Iraq War
The Iraq War was the invasion of Iraq in 2003 by a multinational coalition led by the United States of America. Military operations were conducted by forces from the U.S., the United Kingdom, Australia and Poland, and was supported in various ways by many other countries, some of which allowed attacks to be launched or controlled from their territory. The U.N. neither approved nor censured the war, which was never a formally declared war. The U.S. refers to it as Operation IRAQI FREEDOM. Continuing operations are under the command of Multi-National Force-Iraq.
This war is to be distinguished from the Gulf War of 1991, following the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait in 1990. The Gulf War had United Nations authorization. Further, both these wars should be differentiated from the Iran-Iraq War of 1980-1988.
The war had quick result of the removal (and later execution) of Iraqi dictator Saddam Hussein and the formation of a democratically elected parliament and ratified constitution, which won UN approval. However, an amorphous insurgency since then has produced large numbers of civilian deaths and an unstable Iraqi government. It has generated enormous political controversy in the U.S. and other countries.
The main rationale for the invasion was Iraq’s continued violation of the 1991 agreement (in particular United Nations Resolution 687) that the country allow UN weapons inspectors unhindered access to nuclear facilities, as well as the country’s failure to observe several UN resolutions ordering Iraq to comply with Resolution 687. The US government cited intelligence reports that Iraq was actively supporting terrorists and developing weapons of mass destruction (WMD) as additional and acute reasons to invade. Though there was some justification before October 2002 for believing this intelligence credible, a later Senate investigation found that the intelligence was inaccurate and that the intelligence community failed to communicate this properly to the Bush administration[1].
Factors Leading Up to the Invasion
There were a wide range of opinions that Saddam Hussein's Iraq had a negative effect on regional and world stability, although many of the opinionmakers intensely disagreed on the ways in which it was destabilizing. This idea certainly did not begin with 9/11.
Clinton Policy and Weapons Inspections
After the Gulf War in 1991, United Nations Resolution 687 specified that Iraq must destroy all weapons of mass destruction (WMD). A large amount of WMDs were indeed destroyed under UN supervision (UNSCOM). Two no-fly zones were also instituted in northern and southern Iraq where Iraqi military aircraft were prohibited from flying. The United States and the United Kingdom (and France until 1998) patrolled these zones in, respectively, Operation NORTHERN WATCH and Operation SOUTHERN WATCH. The 1996 Khobar Towers bombing attacked forces, in Saudi Arabia, conducting SOUTHERN WATCH.
However, by late 1997, the the Clinton administration became dissatisfied with Iraq’s increased unwillingness to cooperate with UNSCOM inspectors. As a result of widespread expectations that the Clinton administration would decide to act with military force, the UN weapons inspectors were evacuated from the country. Iraq and the United Nations agreed to resume weapons inspections, but Saddam Hussein continued to obstruct UNSCOM teams throughout the remainder of 1998.
Congress passed the Iraq Liberation Act in October 1998:
It should be the policy of the United States to support efforts to remove the regime headed by Saddam Hussein from power in Iraq and to promote the emergence of a democratic government to replace that regime. [2]
In December 1998, President Clinton authorized military action against Iraq. Between December 16 and 19, 1998, US and UK missiles and aircraft attcked military and government targets in Iraq in Operation DESERT FOX. It was widely understood that the Clinton administration intended Operation Desert Fox to be not merely a campaign of punishment for Iraq’s failure to cooperate but also to weaken the regime in advance of orchestrated efforts to cause regime change. In that respect, Clinton administration policy was ineffective.
As a result of Iraq’s barring inspectors from the country, UNSCOM inspections of Iraq’s WMD effectively came to an end and in March 1999, the UN concluded that the UNSCOM mandate should end. In December 1999, the UN passed UN Security Council Resolution 1284, setting up UNMOVIC (United Nations Monitoring, Verification and Inspection Commission), headed by Swedish diplomat Hans Blix, which was to identify the remaining WMD arsenals in Iraq. Because UNMOVIC was banned from Iraq, the world had to rely on indirect evidence, most of which turned out to be false or inaccurate.[3] Iraq policy during the remainder of the Clinton presidency was marked by a return to the containment regime that existed before Operation Desert Fox, but now without the benefit of direct intelligence.
Bush Administration Policy
Policy before 9/11 Attacks
In the early days of the Bush administration, President George W. Bush expressed dissatisfaction with his predecessor’s foreign policy, in particular with regard to Iraq, which he considered weak and half-hearted. When Bush and Clinton met in the days of transition, on December 19, 2000, Clinton said that his understanding of Bush's priorities, from reading his campaign statements, were national missile defense and Iraq. Bush said that was correct. Clinton suggested Bush consider other priorities, including al-Qaeda, Middle East diplomacy, North Korea, the nuclear competition between India and Pakistan, and, only then, Iraq. Bush did not respond. [4]
During the campaign, Bush had criticized President Clinton as too widely engaged in too many conflicts, acting as the “world’s policeman.” In the end, President Bush believed Clinton had lacked the necessary resolve to hold Saddam Hussein accountable for his failure to comply with UN resolutions. Bush also questioned America’s membership in NATO and involvement in UN diplomacy, which led some to believe he was moving towards a more isolationist view of foreign policy.[5]
At the same time, Bush continued to favor executing the policy President Clinton had approved but not acted on: to actively proceed to effect regime change in Iraq. In January 2002, Time Magazine reported that since President Bush took office he had been grumbling about finishing the job his father started. [6]
On February 16, 2001 a number of US and UK warplanes attacked Baghdad, nearly two years before the start of the Iraq war. [7].
