Confederate States of America
Template:For Template:Infobox Former Country The Confederate States of America (a.k.a. the Confederacy, the Confederate States, and CSA) was the government formed by eleven southern states of the United States of America between 1861 and 1865. Seven states declared their independence from the United States before Abraham Lincoln was inaugurated as president; four more did so after the American Civil War began with the Battle of Fort Sumter when the CSA attacked the USA. The United States of America ("The Union") held secession illegal and refused recognition of the Confederacy. Although no European powers officially recognized the CSA, British commercial interests sold it warships and operated blockade runners to help supply it.
When Robert E. Lee and the other generals surrendered their armies in the spring of 1865, the CSA collapsed, and there was no guerrilla warfare afterwards. A difficult, decade-long process of Reconstruction temporarily gave civil rights and the right to vote to the freedmen, expelled ex-Confederate leaders from office, and permanently re-admitted the states to representation in Congress.
History
Causes for Secession
Historians phrase the cause of secession as either the threat to restrict or end slavery by the Republicans, or that a restriction on states' rights regarding slave ownership in the territories prompted southern states to withdraw from the Union. The "states rights" argument refers to one of two factors: the right claimed by the states for their citizens to take slaves where they wanted (the main cause of the secession the seven cotton states in winter 1860-61), or second, the right of states to be free of federal invasion, which was the main cause of the secession of the four border states in spring 1861.
Some southern religious leaders preached cause of secession. Benjamin M. Palmer (1818-1902), pastor of the First Presbyterian Church of New Orleans, thundered his support for secession in a Thanksgiving sermon in 1860, arguing that white Southerners had a right and duty to maintain slavery out of economic and social self-preservation, in order to act as "guardians" to the "affectionate and loyal" but "helpless" blacks, to safeguard global economic interests, and to defend religion against "atheistic" abolitionism[1]. His sermon was widely distributed across the region.
In what later came to be known as the Cornerstone Speech, C.S. Vice President Alexander Stephens, declared that the "cornerstone" of the new government "rest[ed] upon the great truth that the negro is not equal to the white man; that slavery—subordination to the superior race—is his natural and normal condition. This, our new government, is the first, in the history of the world, based upon this great physical, philosophical, and moral truth."[2] Four of the seceding states, the Deep South states of South Carolina[3], Mississippi[4], Georgia[5], and Texas[6], issued formal declarations of causes, each of which identified the threat to slaveholders’ rights as the cause of, or a major cause of, secession; Georgia also claimed a general Federal policy of favoring Northern over Southern economic interests.
By contrast, C.S. President Jefferson Davis made no explicit reference to slavery in his inaugural address, instead emphasizing States Rights as the reason for secession.[7].
C.S. Vice President Alexander Stephens declared, in the longest portion of the Cornerstone Speech, how this constitution eliminated the tariff and removed the Commerce Clause, taking away congressional power to regulate any aspect of commerce. Stephens believed that the new country would have a clear delineation between Federal and State responsibilities, and took the position similar to that of South Carolina during the nullification crisis that the Federal government should not pay for internal improvements.
Seceding states
Template:Confederate Seven states seceded by February 1861:
- South Carolina (December 20 1860),[1]
- Mississippi (January 9 1861),[2]
- Florida (January 10 1861),[3]
- Alabama (January 11 1861),[4]
- Georgia (January 19 1861),[5]
- Louisiana (January 26 1861),[6]
- Texas (February 1 1861).[7]
After Lincoln called for troops, four more states seceded:
- Virginia (April 17 1861);[8] there was also a rump Union government of Virginia[9]
- Arkansas (May 6 1861),[10]
- North Carolina (May 20 1861)[11]
- Tennessee (June 8 1861).[12][13]
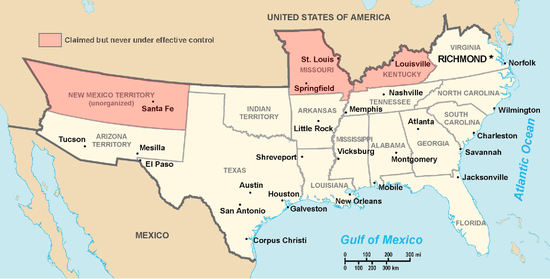
Two more states had rival (or rump) governments. The Confederacy admitted them but they never controlled these states and the pro-Confederate state governments were soon in exile:
- Missouri did not secede but a rump groups proclaimed secession (October 31 1861).[14][15]
- Kentucky did not secede but a rump, unelected group proclaimed secession (November 20, 1861).[16][17]
Both states allowed slavery and both had strong Unionist and Confederate counties, including some Unionist slave-owners. The legalities of the matter remain in dispute to the present day.
