imported>Chunbum Park |
imported>John Stephenson |
| (39 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| == '''[[Battleship]]''' ==
| | {{:{{FeaturedArticleTitle}}}} |
| ----
| | <small> |
| [[Image:USS Arizona memorial.jpg|thumb|right|180px|{{USS Arizona memorial.jpg/credit}}<br />The [[USS Arizona (BB-39)|USS ''Arizona'']] memorial in [[Pearl Harbor, Hawaii]] which spans over the wreckage of the battleship.]]
| | ==Footnotes== |
| [[Image:USS Massachusetts BB-59 Fall RIver.jpg|thumb|right|250px|{{USS Massachusetts BB-59 Fall RIver.jpg/credit}}<br />The [[USS Massachusetts (BB-59)|USS ''Massachusetts'' (BB-59)]] or "Big Mamie," on display as a museum ship in Battleship Cove, [[Fall River, Massachusetts]].]]
| |
| The '''battleship''', though now essentially obsolete as a naval weapon, is a naval vessel intended to engage the most powerful warships of an opposing navy. Evolved from the [[ship of the line]], their main armament consisted of multiple heavy [[cannon]] mounted in movable [[turret]]s. The ships boasted extensive armor and as such were designed to survive severe punishment inflicted upon them by other capital ships.
| |
| | |
| The word "battleship" was coined around 1794 and is a contraction of the phrase "line-of-battle ship," the dominant wooden warship during the [[Age of Sail]].<ref name="OED">"battleship" The Oxford English Dictionary. 2nd ed. 1989. OED Online. Oxford University Press. 4 April 2000.</ref> The term came into formal use in the late 1880s to describe a specific type of [[ironclad warship]] (now referred to by historians as pre-''Dreadnought'' battleships).<ref name="Stoll">Stoll, J. ''Steaming in the Dark?'', Journal of Conflict Resolution Vol. 36 No. 2, June 1992.</ref> In 1906, the commissioning of [[HMS Dreadnought (1905)|HMS ''Dreadnought'']] heralded a revolution in capital ship design. Subsequent battleship designs were therefore referred to as "dreadnoughts." A general criterion from thereon in was that the armor of a true battleship must be sufficiently thick to withstand a hit by its own most powerful gun, within certain constraints. [[#The Diversion of the Battlecruiser|Battlecruiser]]s, while having near-battleship-sized guns, did not meet this standard of protection, and instead were intended to be fast enough to outrun the more heavily armed and armored battleship.<ref name=Massie>{{citation
| |
| | author = Robert K. Massie
| |
| | title = Dreadnought: Britain, Germany and the Coming of the Great War
| |
| | publisher = Ballantine
| |
| | year = 1992
| |
| | isbn = 9780345375568}}</ref>
| |
| | |
| From 1905 to the early 1940s, battleships defined the strength of a first-class navy. The idea of a strong "fleet in being", backed by a major industrial infrastructure, was key to the thinking of the naval strategist per [[Alfred Thayer Mahan]], writing in his 1890 book, ''The Influence of Sea Power upon History, 1660-1763'' (1890). The essence of Mahan from a naval viewpoint is that a great navy is a mark and prerequisite of national greatness. In a 1912 letter to the ''New York Times'', he counseled against relying on international relations for peace, and pointed out that other major nations were all building battleships.<ref>{{citation
| |
| | title =HOPELESSLY OUTFORCED."; Admiral Mahan Prophesies Plight of Nation Without More Battleships.
| |
| | author = [[Alfred Thayer Mahan]]
| |
| | date = 14 April 1912
| |
| | journal = New York Times
| |
| | url = http://query.nytimes.com/mem/archive-free/pdf?_r=1&res=9503E5DF103AE633A25757C1A9629C946396D6CF}}</ref>
| |
| Asymmetrical threats to battleships began, in the early 20th century, with [[torpedo]]es from [[fast attack craft]] and [[mine (naval)|mines]]. These [[#The underwater threat|underwater threats]] could strike in more vulnerable spots than could heavy guns. [[#Aircraft versus battleship|Aircraft]], however, became an even more decisive threat by World War II.
| |
| | |
| ''[[Battleship|.... (read more)]]''
| |
| | |
| {| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" style="width: 90%; float: center; margin: 0.5em 1em 0.8em 0px;"
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="text-align: center;" | [[Battleship#References|notes]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |
| |
| {{reflist|2}} | | {{reflist|2}} |
| |}
| | </small> |
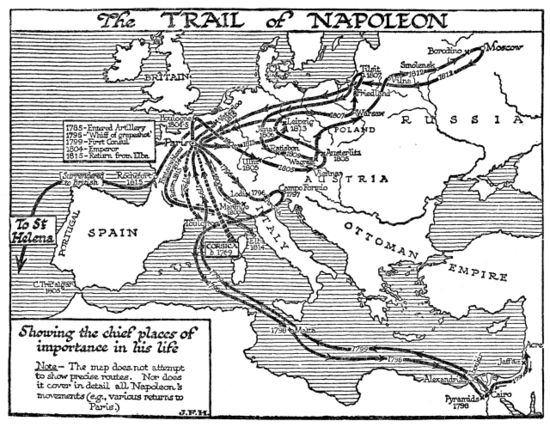
Napoleon (Napoleon Bonaparte or, after 1804, Napoleon I, Emperor of the French) was a world historic figure and dictator of France from 1799 to 1814. He was the greatest general of his age--perhaps any age, with a sure command of battlefield tactics and campaign strategies, As a civil leader he played a major role in the French Revolution, then ended it when he became dictator in 1799 and Emperor of France in 1804 He modernized the French military, fiscal, political legal and religious systems. He fought an unending series of wars against Britain with a complex, ever-changing coalition of European nations on both sides. Refusing to compromise after his immense defeat in Russia in 1812, he was overwhelmed by a coalition of enemies and abdicated in 1814. In 1815 he returned from exile, took control of France, built a new army, and in 100 days almost succeeded--but was defeated at Waterloo and exiled to a remote island. His image and memory are central to French national identity, but he is despised by the British and Russians and is a controversial figure in Germany and elsewhere in Europe.
Rise to Power
Once the Revolution had begun, so many of the aristocratic officers turned against the Revolutionary government, or were exiled or executed, that a vacuum of senior leadership resulted. Promotions came very quickly now, and loyalty to the Revolution was as important as technical skill; Napoleon had both. His demerits were overlooked as he was twice reinstated, promoted, and allowed to collect his back pay. Paris knew him as an intellectual soldier deeply involved in politics. His first test of military genius came at Toulon in 1793, where the British had seized this key port. Napoleon, an acting Lieutenant-Colonel, used his artillery to force the British to abandon the city. He was immediately promoted by the Jacobin radicals under Robespierre to brigadier-general, joining the ranks of several brilliant young generals. He played a major role in defending Paris itself from counter-revolutionaries, and became the operational planner for the Army of Italy and planned two successful attacks in April 1794. He married Josephine (Rose de Beauharnais) in 1796, after falling violently in love with the older aristocratic widow.[1]
- ↑ Englund pp 63-73, 91-2, 97-8