Iraqi WMD and the War on Terror
The attacks of September 11, 2001 shaped the policies of the Bush administration towards Iraq. President Bush saw them as confirmation of his beliefs that the international community’s failure to enforce compliance with UN resolution and America’s irresolute foreign policy had emboldened rogue states and international terrorist groups. Because Iraq was known to have had and used WMD in the past and because Iraq had blocked UN supervision of the destruction of its WMD, there remained great uncertainty about Iraq’s WMD arsenal. The Bush administration made Iraq of central importance to its national security policy. Combined with his isolationist foreign policy beliefs, President Bush started to formulate what has become known as the Bush Doctrine. The doctrine is most fully expressed in the administration’s National Security Strategy of the United States of America, published in September 2002. In it, the President states:
We will disrupt and destroy terrorist organizations by (…) direct and continuous action using all the elements of national and international power. Our immediate focus will be those terrorist organizations of global reach and any terrorist or state sponsor of terrorism which attempts to gain or use weapons of mass destruction (WMD) or their precursors.[8]
The administration included Iraq in a series of states it considered acutely dangerous to world peace. In his 2002 State of the Union President Bush called Iraq part of an “axis of evil” together with Iran and North Korea.[9] In this address the president also claimed the right to wage a preventive war, as distinct from a preemptive attack. Early in 2002, the administration began pressuring Iraq as well as the international community on greater compliance by Iraq with UN resolutions.
The Niger Uranium Forgeries
In February 2002, as a result of the discovery of classified documents initially revealed by Italian intelligence in October 2001, the Pentagon sent Marine General Carlton W. Fulford, Jr. to Niger to investigate the claim that Iraq was attempting to buy uranium to revamp its nuclear WMD program. That same month, the CIA sent former Ambassador Joseph Wilson IV to Niger in February 2002. General Fulford and Ambassador Wilson interviewed several high-ranking Niger government officials. Neither found any evidence for the sale; Mr. Wilson concluded that the claim was “unequivocally wrong.”[10]
There was disagreement about the findings of Mr. Wilson’s report within the intelligence community. CIA analysts believed the report confirmed reports about an Iraq-Niger uranium deal, partly because Mr. Wilson’s report included a comment that an Iraqi envoy had visited the African country in 1999. However, State Department analysts decided that Niger would be unwilling or incapable of supplying Iraq with any uranium.[11] As a result of these conflicting intelligence analyses, the Bush administration remained suspicious and continued to work from the assumption that Saddam Hussein was actively trying to acquire a nuclear weapon. Because of internal disorganization, the CIA failed to obtain copies of the original classified documents, after they were finally made available to American intelligence in October 2002, and ignored warnings from State Department analysts about problems with the documents. The CIA also failed to check the the president’s 2003 State of the Union for factual errors. Consequently, the address included the infamous “sixteen words” that “the British government has learned that Saddam Hussein recently sought significant quantities of uranium from Africa.” [12][13] It was not until March 2003 that the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) revealed with conclusive proof that the documents at the basis of the allegations were forgeries.[14] However, the British government claimed it had evidence to the same effect independent of these documents, but had promised the source not to reveal its identity.
Resumption of Weapons Inspections in 2002
The continued belief that Iraq was pursuing nuclear weapons led the Bush administration to increase diplomatic pressure on the Iraqi regime. During a speech before the General Assembly of the United Nations on September 12, 2002, President Bush outlined a long list of complaints against the Iraqi government. This included active support and harboring of terrorists (among them members of al Qaeda who had fled from Afghanistan after the US invaded that country), continued development of prohibited missiles, diverting funds from the UN “Oil for Food” program to purchase weapons, and violation of several UN resolutions by refusing to be open about its WMD arsenal.[15] On November 8, 2002, the United Nations Security Council unanimously passed resolution 1441 which declared Iraq in material breach of the 1991 ceasefire agreement and demanded Iraq fully comply with its disarmament obligations.[16] As a result, Iraq agreed to let UNMOVIC weapons inspectors, headed by Hans Blix, back into the country.
Strategic planning
Not all the planning dates may seem in proper sequence; this is not anything suspicious as some of the work was already in progress as part of routine staff activity, while other work was started by informal communications.
Even before the 9-11 attacks, regime change in Saddam Hussein's Iraq was a high priority of the George W. Bush Administration. According to This is not to suggest that previous Administrations had not been considering it, and had been steadily carrying out air attacks in support of the no-fly zones (Operation SOUTHERN WATCH and Operation NORTHERN WATCH), as well as air strikes (Operation DESERT FOX). Nevertheless, the priorities changed.
Another change, in the Bush Administration, was an emphasis on military transformation, or using different approaches than "fighting the last war". Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld was a constant advocate of transformation, emphasizing higher technology, more flexibility, and smaller forces, rather than the large heavy forces that were optimized to fight the Soviet Union. This was especially true after early operations in the Afghanistan War (2001-), where large U.S. ground forces were not used, but instead extensive special operations working with Afghan forces and using air power. Every war is different, however, and the reality in Afghanistan is there was an existing civil war and substantial indigenous resistance forces.