Rise and fall of the Confederacy
The American Civil War broke out in April of 1861 with the Battle of Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina. Federal troops of the U.S. had retreated to Fort Sumter soon after South Carolina declared their secession. U.S. President Buchanan had attempted to resupply Sumter by sending the Star of the West, but Confederate forces fired upon the ship, driving it away. U.S. President Abraham Lincoln also attempted to resupply Sumter. Lincoln notified South Carolina Governor Francis W. Pickens that "an attempt will be made to supply Fort Sumter with provisions only, and that if such attempt be not resisted, no effort to throw in men, arms, or ammunition will be made without further notice, [except] in case of an attack on the fort." In response, the Confederate cabinet decided at a meeting in Montgomery to open fire on Fort Sumter in an attempt to force its surrender before the relief fleet arrived. On April 12, 1861, Confederate troops, following orders from Davis and his Secretary of War, fired upon the federal troops occupying Fort Sumter, forcing their surrender. Following the Battle of Fort Sumter, Lincoln called for the remaining states in the Union to send troops to recapture Sumter and other forts and customs-houses[18] in the South that Confederate forces had claimed, some by force. This proclamation was made before Congress could convene on the matter, and the original request from the War Department called for volunteers for only three months of duty.[18] Lincoln's call for troops resulted in four more states voting to secede, rather than provide troops for the Union. Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina joined the Confederacy for a total of 11. Once Virginia joined the Confederate States, the Confederate capital was moved from Montgomery, Alabama, to Richmond, Virginia. All but two major battles took place in Confederate territory.
Alexander H. Stephens maintained that Lincoln's attempt to resupply Sumter had provoked the war.[19]
Kentucky was a border state during the war and, for a time, had two state governments, one supporting the Confederacy and one supporting the Union. The original government remained in the Union after a short-lived attempt at neutrality, but a rival faction from that state was accepted as a member of the Confederate States of America; it did not control any territory. A more complex situation surrounds the Missouri Secession, but, in any event, the Confederacy considered Missouri a member of the Confederate States of America; it did not control any territory. With Kentucky and Missouri, the number of Confederate states can be counted as 13.
The five tribal governments of the Indian Territory — which became Oklahoma in 1907 — also mainly supported the Confederacy, providing troops and one General officer. It was not represented in the Confederate Congress.
Citizens at Mesilla and Tucson in the southern part of New Mexico Territory formed a secession convention and voted to join the Confederacy on March 16, 1861, and appointed Lewis Owings as the new territorial governor. In July, Mesilla appealed to Confederate troops in El Paso, Texas, under Lieutenant Colonel John Baylor for help in removing the Union Army under Major Isaac Lynde that was stationed nearby. The Confederates defeated Lynde at the Battle of Mesilla on July 27. After the battle, Baylor established a territorial government for the Confederate Arizona Territory and named himself governor. In 1862, a New Mexico Campaign was launched under General Henry Hopkins Sibley to take the northern half of New Mexico. Although Confederates briefly occupied the territorial capital of Santa Fe, they were defeated at Glorietta Pass in March and retreated, never to return.
The northernmost slave states (Missouri, Kentucky, Maryland, Delaware and West Virginia) were contested territory, but the Union won control by 1862. In 1861, martial law was declared in Maryland (the state which borders the U.S. capital, Washington, D.C., on three sides) to block attempts at secession. Delaware, also a slave state, never considered secession, nor did Washington, D.C. In 1861, a unionist legislature in Wheeling, Virginia seceded from Virginia, claiming 48 counties, and joined the United States in 1863 as the state of West Virginia with a constitution that gradually abolished slavery.
Attempts to secede from the Confederate States of America by some counties in East Tennessee were held in check by Confederate declarations of martial law[8][9].
The surrender of the Army of Northern Virginia by General Lee at Appomattox Court House on April 9, 1865, is generally taken as the end of the Confederate States. President Davis was captured at Irwinville, Georgia, on May 10, and the remaining Confederate armies surrendered by June 1865. The last Confederate flag was hauled down from CSS Shenandoah on November 6, 1865.
Government and politics
Constitution
The Confederate States Constitution provides much insight into the motivations for secession from the Union. While much of it was a word-for-word duplicate of the United States Constitution, it contained several explicit protections of the institution of slavery, though international slave trading was prohibited. It also reflected a stronger philosophy of states' rights, curtailing the power of the central authority: the Confederate government was prohibited from instituting protective tariffs or from using revenues collected in one state for funding internal improvements in another state. In contrast with the largely secular language of the United States Constitution, the Confederate Constitution overtly asked God's blessing ("invoking the favor of Almighty God.")
The constitution did not specifically include a provision allowing states to secede; the Preamble spoke of each state "acting in its sovereign and independent character" but also of the formation of a "permanent federal government". The Southern leaders met in Montgomery, Alabama, to write their constitution.
The President of the Confederate States of America was to be elected to a six-year term and could not be reelected. The only president was Jefferson Davis; the Confederate States of America was defeated by the federal government before he completed his term. One unique power granted to the Confederate president was the ability to subject a bill to a line item veto, a power held by some state governors. The Confederate Congress could overturn either the general or the line item vetoes with the same two-thirds majorities that are required in the U.S. Congress. In addition, appropriations not specifically requested by the executive branch required passage by a two-thirds vote in both houses of Congress.
