imported>Chunbum Park |
imported>John Stephenson |
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| == '''[[2012 doomsday prophecy]]''' ==
| | {{:{{FeaturedArticleTitle}}}} |
| ----
| | <small> |
| '''2012''' doomsday predictions were irrational fears fueled by certain booksellers, fearmongers, moviemakers and other hucksters to encourage public panic for the purpose of making money. The hoax used dubious claims about [[astronomy]] and ancient Mayan calendars to promote nonsensical predictions regarding apocalyptic events supposed to occur on December 21st or 23rd of 2012. Doomsayers suggested there will be destruction caused by global floods, solar flares, exploding sun, reversals of the magnetic field, or planetary collisions.<ref name=twsMar14g>{{cite news
| | ==Footnotes== |
| |author= Maria Puente
| |
| |title= Oh, Maya! Is 2012 the end? Film boosts doomsday frenzy
| |
| |publisher= USA Today
| |
| |date= 2009-11-12
| |
| |url= http://www.usatoday.com/life/lifestyle/2009-11-12-2012_CV_N.htm
| |
| |accessdate= 2010-03-14
| |
| }}</ref><ref name=twsMar14k>{{cite news
| |
| |title= Scared Of Planet Nibiru? NASA Would Like To Help
| |
| |publisher= NPR
| |
| |date= November 15, 2009
| |
| |url= http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=120436493
| |
| |accessdate= 2010-03-14
| |
| }}</ref> Many people are scared.<ref name=twsMar14f>{{cite news
| |
| |author= Brian Handwerk
| |
| |title= 2012 Prophecies Sparking Real Fears, Suicide Warnings
| |
| |publisher= Huffington Post, National Geographic News
| |
| |date= 2009-11-10
| |
| |url= http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2009/11/10/2012-prophecies-sparking_n_352296.html
| |
| |accessdate= 2010-03-14
| |
| }}</ref><ref name=twsMar14m>{{cite news
| |
| |author= CHRISTINE BROUWER
| |
| |title= Will the World End in 2012?
| |
| |publisher= ABC News
| |
| |date= July 3, 2008
| |
| |url= http://a.abcnews.com/international/story?id=5301284&page=1
| |
| |accessdate= 2010-03-14
| |
| }}</ref>
| |
| | |
| Scientists agree 2012 doomsday forecasts are "bunk".<ref name=twsMar14b>{{cite news
| |
| |author= Mark Stevenson, Associated Press
| |
| |title= Scientists debunk 2012 as doomsday date
| |
| |publisher= San Francisco Chronicle
| |
| |date= October 11, 2009
| |
| |url= http://articles.sfgate.com/2009-10-11/news/17183490_1_meteor-tablet-stone
| |
| |accessdate= 2010-03-14
| |
| }}</ref><ref name=twsMar14e>{{cite news | |
| |author= DENNIS OVERBYE
| |
| |title= Is Doomsday Coming? Perhaps, but Not in 2012
| |
| |publisher= The New York Times
| |
| |date= November 16, 2009
| |
| |url= http://www.nytimes.com/2009/11/17/science/17essay.html
| |
| |accessdate= 2010-03-14
| |
| }}</ref> | |
| | |
| The 2012 doomsday pop culture phenomenon was similar in many respects to the "Y2K" phenomenon which marked New Year's Eve in 1999, when the new millennium happened. The hysteria has also been compared to the panic created by Orson Welles radio program ''War of the Worlds''. But the "2012 apocalypse business is booming", according to the ''Huffington Post''. The 2012 doomsday prediction was one more example of a patten repeated over the centuries; for example, Baptist preacher William Miller convinced perhaps a hundred thousand Americans that the second coming of [[Jesus Christ]] would happen in 1843; it didn't. Doomsday predictions tend to be within the span of about ten years from the present, according to University of Wisconsin historian Paul Boyer, since the sense of "imminence" and that it will "happen soon" is necessary for these hysterias to catch the public imagination.<ref name=twsMar14f/>
| |
| [[Image:Planet.jpg|thumb|left|alt=Planet.|Planet "Nibiru" doesn't exist except in the minds of believers of disaster scenarios such as 2012.]]
| |
| | |
| ''[[2012 doomsday prophecy|.... (read more)]]''
| |
| | |
| {| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" style="width: 90%; float: center; margin: 0.5em 1em 0.8em 0px;"
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="text-align: center;" | [[2012 doomsday prophecy#References|notes]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |
| |
| {{reflist|2}} | | {{reflist|2}} |
| |}
| | </small> |
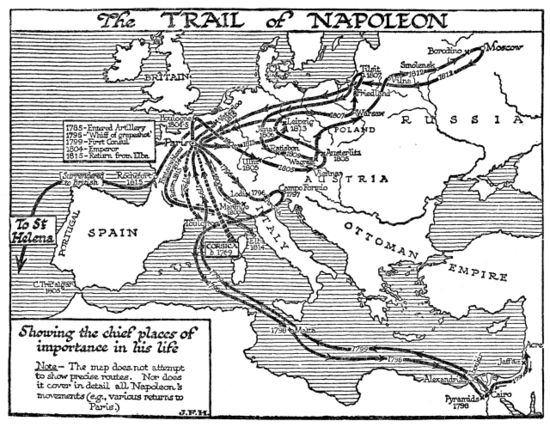
Napoleon (Napoleon Bonaparte or, after 1804, Napoleon I, Emperor of the French) was a world historic figure and dictator of France from 1799 to 1814. He was the greatest general of his age--perhaps any age, with a sure command of battlefield tactics and campaign strategies, As a civil leader he played a major role in the French Revolution, then ended it when he became dictator in 1799 and Emperor of France in 1804 He modernized the French military, fiscal, political legal and religious systems. He fought an unending series of wars against Britain with a complex, ever-changing coalition of European nations on both sides. Refusing to compromise after his immense defeat in Russia in 1812, he was overwhelmed by a coalition of enemies and abdicated in 1814. In 1815 he returned from exile, took control of France, built a new army, and in 100 days almost succeeded--but was defeated at Waterloo and exiled to a remote island. His image and memory are central to French national identity, but he is despised by the British and Russians and is a controversial figure in Germany and elsewhere in Europe.
Rise to Power
Once the Revolution had begun, so many of the aristocratic officers turned against the Revolutionary government, or were exiled or executed, that a vacuum of senior leadership resulted. Promotions came very quickly now, and loyalty to the Revolution was as important as technical skill; Napoleon had both. His demerits were overlooked as he was twice reinstated, promoted, and allowed to collect his back pay. Paris knew him as an intellectual soldier deeply involved in politics. His first test of military genius came at Toulon in 1793, where the British had seized this key port. Napoleon, an acting Lieutenant-Colonel, used his artillery to force the British to abandon the city. He was immediately promoted by the Jacobin radicals under Robespierre to brigadier-general, joining the ranks of several brilliant young generals. He played a major role in defending Paris itself from counter-revolutionaries, and became the operational planner for the Army of Italy and planned two successful attacks in April 1794. He married Josephine (Rose de Beauharnais) in 1796, after falling violently in love with the older aristocratic widow.[1]
- ↑ Englund pp 63-73, 91-2, 97-8