Late in the evening of 9/11, the President had been told, by CIA chief George Tenet, that there was strong linkage to al-Qaeda. [17] On September 12, President Bush directed counterterrorism adviser Richard Clarke to review all information and reconsider if Saddam was involved in 9/11.[18]
Deputy Secretary of Defense Paul Wolfowitz sent Rumsfeld a memo, on September 17, called "Preventing More Events"; it argued that there was a better than 1 in 10 chance that Saddam was behind 9/11. [19] He had been told, by the CIA and FBI, that there was clear linkage to al-Qaeda, but said the CIA lacked imagination.[20]
On September 19, 2001, the advisory Defense Advisory Board, chaired by Richard Perle, met for two days. Iraq was the focus. Among the speakers was Ahmed Chalabi, a controversial Iraqi exile who argued for an approach similar to the not-yet-executed approach to Afghanistan: U.S. air and other support to insurgent Iraqis. [21]
Reviews by Rumsfeld
CENTCOM had a contingency plan for a new war with Iraq, designated OPLAN 1003-98. It assumed Iraq would launch an attack as it had done in 1990. According to GEN Anthony Zinni, who had been CENTCOM commander when Franks commanded its Army component, Franks was "the major contributor to [its] force levels and its planning and everything else. He was more involved in it than just about anyonene else." [22] Zinni had recommended that Franks succeed him at CENTCOM.
Rumsfeld had OPLAN 1003-98 presented by LTG Greg Newbold, director of operations for the Joint Chiefs of Staff, in late 2001. Rumsfeld believed the plan, which called for up to 500,000 troops, was far too large; Rumsfeld thought that no more than 125,000 would be needed. Newbold later said he regretted he did not say, at the time,
Mr. Secretary, if you try to put a number on a mission like this, you may cause enormous mistakes. Give the military the task, give the military what you would like to see them do, and let them come up with it. I was the junior military man in the room, but I regret not saying it[23]
Informally, Franks had called it "DESERT STORM II", using three corps as in 1991, but to force collapse of Saddam Hussein's regime. On November 27, he told the Secretary of Defense that he had a new concept, but that detailed planning would be needed. [24] Franks told Rumsfeld, during a videoconference on December 4, 2001, that it was a stale, troop-heavy concept. Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (CJCS) Dick Myers, Vice CJCS Peter Pace, and Undersecretary of Defense Douglas Feith were on the Washington end. Franks intended to ignore Feith, who he described as a "master of the off-the-wall question that rarely had relevance to perational problems." [25]
Franks proposed three basic options:
- ROBUST OPTION: Every country in the region providing support; operations from Turkey in the north, Jordan and Saudi Arabia and Kuwait in the south, air and naval bases in the Gulf states, with support bases in Egypt, Central Asia, Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria. This would allow near-simultaneous ground and air operations.
- REDUCED OPTION: A lesser number of countries supporting would mean a sequential air and ground operation.
- UNILATERAL OPTION: If launching forces from Kuwait, U.S. ships, and U.S. aircraft from distant bases, the air and ground operations would be "absolutely sequential" due to the lack of infrastructure to bring in all ground forces at once.
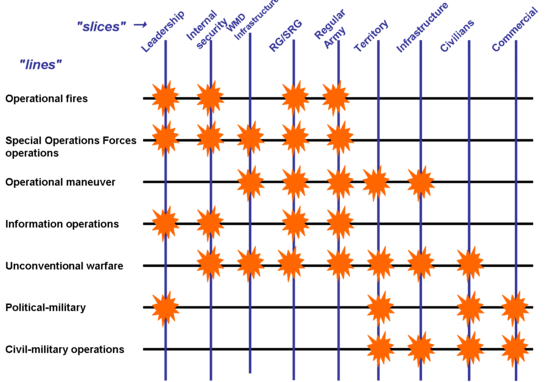
Franks wrote that during the Afghanistan planning, he had developed a technique that presented, visiually, the tasks to be done ("lines of operation") and the country or resource that would be affected by these tasks ("slices"). It is not clear when he first drew this visual aid for Iraq, although it was part of the December 12 briefing to Rumsfeld; the version reproduced in his book was dated December 8.
In this model, operational fires are strikes by aircraft, artillery, and missiles. Special Operations Forces operations are principally special reconnaissance and direct action (military); unconventional warfare involves both military and CIA guerillas. Information operations, as a line, includes psychological operations, electronic warfare, deception, and computer network operations; politicomilitary and civil-military operations are doctrinally part of information operations but are shown separately here. RG and SRG are, respectively, the Iraqi Republican Guard and Special Republican Guard elite combat formations.
Rumsfeld liked the presentation. He asked Franks what came next, and Franks said improving the forces in the region. Rumsfeld cautioned him that the President had not made the go-to-war decision, and Franks clarified that he referred to preparation:
- Triple the size of the ground forces now in Kuwait
- Increase the number of carrier strike groups in the area
- Improve infrastructure
- Discuss contingency requirements with allies
Franks said the activities could look like routine training. He pointed out that an additional 100,000 troops and 250 aircraft would not fit into Kuwait, and more basing would be needed. Rumsfeld urged that it would have to be done faster "more quickly than the military usually works". The next step was a face-to-face briefing on December 27. [26]
Rumsfeld calls for new planning
Early warning of Rumsfeld's desires came to LTC Thomas Reilly, chief of planning for Third United States Army, still based at Fort McPherson in the U.S. While Third Army would become the Coalition Forces Land Component of CENTCOM, it had not yet been so designated, whenn Reilly received the notice on September 13, 2001. It used the term POLO STEP, the code word for Franks' concept of operations. [27]
On October 9, 2002, GEN Eric Shinseki, Chief of Staff of the Army, told staff officers "From today forward the main effort of the US Army must be to prepare for war with Iraq". [28]
Special operations
George Tenet, Director of Central Intelligence, had a major role in the decision to go to war, but also how it was to be fought. In the mid-nineties, CIA had found that a first coup attempt simply had gotten Iraqi CIA assets killed. The lesson learned from Afghanistan was that "covert action, effectively coupled with a larger military plan, could succeed. What we were telling the vice president that day [in early 2002] was that CIA could not go it alone in toppling Saddam...in Iraq, unlike in Afghanistan, CIA's role was to provide information to the military...assess the political environment...coordinate the efforts of indigenous networks of supporters for U.S. military advances..." In February 2002, the Agency re-created the Northern Iraq Liaison Element (NILE) teams to work with the Kurds. Later, CIA officers worked to encourage surrender, but this soon proved impractical; the U.S. forces were so small that the prisoners would have outnumbered the invaders. [29]
Theater/operational planning
In the Gulf War, there was no common commander for all land forces; GEN H Norman Schwarzkopf Jr. gave direct orders to the U.S. Army and Marine unites. Experience both then and in WWII showed the need for a land forces commander.