Printed currency in the forms of bills and stamps was authorized and put into circulation, although by the individual states in the Confederacy's name. The government considered issuing Confederate coinage. Plans, dies and 4 "proofs" were created, but a lack of bullion prevented any public coinage.
Civil liberties
The Confederacy actively used the military to arrest people suspected of loyalty to the United States. Historian Mark Neely found 2,700 names of men arrested and estimated the full list was much longer. They arrested at about the same rate as the Union arrested Confederate loyalists. Neely concludes:
- "The Confederate citizen was not any freer than the Union citizen — and perhaps no less likely to be arrested by military authorities. In fact, the Confederate citizen may have been in some ways less free than his Northern counterpart. For example, freedom to travel within the Confederate states was severely limited by a domestic passport system." [Neely 11, 16]
Capital
The capital of the Confederate States of America was Montgomery, Alabama, from February 4, 1861, until May 29, 1861. Richmond, Virginia, was named the new capital on May 6, 1861. Shortly before the end of the war, the Confederate government evacuated Richmond, planning to relocate further south. Little came of these plans before Lee's surrender at Appomattox Court House. Danville, Virginia, served as the last capital of the Confederate States of America, from April 3 to April 10, 1865.
International diplomacy
Once the war with the United States began, the best hope for the survival of the Confederacy was military intervention by Britain and France. The U.S. realized that too and made it clear that recognition of the Confederacy meant war with the United States — and the cutoff of food shipments into Britain. The Confederates who had believed that "cotton is king" — that is, Britain had to support the Confederacy to obtain cotton — were proven wrong. Britain, in fact, had ample stores of cotton in 1861 and depended much more on grain from the Union states.
During its existence, the Confederate government sent repeated delegations to Europe; historians do not give them high marks for diplomatic skills. James M. Mason was sent to London as Confederate minister to Queen Victoria, and John Slidell was sent to Paris as minister to Napoleon III. Both were able to obtain private meetings with high British and French officials, but they failed to secure official recognition for the Confederacy. Britain and the United States were at sword's point during the Trent Affair in late 1861. Mason and Slidell had been illegally seized from a British ship by an American warship. Queen Victoria's husband, Prince Albert, helped calm the situation, and Lincoln released Mason and Slidell, so the episode was no help to the Confederacy.
Throughout the early years of the war, both British foreign secretary Lord Russell and Napoleon III, and, to a lesser extent, British Prime Minister Lord Palmerston, were interested in the idea of recognition of the Confederacy, or at least of offering a mediation. Recognition meant certain war with the United States, loss of American grain, loss of exports to the United States, loss of huge investments in American securities, possible war in Canada and other North American colonies, much higher taxes, many lives lost and a severe threat to the entire British merchant marine, in exchange for the possibility of some cotton. Many party leaders and the general public wanted no war with such high costs and meager benefits. Recognition was considered following the Second Battle of Manassas when the British government was preparing to mediate in the conflict, but the Union victory at the Battle of Antietam and Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation, combined with internal opposition, caused the government to back away.
In November 1863, Confederate diplomat A. Dudley Mann met Pope Pius IX and received a letter addressed "to the Illustrious and Honorable Jefferson Davis, President of the Confederate States of America.” Mann, in his dispatch to Richmond, interpreted the letter as "a positive recognition of our Government," and some have mistakenly viewed it as a de facto recognition of the C.S.A. Confederate Secretary of State Judah P. Benjamin, however, interpreted it as "a mere inferential recognition, unconnected with political action or the regular establishment of diplomatic relations" and thus did not assign it the weight of formal recognition.[10] For the remainder of the war, Confederate commissioners continued meeting with Cardinal Antonelli, the Vatican Secretary of State. In 1864, Catholic Bishop Patrick N. Lynch of Charleston traveled to the Vatican with an authorization from Jefferson Davis to represent the Confederacy before the Holy See.
No country appointed any diplomat officially to the Confederacy, but several maintained their consuls in the South who had been appointed before the war. In 1861, Ernst Raven applied for approval as the Saxe-Coburg-Gotha consul, but he was a citizen of Texas and there is no evidence that Saxe officials knew what he was doing. In 1863, the Confederacy expelled all foreign consuls (all of them British or French diplomats) for advising their subjects to refuse to serve in combat against the U.S.
Throughout the war most European powers adopted a policy of neutrality, meeting informally with Confederate diplomats but withholding diplomatic recognition. None ever sent an ambassador or official delegation to Richmond. However, they applied international law principles that recognized the Union and Confederate sides as belligerents. Canada allowed both Confederate and Union agents to work openly within its borders, and some state governments in northern Mexico negotiated local agreements to cover trade on the Texas border.
Died of States Rights?
