CZ:Featured article/Current: Difference between revisions
imported>Chunbum Park (→Refrigerator car: Ontological pluralism) |
imported>John Stephenson (template) |
||
| (27 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{:{{FeaturedArticleTitle}}}} | |||
<small> | |||
==Footnotes== | |||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
</small> | |||
Latest revision as of 10:19, 11 September 2020
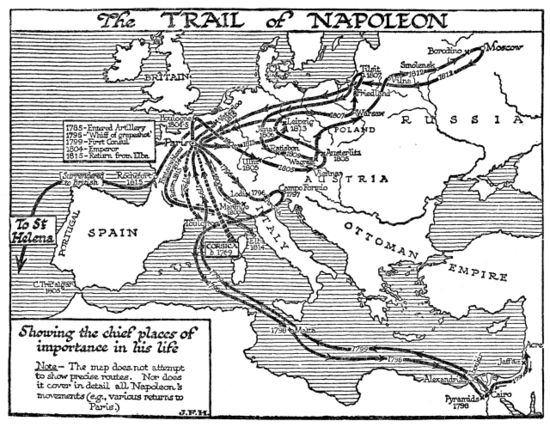
Napoleon (Napoleon Bonaparte or, after 1804, Napoleon I, Emperor of the French) was a world historic figure and dictator of France from 1799 to 1814. He was the greatest general of his age--perhaps any age, with a sure command of battlefield tactics and campaign strategies, As a civil leader he played a major role in the French Revolution, then ended it when he became dictator in 1799 and Emperor of France in 1804 He modernized the French military, fiscal, political legal and religious systems. He fought an unending series of wars against Britain with a complex, ever-changing coalition of European nations on both sides. Refusing to compromise after his immense defeat in Russia in 1812, he was overwhelmed by a coalition of enemies and abdicated in 1814. In 1815 he returned from exile, took control of France, built a new army, and in 100 days almost succeeded--but was defeated at Waterloo and exiled to a remote island. His image and memory are central to French national identity, but he is despised by the British and Russians and is a controversial figure in Germany and elsewhere in Europe.
Rise to Power
Once the Revolution had begun, so many of the aristocratic officers turned against the Revolutionary government, or were exiled or executed, that a vacuum of senior leadership resulted. Promotions came very quickly now, and loyalty to the Revolution was as important as technical skill; Napoleon had both. His demerits were overlooked as he was twice reinstated, promoted, and allowed to collect his back pay. Paris knew him as an intellectual soldier deeply involved in politics. His first test of military genius came at Toulon in 1793, where the British had seized this key port. Napoleon, an acting Lieutenant-Colonel, used his artillery to force the British to abandon the city. He was immediately promoted by the Jacobin radicals under Robespierre to brigadier-general, joining the ranks of several brilliant young generals. He played a major role in defending Paris itself from counter-revolutionaries, and became the operational planner for the Army of Italy and planned two successful attacks in April 1794. He married Josephine (Rose de Beauharnais) in 1796, after falling violently in love with the older aristocratic widow.[1]
Footnotes
- ↑ Englund pp 63-73, 91-2, 97-8