In November 2001, the commander of United States Central Command, Tommy Franks[30] designated Third United States Army as the CENTCOM Land Forces Component Command (CFLCC). LTG David McKiernan took command of Third Army in September 2002. According to MG Henry "Hank" Stratman, deputy commanding general for support of Third Army, eventual combat with Iraq was assumed when he took his post in the summer of 2001, even before the 9-11 attack.
With the recommendation of Newt Gingrich, COL Doug Macgregor prepared a briefing, which went to Runsfeld, which went against the conventional wisdom that large forces would be needed to defeat Saddam. [31] Macgregor geve the briefing to Gingrich on December 31, 2001. It advocated a quick strike into Baghdad by three brigade-sized forces, followed by 15,000 light infantry forces to maintain order.
Macgregor was sent to brief GEN Tommy Franks, commanding U.S. Central Command, on January 12, 2002. After Macgregor briefed Franks, Franks responded, "Attack from a cold start. I agree. Straight at Baghdad. Small and fast. I agree. Simultaneous air and ground. Probably, but not sure yet." After his return to Washington, Macgregor decided that Franks had given him a polite reception as a courtesy to Rumsfeld; Macgregor wrote a memo of the meeting, which Gingrich forwarded to Dick Cheney and other political contacts. Franks' planner, MG Gene Renuart, argued to Rumsfeld that Macgregor's plan was too light.
Detailed planning by CENTCOM began while active combat was ongoing in Afghanistan, in December 2002.[32] At the time, GEN Eric Shinseki, then Chief of Staff of the Army, testified to Congress that the number of troops approved by Rumsfeld was inadequate. Shinseki, however, was not in the chain of command for operational deployment. Although the Chief of Staff is the senior officer of the United States Army, he is responsible for developing doctrine and preparing forces for use by the combatant commanders.
GEN Franks briefed Secretary Rumsfeld on February 1, with two alternative plans. The first, informally called "DESERT STORM II", repeated the sequential approach of Operation DESERT STORM:[33]
- Phase I: buildup of forces before invasion, with increased air strikes in the no-fly zones and early staging of special operations forces; prestaging of approximately 160,000 troops
- Phase II: Air-centric operations of approximately 3 weeks, preparing the battlefield for the major ground forces attacks
- Phase III: Major ground forces attack with approximately 105,000 troops
- Phase IV: Occupation and reconstruction
The alternative, preferred by Franks, was called RUNNING START, and was chosen as the next planning point. It moved Special Operations preparation into Phase I, made the air and ground phases essentially simultaneous (i.e., merged into a combined Phase III of decisive combat operations), and then a reconstruction phase; the phases were not renumbered.
In the next review, additional alternatives were introduced, still assuming some level of simultaneous air and ground attack, as distinct from the separate air phase of Operation DESERT STORM. They varied with the number of troops required:
- GENERATED START took the most troops, and was considered impractical almost from the beginning; Saddam had learned not to give the U.S. time to prepare. GENERATED START assumed the U.S. would launch an attack only when it had all forces in theater, which would take the longest time and be inflexible.
- RUNNING START option, which assumed launching combat operations with minimum forces and continuing to deploy forces and employ them as they arrived. The final option stemmed from wargaming the running start.
- HYBRID PLAN, which evolved from war-gaming RUNNING START. reflected an assessment that the minimum force required reached a higher number of troops than envisioned in the running start option.
The selected plan was a compromise solution between HYBRID and RUNNING SSTART, with more forces than the latter but fewer than the former. RUNNING START offered operational surprise and less demand for synchronization than HYBRID PLAN.
Critical factors
Several key factors had the potential to override any plan. First, the Iraqi oil infrastructure had to be protected from sabotage, as its revenue would be key in reconstruction. The military and CIA had different information as to Saddam's intentions; as a practical matter, the oil facilities were kept under close surveillance as the attack grew closer. [34]
Second, Saddam Hussein was the key to Iraqi resistance. Ideally, he would leave the country. If, however, he could be located and killed by air attack, that also would change priorities.