Historian Frank Lawrence Owsley argued that the Confederacy "died of states rights."[20] That is, strong-willed governors and state legislatures refused to give the national government the soldiers and money it needed because they feared that Richmond was encroaching on the rights of the states. Historians agree that northern governors were much more supportive of Lincoln's policies. Georgia's governor Joseph Brown warned that he saw the signs of a deep-laid conspiracy on the part of Jefferson Davis to destroy states' rights and individual liberty. Brown declaimed: "Almost every act of usurpation of power, or of bad faith, has been conceived, brought forth and nurtured in secret session." To grant the Confederate government the power to draft soldiers was the "essence of military despotism." [21] In 1863 governor Pendleton Murrah of Texas insisted that Texas troops were needed for self-defense (against Indians or a threatened Union invasion), and refused to send them East.[22] Zebulon Vance, the governor of North Carolina was notoriously hostile to Davis and his demands. Opposition to conscription in North Carolina was intense and its results were disastrous for recruiting. Governor Vance's faith in states' rights drove him into a stubborn opposition. [23]
Vice President Stephens broke publicly with President Davis, saying any accommodation would only weaken the republic, and he therefore had no choice but to break publicly with the Confederate administration and the president. Stephens charged that to allow Davis to make "arbitrary arrests" and to draft state officials conferred on him more power than the English Parliament had ever bestowed on the king. History proved the dangers of such unchecked authority." He added that Davis intended to suppress the peace meetings in North Carolina and "put a muzzle upon certain presses" (especially the antiwar newspaper Raleigh Standard) in order to control elections in that state. Echoing Patrick Henry's "give me liberty or give me death" Stephens warned the Southerners they should never view liberty as "subordinate to independence" because the cry of "independence first and liberty second" was a "fatal delusion." As historian George Rable concludes, "For Stephens, the essence of patriotism, the heart of the Confederate cause, rested on an unyielding commitment to traditional rights. In his idealist vision of politics, military necessity, pragmatism, and compromise meant nothing."[24]
The survival of the Confederacy depended on a strong base of civilians and soldiers devoted to victory. The soldiers performed well, though increasing numbers deserted in the last year. The civilians, although enthusiastic in 1861-62 seem to have lost faith in the nation's future by 1864, and instead looked to protect their homes and communities instead. As Rable explains, "As the Confederacy shrank, citizens' sense of the cause more than ever narrowed to their own states and communities. This contraction of civic vision was more than a crabbed libertarianism; it represented an increasingly widespread disillusionment with the Confederate experiment. [25]
Relations with the United States
For the four years of its existence, the Confederate States of America asserted its independence and appointed dozens of diplomatic agents abroad. The United States government, by contrast, asserted that the Southern states were provinces in rebellion and refused any formal recognition of their status. Thus, U.S. Secretary of State William H. Seward issued formal instructions to Charles Francis Adams, the new minister to Great Britain:
- You will indulge in no expressions of harshness or disrespect, or even impatience concerning the seceding States, their agents, or their people. But you will, on the contrary, all the while remember that those States are now, as they always heretofore have been, and, notwithstanding their temporary self-delusion, they must always continue to be, equal and honored members of this Federal Union, and that their citizens throughout all political misunderstandings and alienations, still are and always must be our kindred and countrymen."[26]
However, if the British seemed inclined to recognize the Confederacy, or even waver in that regard, they were to be sharply warned, with a strong hint of war:
- [if Britain is] tolerating the application of the so-called seceding States, or wavering about it, you will not leave them to suppose for a moment that they can grant that application and remain friends with the United States. You may even assure them promptly, in that case, that if they determine to recognize, they may at the same time prepare to enter into alliance with the enemies of this republic."[27]
The Confederate Congress responded to the hostilities by formally declaring war on the United States in May 1861 — calling it "The War between the Confederate States of America and the United States of America." The Union government never declared war but conducted its war efforts under a proclamation of blockade and rebellion. Mid-war negotiations between the two sides occurred without formal political recognition, though the laws of war governed military relationships.
Four years after the war, in 1869, the United States Supreme Court ruled in Texas v. White that secession was unconstitutional and legally null. The court's opinion was authored by Chief Justice Salmon P. Chase. Jefferson Davis, former president of the Confederacy, and Alexander Stephens, its former vice-president, both penned arguments in favor of secession's legality, most notably Davis' The Rise and Fall of the Confederate Government.
Confederate flags
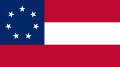
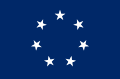
The official flag of the Confederate States of America, and the one actually called the "Stars and Bars", has seven stars, for the seven states that initially formed the Confederacy. This flag was sometimes difficult to distinguish from the Union flag under battle conditions, so the Confederate battle flag, the "Southern Cross", became the one more commonly used in military operations. The Southern Cross has 13 stars, adding the four states that joined the Confederacy after Fort Sumter, and the two divided states of Kentucky and Missouri.
As a result of its depiction in 20th century popular media, the "Southern Cross" is a flag commonly associated with the Confederacy today. The actual "Southern Cross" is a square-shaped flag, but the more commonly seen rectangular flag is actually the flag of the First Tennessee Army, also known as the Naval Jack because it was first used by the Confederate Navy.
