [3].
References
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 C. Stuart and T. Stuart (1997). Field guide to the larger mammals of Africa=. Struik publishers.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 J. Skinner and C. Chimimba (2005). The mammals of the southern african subregion=. Cambridge University Presspages=.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Template:Personnal communication, 2005
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Template:Cite Thesis