V Corps
While V Corps was stationed in Germany, all plans assumed it would be the heavy striking force in any attack against southern Iraq. Planning for such an attack had long been one of its responsibilities. Planning intensity intensified in April 2002. It deployed to Poland and conducted Exercise VICTORY STRIKE, a training exercise with Iraq in mind. Under CFLCC, a command exercise, LUCKY WARRIOR, in Kuwait, involved V Corps and I MEF. Next, the annual CENTCOM exercise, INTERNAL LOOK, added practice for the Joint Force Air Component Command (JFACC), while Special Operations Command for CENTCOM (SOCCENT) formally established two Joint Special Operations Task Forces (JSOTF): JSOTF-North and JSOTF-West. It assumed I MEF with part of its air wing, 1st Marine Division with two regimental combat teams, and V Corps with all of 3rd ID, an attack helicopter regiment, and part of the corps artillery. [28]
I MEF
U.S. Marine planning had, since the Second World War, focused on relatively small, quick-response operations from the sea, typically by brigade-sized Marine Expeditionary Units. They had fought a large-scale operation in Operation DESERT SABER.
Nevertheless, the first Operational Planning Team, held in March 2002, assumed that the I MEF effort would support large-scale Army movement. Its concept was that the Marines would send "Task Force South" to move from Kuwait, capture Jalibah Airport, and stage from there to capture Qalat Sikar and An Kut airfields closer to Baghdad. They would then secure southern Iraq, while the Army brought in resources for the main attack.
This was too deliberate and logistics-intense for Rumsfeld's "RUNNING START" model. Counterproposals were sent back to plan for single Army and Marine brigades to start individual advances. I MEF countered that it was a better overall headquarters than V Corps, since it was experienced in controlling air operations where an Army corps was not. In the planning of July 2002, it was tentatively accepted that I MEF might indeed be the main headquarters. The U.S. Marines also welcomed the participation of British Royal Marines.[35]
The Marines also needed to coordinate with Special Operations forces.
Special Operations forces
Special Operations had played a major and effective part in Afghanistan, and were visible to Rumsfeld and Franks. As in Afghanistan, they divided into "white" (i.e., acknowledged) and "black" (i.e., covert forces).
The main white operations were 5th Special Forces Group in the south, and 10th Special Forces Group in the north.
Larger, however, was Task Force 20, secretly located on Saudi soil at Ar'ar, commanded by MG Dell Dailey, who was also the overall head of Joint Special Operations Command. TF 20 included Delta Force, the 75th Ranger Regiment, MC-130 COMBAT TALON and other large Air Force Special Operations Command aircraft and helicopters from the 160th Special Operations Aviation Regiment. In an unprecedented move, the task force had been supplemented with a conventional paratroop battalion from the 82nd Airborne Division. [36]
One of the key, although controversial, contingency missions for TF 20 was seizure of Baghdad International Airport, especially if the Saddam Hussein regime collapsed. The latter was always at the minds of the senior civilian leaders, but contingency planning for leadership collapse went back to the Second World War: Operation RANKIN CASE C. In WWII, that indeed was an airborne mission. In this war, however, the 3rd Infantry Division staff felt they could do the job more efficiently and with less risk.
Delta and supporting TF20 units, however, had other missions.
The Turkish front
Relations among Turkey, the Iraqi government, the Kurds of Iraq, separatist Kurds in Turkey, and, to a lesser extent, Kurds in neighboring countries has always been sensitive.
The planners wanted to launch a northern front from Turkey, but Turkish public opinion was opposed. On March 1, the Turkish Parliament refused to consent to any U.S. operations, including overflights by cruise missiles or aircraft, search and rescue, much less ground troops. At this point, the 4th Infantry Division was already in ships off the Turkish coast. Colin Powell had considered the need for a northern front overrated. If there were no northern front and Iraqi forces moved south, that would simply make them better targets. He did think Rumsfeld liked the idea as part of keeping the southern force smaller.
Eventually, Turkey gave some limited and low-visibility access, including overflights by aircraft and missiles, and operations by the 10th Special Forces Group, under COL Charlie Cleveland. On March 22, it flew to the Bashur and Sulaymaniyah areas in the Turkish zones of northern Iraq, using a circuitous, low-altitude, and dangerous path over the Sinai Peninsula, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia. Turkey did allow one damaged MC-130 COMBAT TALON to make an emergency landing in Turkey. The 10th Group eventually raised 70,000 Kurdish fighters that interfered with the southern movement of Iraqi Army units. [37]
McKiernan, in February, had recommended to Franks essentially the same thing as did Powell: send the 4th ID to the south. If the Turks changed their position, units could always be sent there. [38] Franks, however, thought that keeping a northern threat would keep the Iraqis distracted. He believed that the Iraqis focused on the 4th ID as the main invasion force; even when its ships moved south through the Suez Canal, Arab media reports assumed that it would land in Jordan and attack from the west. By not committing the division to the south, he believed he could maintain a diversion. [39]
Phase IV Planning
During the planning phase, Rumsfeld told Franks that LTG Jay Garner would be responsible for reconstruction, reporting to CENTCOM. [40] A number of retired generals have been highly critical of the plan, focused especially on what they considered the unrealistic goals of Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld. They include Paul Eaton, who headed training of the Iraqi military in 2003-2004; formal chiefs of United States Central Command (Anthony Zinni and Joseph Hoar); Greg Newbold, Director of the Joint staff from 2000 to 2002; John Riggs, a planner who had criticized personnel levels, in public, while on duty; division commanders Charles Swannack and John Baptiste.[41]
Major combat phase
The "RUNNING START" began with near-simultaneous air and ground attacks. The original plan had been to conduct limited air strikes against border operation posts on March 19, along with infiltration, under air cover, of Special Operations Forces from the military and CIA, the latter designated the Southern Iraq Liaison Element. Full-strength bombing was to begin on March 21.