Political leaders
Executive

| OFFICE | NAME | TERM |
| President | Jefferson Davis | 1861-1865 |
| Vice President | Alexander Stephens | 1861-1865 |
| Secretary of State | Robert Toombs | 1861 |
| Robert M.T. Hunter | 1861-1862 | |
| Judah P. Benjamin | 1862-1865 | |
| Secretary of the Treasury | Christopher Memminger | 1861-1864 |
| George Trenholm | 1864-1865 | |
| John H. Reagan | 1865 | |
| Secretary of War | Leroy Pope Walker | 1861 |
| Judah P. Benjamin | 1861-1862 | |
| George W. Randolph | 1862 | |
| James Seddon | 1862-1865 | |
| John C. Breckinridge | 1865 | |
| Secretary of the Navy | Stephen Mallory | 1861-1865 |
| Postmaster General | John H. Reagan | 1861-1865 |
| Attorney General | Judah P. Benjamin | 1861 |
| Thomas Bragg | 1861-1862 | |
| Thomas H. Watts | 1862-1863 | |
| George Davis | 1864-1865 | |
Legislative
The legislative branch of the Confederate States of America was the Confederate Congress. Like the United States Congress, the Confederate Congress consisted of two houses: the Confederate Senate, whose membership included two senators from each state (and chosen by the state legislature), and the Confederate House of Representatives, with members popularly elected by residents of the individual states.
Speakers of the Provisional Congress
- Robert Woodward Barnwell of South Carolina - February 4 1861
- Howell Cobb, Sr. of Georgia - February 4 1861-February 17 1862
- Thomas Stanhope Bocock of Virginia - February 18, 1862-March 18, 1865
Presidents pro tempore
- Howell Cobb, Sr. of Georgia
- Robert Woodward Barnwell of South Carolina
- Josiah Abigail Patterson Campbell of Mississippi
- Thomas Stanhope Bocock of Virginia
Tribal Representatives to Confederate Congress
- Elias Cornelius Boudinot 1862-65 - Cherokee
- Burton Allen Holder 1864-1865 Chickasaw
- Robert McDonald Jones 1863-65 - Choctaw
Sessions of the Confederate Congress
Judicial
A Judicial branch of the government was outlined in the constitution, but the "Supreme Court of the Confederate States" was never created or seated because of the ongoing war.[11] Some Confederate district courts were, however, established within some of the individual states of the Confederate States of America; namely, South Carolina, Arkansas, Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, North Carolina, Tennessee, Texas and Virginia (and possibly others). At the end of the war, U.S. district courts resumed jurisdiction.[12]
The state and local courts generally continued to operate as they had been, simply recognizing the CSA, rather than the U.S., as the national government.[13]
Supreme Court - not established
District Court
- Asa Biggs 1861-1865
- John White Brockenbrough 1861
- Alexander Mosby Clayton 1861
- Jesse J. Finley 1861-1862
Geography
The Confederate States of America claimed a total of 2,919 miles (4,698 km) of coastline. A large part of this territory lay on the sea coast with level and sandy ground. The interior portions were hilly and mountainous, and the far western territories were deserts. The lower reaches of the Mississippi River bisected the country, with the western half often referred to as the Trans-Mississippi. The highest point (excluding Arizona and New Mexico) was Guadalupe Peak in Texas at 8,750 feet (2,667 m).
Climate
Much of the area claimed by the Confederate States of America had a humid subtropical climate with mild winters and long, hot, humid summers. The climate varied to semi-arid steppe and arid desert west of longitude 96 degrees west. The subtropical climate made winters mild but allowed infectious diseases to flourish. Consequently disease killed more soldiers than did enemy action.
River system
In peacetime, the vast system of navigable rivers allowed for cheap and easy transportation of farm products. The railroad system was built as a supplement, tying plantation areas to the nearest river or seaport. The vast geography made for difficult Union logistics, and Union soldiers were used to garrison captured areas and protect rail lines. But the Union Navy seized most of the navigable rivers by 1862, making its own logistics easy and Confederate movements difficult. After the fall of Vicksburg in July 1863, it became impossible for units to cross the Mississippi since Union gunboats constantly patrolled it. The South thus lost use of its western regions.
Rural areas
The area claimed by the Confederate States of America was overwhelmingly rural. Small towns of more than 1,000 were few — the typical county seat had a population of less than 500 people. Cities were rare. New Orleans was the only Southern city in the list of top 10 largest U.S. cities in the 1860 census, and it was captured by the Union in 1862. Only 13 Confederate cities ranked among the top 100 U.S. cities in 1860, most of them ports whose economic activities were shut down by the Union blockade. The population of Richmond swelled after it became the national capital, reaching an estimated 128,000 in 1864 (Dabney 1990:182). Other large Southern cities (Baltimore, St. Louis, Louisville, and Washington, as well as Wheeling, West Virginia, and Alexandria, Virginia) were never under the control of the Confederate government.
