imported>Chunbum Park |
imported>John Stephenson |
| (44 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| == '''[[Mission San Juan Capistrano]]''' ==
| | {{:{{FeaturedArticleTitle}}}} |
| ----
| | <small> |
| '''Mission San Juan Capistrano''' is a former religious outpost established by [[Spain|Spanish]] colonists on the west coast of [[North America]] in the present-day State of [[California]]. Officially founded on November 1 ("All Saints Day"), 1776 by [[Roman Catholic Church|Roman Catholics]] of the Franciscan Order, the settlement was the seventh in the twenty-one mission [[Alta California]] chain. Named after a 15th-century theologian and "warrior priest" who resided in the Abruzzo region of [[Italy]], San Juan Capistrano has the distinction of being home to the oldest building in California still in use, a chapel constructed in 1782. Known alternately as "Serra's Chapel" and "Father Serra's Church," it is the only extant structure wherein it has been documented that the ''padre'' officiated over mass. One of the best known of the Alta California missions, it was the only mission to have been founded twice — the site was originally consecrated on October 30, 1775 but was quickly abandoned due to [[Mission San Diego de Alcalá#Mission Period (1769–1833)|unrest among the indigenous population in San Diego]].
| | ==Footnotes== |
| | |
| The Mission entered a long period of gradual decline after secularization in 1833. Numerous efforts were made over the years to restore the Mission to its former glory, but none met with great success until the arrival of Father O'Sullivan in 1910. The remains of Father (later Monsignor) O'Sullivan, who recognized the property's historic value and worked tirelessly to conserve and rebuild its structures, are buried at the entrance to the cemetery, and a statue raised in his honor stands at the head of the crypt. The surviving chapel also serves as the final resting place of three padres who passed on while serving at the Mission: Fathers José Barona, Vicente Fustér, and Vicente Pascual Oliva are all entombed beneath the sanctuary floor. Though ruins of "The Great Stone Church" (which was all but leveled by an 1812 earthquake) are a renowned architectural wonder, the Mission is perhaps best known for the annual "Return of the Swallows" which is traditionally observed every March 19 (''Saint Joseph's Day''). Mission San Juan Capistrano has served as a favorite subject for many notable artists, and has been immortalized in literature and on film numerous times, perhaps more than any other mission. Over 500,000 people visit the site every year. Designated as a historic landmark at both the state and national levels, Pope John Paul II conferred the rank of Minor Basilica to the Mission in 2000. Today "Serra's Chapel" serves as a parish church within the Roman Catholic Diocese of Orange.
| |
| | |
| ''[[Mission San Juan Capistrano|.... (read more)]]''
| |
| | |
| {| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" style="width: 90%; float: center; margin: 0.5em 1em 0.8em 0px;"
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="text-align: center;" | [[Mission San Juan Capistrano#Notes and references|notes]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |
| |
| {{reflist|2}} | | {{reflist|2}} |
| |}
| | </small> |
Latest revision as of 10:19, 11 September 2020
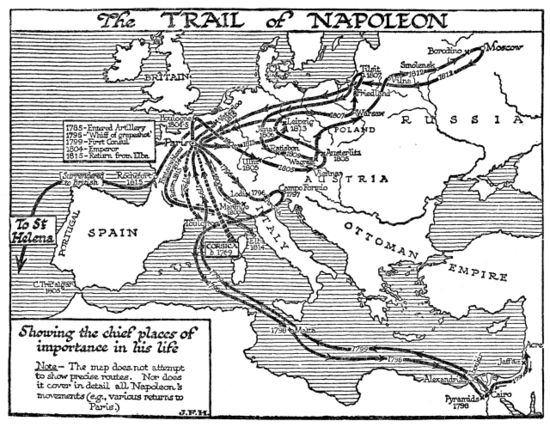
Napoleon (Napoleon Bonaparte or, after 1804, Napoleon I, Emperor of the French) was a world historic figure and dictator of France from 1799 to 1814. He was the greatest general of his age--perhaps any age, with a sure command of battlefield tactics and campaign strategies, As a civil leader he played a major role in the French Revolution, then ended it when he became dictator in 1799 and Emperor of France in 1804 He modernized the French military, fiscal, political legal and religious systems. He fought an unending series of wars against Britain with a complex, ever-changing coalition of European nations on both sides. Refusing to compromise after his immense defeat in Russia in 1812, he was overwhelmed by a coalition of enemies and abdicated in 1814. In 1815 he returned from exile, took control of France, built a new army, and in 100 days almost succeeded--but was defeated at Waterloo and exiled to a remote island. His image and memory are central to French national identity, but he is despised by the British and Russians and is a controversial figure in Germany and elsewhere in Europe.
Rise to Power
Once the Revolution had begun, so many of the aristocratic officers turned against the Revolutionary government, or were exiled or executed, that a vacuum of senior leadership resulted. Promotions came very quickly now, and loyalty to the Revolution was as important as technical skill; Napoleon had both. His demerits were overlooked as he was twice reinstated, promoted, and allowed to collect his back pay. Paris knew him as an intellectual soldier deeply involved in politics. His first test of military genius came at Toulon in 1793, where the British had seized this key port. Napoleon, an acting Lieutenant-Colonel, used his artillery to force the British to abandon the city. He was immediately promoted by the Jacobin radicals under Robespierre to brigadier-general, joining the ranks of several brilliant young generals. He played a major role in defending Paris itself from counter-revolutionaries, and became the operational planner for the Army of Italy and planned two successful attacks in April 1794. He married Josephine (Rose de Beauharnais) in 1796, after falling violently in love with the older aristocratic widow.[1]
- ↑ Englund pp 63-73, 91-2, 97-8