When communications intelligence on March 19 indicated that Saddam might be at a location called Dora Farms, a contingency air operation went began on the 20th.[42] Times were tight; the ultimatum to Saddam expired at 4 AM local time; the F-117 aircraft had to be out of the area before dawn at approxiately 5:30. They took off at 3:30.[43] Cruise missile hit aboveground targets at Dora Farms five minutes after the F-117's had dropped ground-penetrating bombs. Saddam, however, was not at the site.
Special operations forces were already operating in Iraq. Special operations forces (SOF) also moved into action, seizing oil and gas platforms in the south. SOF in the west positioned themselves to strike at airfields, missile sites, and suspected WMD facilities. In the north, they worked with the Kurdish resistance to pin the Iraqi forces in that area.
Iraq countered with surface-to-surface missiles fired at U.S. headquarters on the afternoon of the 20th. They were shot down. [44]
Initial operations
The main operation of the "shaping the battlefield" phase began with breaking through a 10km wide Iraqi defensive line, on March 20. This phase lasted until March 23.
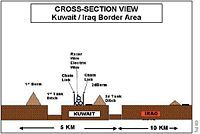
The major units positioned themselves for penetrating the Iraqi border. This was called crossing the "berm", although the berms (plural) were earthen walls that made up part of the physical barriers at the border. Note that a substantial amount of the barrier was in Kuwait. According to the U.S. Army history, much of the actual breaching was done by Kuwaitis contractors, who considered it an honor, but could also disguise some of the preparation as routine maintenance. [45] Another account, however, said that the Kuwaitis were reluctant to plow over the defenses they had built, including an electrified fence; they arranged, in discussions with McKiernan's staff, to have contrators take down sections of their barriers.[46]
Breaching the berms proper was separate from creating lanes through the defensive line, which was done by combined arms units, such as TF3-15, based on two mechanized infantry companies (Alpha and Bravo, 3rd Battalion, 15th Infantry), one attached tank company (Bravo Company, 4-64 Armor), one engineer company (Alpha Company, 10th EN), and a psychological operations. It split into organized into two elements, one of armored fighting vehicles and one of wheeled vehicles.
The first combat by conventional forces, took at 3:57 PM local time, but south of the Iraqi border, between Iraqi vehicles and U.S. Marine Corps LAV-25 reconnaissance vehicles from the 3rd Light Armored Reconnaissance Battalion. Marines began the actual attacks with artillery fire in the late afternoon, preceding the border crossing by the 1st Marine Division under I Marine Expeditionary Force under then-LTG James Conway. The Division cooperated closely with 1 Armored Division (U.K.) and the Army's 3d Infantry Division (U.S.)[47] The Army units were under V Corps.
Lane-clearing teams were ready on the 20th, waiting for movement on the 22nd. While they waited, they were in chemical protective clothing, donning masks when Iraqi surface-to-surface missiles were fired.
Lead Marine units first crossed the Kuwait-Iraq border and began an intensive attack on Safwan Hill, in Iraq just north of the border. [48]
Oil fields
The first Army unit to enter Iraq was the 3rd Squadron, 7th Cavalry Regiment, part of the 3rd Infantry division, at approximately 1 AM local time on the 20th according to CNN, although Defense Department reports suggest the movement was four hours later. [47] In either case, the attack time was accelerated due to concern over the Iraqis' damaging oil facilities.
When Marines seized the Crown Jewel pumping station in Zubayr, 10 miles southwest of Basra, they were concerned that machinery had been damaged, but the Iraqi managers said this was the normal state of the equipment; the Iraqi petroleum industry needed rehabilitation. [49]
As the Marines moved into the Rumaylah oil field, British forces took control of the Faw Peninsula oil facilities, as well as the port of Umm Qasr. U.S. Navy SEALs captured some of the offshore facilities. A U.S. Marine helicopter crashed, killing Marines from both countries. [50]
Attack on Talil Airfield and on Basra
On the 22nd, the 3rd Infantry division drove troughly 150 miles into Iraq, halfway to Baghdad, to the Tal Airfield. The 3rd Brigate attacked the airfield with the 1/30 Infantry protecting the flanks and the 1/15 attacking the Iraqi 11th Infantry division in defense. The 3rd Brigade captured the Talil airfield after its artillery began shelling Iraqi military emplacements there. While the 1-30th Infantry protected its flanks preventing intervention by forces in Nasiriyah, the 1-15th Infantry Regiment assaulted the airfield inflicting serious losses on Iraq's 11th Infantry Division, which was defending the location. The 3rd ID used a bounding overwatch, where one brigade at a time would attack, covered by another. [51] The 11th Infantry later surrendered resulting in the capture of some 300 prisoners.
In parallel, 1st Marine Division drove toward Bastra, destroying 10 dug-in T-55 tanks with hand-held and HMWWV-launched antitank missiles.
Eight miles south of Basra at a turnoff to Zubair, the 3rd Battalion, 7th Marines Regiment took over an abandoned Iraqi command and control facility and used it as a field headquarters. The marines left this position later in the day as forces began heading closer to Basra.
Resistance by irregulars
On the 23rd, the advancing forces ran into unexpected resistance from Fedayeen irregulars, which did not present a threat to the armored fighting vehicles, but caused a problem for supply lines. They also faked surrenders and used human shields. [52] Part of the Army 509th Maintenance Company, having taken a wrong turn and driven into the city of An Nasiriyah, were ambushed and prisoners, including Jessica Lynch, taken. [53]
Major combat operations
After breaching the berm, it would take at least two movements to reach Baghdad; there would need to be regrouping on the 400 km drive to the north from Kuwait. The contingency of sudden collapse of the Iraqi leadership was always considered as a contingency.