| # | City | 1860 Population | US Rank | return to USA control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | New Orleans, Louisiana | 168,675 | 6 | 1862 |
| 2. | Charleston, South Carolina | 40,522 | 22 | 1865 |
| 3. | Richmond, Virginia | 37,910 | 25 | 1865 |
| 4. | Mobile, Alabama | 29,258 | 27 | 1865 |
| 5. | Memphis, Tennessee | 22,623 | 38 | 1862 |
| 6. | Savannah, Georgia | 22,292 | 41 | 1864 |
| 7. | Petersburg, Virginia | 18,266 | 50 | 1865 |
| 8. | Nashville, Tennessee | 16,988 | 54 | 1862 |
| 9. | Norfolk, Virginia | 14,620 | 61 | 1862 |
| 10. | Augusta, Georgia | 12,493 | 77 | 1865 |
| 11. | Columbus, Georgia | 9,621 | 97 | 1865 |
| 12. | Atlanta, Georgia | 9,554 | 99 | 1864 |
| 13. | Wilmington, North Carolina | 9,553 | 100 | 1865 |
(See also Atlanta in the Civil War, Charleston, SC in the Civil War, Nashville in the Civil War, New Orleans in the Civil War, and Richmond in the Civil War).
Economy
The Confederacy had an agrarian economy with exports, to a world market, of cotton, and, to a lesser extent, tobacco and sugarcane. Local food production included grains, hogs, cattle, and gardens. The 11 states produced $155 million in manufactured goods in 1860, chiefly from local grist mills, and lumber, processed tobacco, cotton goods and naval stores such as turpentine. The CSA adopted a low tariff of 15 per cent, but imposed it on all imports from the rest of the United States.[14] The tariff mattered little; the Confederacy's ports were blocked to commercial traffic by the Union's blockade, and very few people paid taxes on goods smuggled from the Union states. The government collected about $3.5 million in tariff revenue from the start of their war against the Union to late 1864. The lack of adequate financial resources led the Confederacy to finance the war through printing money, which led to high inflation.
Armed forces
The military armed forces of the Confederacy was comprised of three branches:
The Confederate military leadership included many veterans from the United States Army and United States Navy who had resigned their Federal commissions and had been appointed to senior positions in the Confederate armed forces. Many had served in the Mexican-American War (including Robert E. Lee and Jefferson Davis), but others had little or no military experience (such as Leonidas Polk, who had attended West Point but did not graduate.) The Confederate officer corps was composed in part of young men from slave-owning families, but many came from non-owners. The Confederacy appointed junior and field grade officers by election from the enlisted ranks. Although no Army service academy was established for the Confederacy, many colleges of the South (such as the The Citadel and Virginia Military Institute) maintained cadet corps that were seen as a training ground for Confederate military leadership. A naval academy was established in 1863, but no midshipmen had graduated by the time the Confederacy collapsed.
The rank and file of the Confederate armed forces consisted of white males with an average age between 16 and 28. Many thousands of slaves served as laborers, cooks, pioneers and in other non-combat roles. The Confederacy adopted conscription in 1862. Depleted by casualties, the military suffered chronic manpower shortages. After agitation from the Army, and at the demand of General Lee, slaves were enrolled in new combat units in the spring of 1865, with the promise of emancipation; they were in training when the war ended and did not serve in actual combat. [28]
Military leaders
Military leaders of the Confederacy (with their state of birth and highest rank[29]) included:
- Robert E. Lee (Virginia) - General and General-in-Chief (1865)
- Albert Sidney Johnston (Kentucky) - General
- Joseph E. Johnston (Virginia) - General
- Braxton Bragg (North Carolina) - General
- P.G.T. Beauregard (Louisiana) - General
- Richard Stoddert Ewell (Virginia) - Lieutenant General
- Samuel Cooper (New York) - General (Adjutant General and highest ranking general in the Army); not in combat
- James Longstreet (South Carolina) - Lieutenant General
- Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson (Virginia)- Lieutenant General
- John Hunt Morgan (Kentucky) - Brigadier General
- A.P. Hill (Virginia) - Lieutenant General
- John Bell Hood (Texas) - Lieutenant General
- Wade Hampton III (South Carolina) - Lieutenant General
- Nathan Bedford Forrest (Tennessee) - Lieutenant General
- J.E.B. Stuart (Virginia) - Major General
- Edward Porter Alexander (Georgia) - Brigadier General
- Franklin Buchanan (Maryland) - Admiral
- Raphael Semmes (Maryland) - Rear Admiral
- Josiah Tattnall (Georgia) - Commodore
- Stand Watie (Indian Territory, now Oklahoma) - Brigadier General (last to surrender)
- Leonidas Polk (North Carolina) - Lieutenant General
- Sterling Price (Virginia) - Major General
- Jubal Anderson Early (Virginia) - Lieutenant General
- Richard Taylor (Kentucky) - Lieutenant General (Son of U.S. President Zachary Taylor)
- Lloyd J. Beall (South Carolina) - Colonel - Commandant of the Confederate States Marine Corps
- Stephen Dodson Ramseur (North Carolina) Major General
- Camille Armand Jules Marie, Prince de Polignac (France) Major General
- John Austin Wharton (Tennessee) Major General
- Thomas L. Rosser (Virginia) Major General
Significant dates
See also
- Burr conspiracy
- Triangular Trade
- Golden Circle (Slavery)
- Origins of the American Civil War
- Southern United States
- History of the Southern United States
- Flags of the Confederate States of America
- Seal of the Confederate States of America
- Confederate States of America dollar
- Military history of the Confederate States
- Stamps and postal history of the Confederate States
- Confederados
- C.S.A.: The Confederate States of America, a 2004 mockumentary. Fictional account of an alternate history in which the Confederates won the American Civil War.