The "darkest day"
Some of the hardest fighting came on the night of the 23rd and 24th. One component was an unsuccessful deep strike by AH-64 Apache helicopters at the Battle of Karbala. [54] This was a pure air attack; the 101st decided to defer its originally planned near-simultaneous attack, on the 14th Brigade of the Medina Division, until the 28th.[55]
U.S. Political factors
LTG Wallace had given an interview to U.S. newspapers on the 27th, in which he suggested the war might take longer than planned, due to the paramilitaries and the weather. [56] According to Gordon and Trainor, Rumsfeld felt this was disloyal, and raised it to Franks, who expressed to McKiernan that he was considering relieving Wallace. Franks had unfavorably compared the aggressiveness of V Corps to the Special Operations forces.[57] Rumsfeld, however, denied he had read the interview, but warned Syria and Iran to stay out of the irregular fighting. [58] Franks said he was told of the incident by his press officer, COL Jim Wilkinson, on the morning of the 27th, who said "a couple of reporters ambushed Scott Wallace when he popped in to visit General Petraeus at the command post." Franks said he described it as basically accurate from the perspective of a corps commander, but definitely pessimistic. Wilkinson described it as "A friggin' disaster, General. The takeaway is that we're bogged down and didn't plan this operation worth a damn." When Franks said this was untrue, Wilkinson said "perception is reality in the media. My phone has been ringing off the hook for the last hour. Everyone wants to interview you about Wallace's comments." Franks told Wilkinson to stay with operational truth, and he would talk to McKiernan. When Franks talked to McKiernan, the latter said he had warned Wallace, and Franks said "that's good enough for me. Scott is a hell of a commander. Tell him I love him and trust him."[59]
Deliberate defense
As opposed to the situation in the Afghanistan War (2001-), there was no meaningful Iraqi resistance that could be assisted by Special Operations forces, at least in Southern Iraq. The Kurds in the north were quite another matter.
Instead, the Iraqi irregular Fedayeen were a real threat to the rear areas of the advancing forces. By the 28th, Conway described the main Iraqi military as in a deliberate defense. complemented by the Fedayeen.[60] Wallace, McKiernan and Conway were all concerned with protecting their rear areas; McKiernan had released the the 82nd Airborne Division and to V Corps, for rear security, on the 26th. [61]McKiernan said that before moving north, he wanted the Republican Guard reduced by 50%, and the 101st Airborne Division committed to rear security. [62]
Interim Military Government
On April 16, Franks declared the end of major combat,[63] and ordered the withdrawal of the major U.S. combat units. The CENTCOM forward headquarters in Qatar and I MEF were to be withdrawn. U.S. forces would be reduced to 30,000 by the end of August, which the U.S. believed was adequate. [64]
CFLCC was redesignated Combined Joint Task Force 7 (CJTF-7) on May 1, but McKiernan's headquarters was replaced by V Corps, then under LTG Wallace. MG Ricardo Sanchez, then commanding 1st Armored Division (U.S.) in Germany, was promoted to LTG and given command of V Corps. According to Sanchez, Franks had not specified a specific Phase IV role for CENTCOM or V Corps. [65]
Insurgency, Counterinsurgency, or Occupation, depending on perspective
The headquarters for foreign military units in Iraq is Multi-national Force-Iraq (MNF-I). On an overall basis, it reports to the United States Central Command, which also commands the U.S. troops in MNF-I. Other units report to their home nations, although there are a number of non-US commanders from the MNF-I Deputy Commanding General, and Australian, British and Polish commanders at division level.
References
- ↑ United States Senate (July 7, 2004), Report on the U.S. Intelligence Community's Prewar Intelligence Assessments on Iraq
- ↑ Iraq Liberation Act of 1998
- ↑ Ali A. Allawi. The Occupation of Iraq: Winning the War, Losing the Peace. New Haven (Conn.): Yale University Press, 2007, p. 72.
- ↑ Michael R. Gordon, Bernard E. Trainor (2006), COBRA II: the inside story of the invasion and occupation of Iraq, Pantheon, ISBN 0375422625, p. 14
- ↑ Cameron G. Thies. “From Containment to the Bush Doctrine: The Road to War with Iraq.” In: John Davis ed. Presidential Policies and the Road to the Second Iraq War. Aldershot (UK)/Burlington (VT):Ashgate, 193-207, here p. 200.
- ↑ http://www.time.com/time/world/article/0,8599,235395,00.html Time Magazine reports
- ↑ http://archives.cnn.com/2001/WORLD/meast/02/16/iraq.airstrike/ CNN reports
- ↑ National Security Strategy of the United States of America, The White House, September 2002. (Page 6 in the printed edition). Retrieved May 8, 2008.
- ↑ 2002 State of the Union address, President George W. Bush, January 29, 2002. Retrieved May 8, 2008.
- ↑ Report on the U.S. Intelligence Community's Prewar Intelligence Assessments on Iraq United States Senate, ordered July 7, 2004. Chapter 2-b. Retrieved May 8, 2008.
- ↑ Report on the U.S. Intelligence Community's Prewar Intelligence Assessments on Iraq United States Senate, ordered July 7, 2004. Chapter 2-k. Conclusion 13. Retrieved May 9, 2008.
- ↑ 2003 State of the Union Address, President George W. Bush, January 28, 2003. Retrieved May 8, 2008.