Notes
- ↑ The text of South Carolina's Ordinance of Secession.
- ↑ The text of Mississippi's Ordinance of Secession.
- ↑ The text of Florida's Ordinance of Secession.
- ↑ The text of Alabama's Ordinance of Secession.
- ↑ The text of Georgia's Ordinance of Secession.
- ↑ The text of Louisiana's Ordinance of Secession.
- ↑ The text of Texas' Ordinance of Secession.
- ↑ The text of Virginia's Ordinance of Secession.
- ↑ Virginia did not turn over its military to the Confederate States until June 8 1861 and the Constitution of the Confederate States was ratified on June 19 1861.
- ↑ The text of Arkansas' Ordinance of Secession.
- ↑ The text of North Carolina's Ordinance of Secession.
- ↑ The text of Tennessee's Ordinance of Secession.
- ↑ The Tennessee legislature ratified an agreement to enter a military league with the Confederate States on May 7 1861. Tennessee voters approved the agreement on June 8 1861.
- ↑ The text of Missouri's Ordinance of Secession.
- ↑ The pro-Confederate politicians tried to meet in Neosho, Missouri, and then were driven out of the entire state.
- ↑ The text of Kentucky's Ordinance of Secession.
- ↑ Russellville Convention
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Lincoln's proclamation calling for troops from the remaining states (bottom of page); Department of War details to States (top)
- ↑ Alexander H. Stephens A Constitutional View of the Late War Between the States (1870), Vol. 2, p. 36. 75 MB PDF file "I maintain that it was inaugurated and begun, though no blow had been struck, when the hostile fleet, styled the "Relief Squadron," with eleven ships, carrying two hundred and eighty-five guns and two thousand four hundred men, was sent out from New York and Norfolk, with orders from the authorities at Washington, to reenforce Fort Sumter peaceably, if permitted "but forcibly if they must."
- ↑ Frank L. Owsley, State Rights in the Confederacy (Chicago, 1925),
- ↑ Rable (1994) 257; however Wallace Hettle in The Peculiar Democracy: Southern Democrats in Peace and Civil War (2001) p. 158 says Owsley's "famous thesis...is overstated."
- ↑ John Moretta; "Pendleton Murrah and States Rights in Civil War Texas," Civil War History, Vol. 45, 1999
- ↑ Albert Burton Moore,Conscription and Conflict in the Confederacy. (1924) p. 295.
- ↑ Rable (1994) 258-9
- ↑ Rable (1994) p 265
- ↑ William Seward to Charles Francis Adams, April 10, 1861 in Marion Mills Miller, Ed. Life And Works Of Abraham Lincoln (1907) Vol 6.
- ↑ ibid
- ↑ Ervin L. Jordan, Jr. Black Confederates and Afro-Yankees in Civil War Virginia (1995)
- ↑ Eicher, Civil War High Commands
References
- Eicher, John H., & Eicher, David J., Civil War High Commands, Stanford University Press, 2001, ISBN 0-8047-3641-3.
- Wilentz, Sean, The Rise of American Democracy, W.W. Norton & Co., ISBN 0-393-32921-6.
Bibliography
- Current, Richard N., ed. Encyclopedia of the Confederacy (4 vol), 1993. 1900 pages, articles by scholars.
- Faust, Patricia L. ed, Historical Times Illustrated Encyclopedia of the Civil War, 1986.
- Heidler, David S., et al. Encyclopedia of the American Civil War : A Political, Social, and Military History, 2002. 2400 pages (ISBN 0-393-04758-X)
- Steven E. Woodworth, ed. The American Civil War: A Handbook of Literature and Research, 1996. 750 pages of historiography and bibliography
Economic & Social History
see Economy of the Confederate States of America
- Black, Robert C., III. The Railroads of the Confederacy, 1988.
- Clinton, Catherine, and Silber, Nina, eds. Divided Houses: Gender and the Civil War, 1992.
- Dabney, Virginius. Richmond: The Story of a City. Charlottesville: The University of Virginia Press, 1990. ISBN 0-8139-1274-1.
- Faust, Drew Gilpin. Mothers of Invention: Women of the Slaveholding South in the American Civil War, 1996.
- Faust, Drew Gilpin. The Creation of Confederate Nationalism: Ideology and Identity in the Civil War South, 1988.