- ↑ Senate Intelligence Committee Report (see previous note), Chapter 2-k. Conclusions 18-19, 21.
- ↑ Transcript of ElBaradei's U.N. presentation, posted at CNN. March 7, 2003. Retrieved May 8, 2008.
- ↑ President George W. Bush’s 2002 Address to the UN General Assembly, United Nations, General Assembly 57, Meeting 2. Verbatim Report. Retrieved May 9, 2008.
- ↑ United Nations Security Council Resolution 1441, posted at CNN.com, November 8, 2002. Retrieved May 9, 2008.
- ↑ George Tenet with Bill Harlow (2007), At the Center of the Storm: My Years at the CIA, Harpercollins, ISBN 9780061147784, p. 169
- ↑ Richard A. Clarke (2004), Against all Enemies: Inside America's War on Terror, Free Press, Simon & Schuster, ISBN 0743260244, p. 31
- ↑ Michael Isikoff, David Corn (2006), HUBRIS: the Inside Story of Spin, Scandal and the Selling of the Iraq War, Crown/Random house, ISBN 0307346811, p. 80}}
- ↑ Isikoff & Corn, p. 108
- ↑ COBRA II, p. 27
- ↑ COBRA II, p. 27}}
- ↑ COBRA II, p. 4
- ↑ Franks, Tommy & Malcolm McConnell (2004), American Soldier, p. 315
- ↑ Franks, p. 331
- ↑ Franks, pp. 340-345
- ↑ COBRA II, pp. 19-20
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Gregory Fontenot, E. J. Degen, David Tohn. United States Army Operation Iraqi Freedom Study Group (2005), Chapter 2: Prepare, Mobilize, and Deploy, On Point: The United States Army in Operation Iraqi Freedom, Center for Army Lessons Learned
- ↑ Tenet, pp. 385-387
- ↑ unrelated to Gen. Fred Franks in the Gulf War
- ↑ COBRA II, pp. 33-35
- ↑ Franks, pp. 329-335
- ↑ Franks, p. 366-370
- ↑ COBRA II, pp. 166-167
- ↑ Nicholas E. Reynolds (2005), Basrah, Baghdad, and beyond: the U.S. Marine Corps in the second Iraq War, Naval Institute Press, ISBN 1591147174, pp. 31-33
- ↑ COBRA II, pp. 327-328
- ↑ Isaac J. Peltier (Academic Year 2004-2005), Surrogate Warfare: The Role of U.S. Army Special Forces, School of Advanced Military Studies, Command and General Staff College, p. 7
- ↑ COBRA II, pp. 115-116
- ↑ Franks p. 559
- ↑ Franks, pp. 422-423
- ↑ Deary, David S. (February 23, 2007), Six agaist the Secretary: the Retired Generals and Donald Rumsfeld, Air War College
- ↑ Gellman, Barton & Dana Priest (March 20, 2003), CIA Had Fix on Hussein: Intelligence Revealed 'Target of Opportunity'
- ↑ Eric Schmit (April 25, 2003), "Back From Iraq, High-Tech Fighter Pilots Recount Exploits", New York Times
- ↑ COBRA II, p. 178
- ↑ Gregory Fontenot, E. J. Degen, David Tohn. United States Army Operation Iraqi Freedom Study Group (2005), Crossing the Berm, Chapter 3: The Running Start; On Point: The United States Army in Operation Iraqi Freedom, Center for Army Lessons Learned
- ↑ COBRA II, p. 188
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 Operation Iraqi Freedom - March 19/20 Day One, Globalsecurity
- ↑ United States Marine Corps, 3rd Light Armored Reconnaissance Battalion
- ↑ COBRA II, p. 193
- ↑ Andrew Buncombe in Kuwait City (March 22, 2003), "Burning oil wells may have caused death of marines", Independent (U.K.)
- ↑ Operation Iraqi Freedom - March 22: Day Three, Globalsecurity
- ↑ Franks, pp. 486-490
- ↑ Tim Pritchard (December 5, 2006), "Op-Ed Contributor: When Iraq Went Wrong", New York Times
- ↑ Ryan O'Rourke (June 4, 2003), Iraq War: Defense Program Implications for Congress, Congressional Research Service, at CRS-36
- ↑ Gregory Fontenot, E. J. Degen, David Tohn. United States Army Operation Iraqi Freedom Study Group (2005), The 101st Goes Deep, Chapter 4: The March Up-Country; On Point: The United States Army in Operation Iraqi Freedom, Center for Army Lessons Learned
- ↑ Thomas E. Ricks (March 27, 2003), "War Could Last Months, Officers Say", Washington Post
- ↑ COBRA II, pp. 312-313
- ↑ Lisa Burgess (March 29, 2003), "Rumsfeld warns Syria, Iran against involvement in Iraq war", Stars and Stripes
- ↑ Franks, pp. 508-509
- ↑ COBRA II, p. 310
- ↑ Gregory Fontenot, E. J. Degen, David Tohn. United States Army Operation Iraqi Freedom Study Group (2005), Securing the Lines of Communication, Chapter 4: The March Up-Country; On Point: The United States Army in Operation Iraqi Freedom, Center for Army Lessons Learned
- ↑ COBRA II, pp. 307-308
- ↑ Franks, pp. 528-529
- ↑ Ricardo S. Sanchez with Donald T. Phillips (2008), Wiser in Battle: a Soldier's Story, HarperCollins, ISBN 9780061562426, pp. 168
- ↑ Sanchez, p. 171