- Grimsley, Mark. The Hard Hand of War: Union Military Policy toward Southern Civilians, 1861-1865, 1995.
- Lentz, Perry Carlton. Our Missing Epic: A Study in the Novels about the American Civil War, 1970.
- Massey, Mary Elizabeth. Bonnet Brigades: American Women and the Civil War, 1966.
- Massey, Mary Elizabeth. Refugee Life in the Confederacy, 1964.
- Rable, George C. Civil Wars: Women and the Crisis of Southern Nationalism, 1989.
- Ramsdell, Charles. Behind the Lines in the Southern Confederacy, 1994.
- Roark, James L. Masters without Slaves: Southern Planters in the Civil War and Reconstruction, 1977.
- Rubin, Anne Sarah. A Shattered Nation: The Rise and Fall of the Confederacy, 1861-1868, 2005. A cultural study of Confederates' self images.
- Thomas, Emory M. The Confederacy as a Revolutionary Experience, 1992.
- Wiley, Bell Irwin. Confederate Women, 1975.
- Wiley, Bell Irwin. The Plain People of the Confederacy, 1944.
- Woodward, C. Vann, ed. Mary Chesnut's Civil War, 1981.
Politics
- Alexander, Thomas B., and Beringer, Richard E. The Anatomy of the Confederate Congress: A Study of the Influences of Member Characteristics on Legislative Voting Behavior, 1861-1865, 1972.
- Boritt, Gabor S., et al, Why the Confederacy Lost, 1992.
- Cooper, William J, Jefferson Davis, American, 2000. Standard biography.
- Coulter, E. Merton. The Confederate States of America, 1861-1865, 1950.
- William C. Davis (2003). Look Away! A History of the Confederate States of America. New York: Free Press. ISBN 0-684-86585-8.
- Eaton, Clement. A History of the Southern Confederacy, 1954.
- Eckenrode, H. J., Jefferson Davis: President of the South, 1923.
- Gallgher, Gary W., The Confederate War, 1999.
- Neely, Mark E., Jr., Confederate Bastille: Jefferson Davis and Civil Liberties, 1993.
- Rembert, W. Patrick. Jefferson Davis and His Cabinet, 1944.
- Rable, George C., The Confederate Republic: A Revolution against Politics, 1994.
- Roland, Charles P. The Confederacy, 1960. brief
- Thomas, Emory M. Confederate Nation: 1861-1865, 1979. Standard political-economic-social history
- Wakelyn, Jon L. Biographical Dictionary of the Confederacy Greenwood Press ISBN 0-8371-6124-X
- Williams, William M. Justice in Grey: A History of the Judicial System of the Confederate States of America, 1941.
- Yearns, Wilfred Buck. The Confederate Congress, 1960.
Primary sources
- Carter, Susan B., ed. The Historical Statistics of the United States: Millennial Edition (5 vols), 2006.
- Davis, Jefferson, The Rise and Fall of the Confederate Government (2 vols), 1881.
- Harwell, Richard B., The Confederate Reader (1957)
- Jones, John B. A Rebel War Clerk's Diary at the Confederate States Capital, edited by Howard Swiggert, [1935] 1993. 2 vols.
- Richardson, James D., ed. A Compilation of the Messages and Papers of the Confederacy, Including the Diplomatic Correspondence 1861-1865, 2 volumes, 1906.
- Yearns, W. Buck and Barret, John G.,eds. North Carolina Civil War Documentary, 1980.
- Confederate official government documents major online collection of complete texts in HTML format, from U. of North Carolina
- Journal of the Congress of the Confederate States of America, 1861-1865 (7 vols), 1904. Available online at the Library of Congress [15]
External links
- Confederate offices Index of Politicians by Office Held or Sought
- Civil War Research & Discussion Group -*Confederate States of Am. Army and Navy Uniforms, 1861
- The Countryman, 1862-1866, published weekly by Turnwold, Ga., edited by J.A. Turner
- The Federal and the Confederate Constitution Compared
- The Making of the Confederate Constitution, by A. L. Hull, 1905.
- Photographic History of the Civil War, 10 vols., 1912.
- DocSouth: Documenting the American South - numerous online text, image, and audio collections.
- The Geographical Reader for the Dixie Children - a Confederacy textbook written in 1863.
- Confederate States of America: A Register of Its Records in the Library of Congress
ast:Estaos Confederaos d'América ca:Estats Confederats d'Amèrica da:Amerikas Konfødererede Stater de:Konföderierte Staaten von Amerika et:Ameerika Riikide Konföderatsioon es:Estados Confederados de América eo:Konfederaciitaj Ŝtatoj de Ameriko fr:États confédérés d'Amérique gl:Estados Confederados de América ko:남부동맹 hr:Konfederativne Države Amerike it:Stati Confederati d'America he:קונפדרציית המדינות של אמריקה nl:Geconfedereerde Staten van Amerika ja:アメリカ連合国 no:Amerikas konfødererte stater nn:Confederate States of America pl:Skonfederowane Stany Ameryki pt:Estados Confederados da América ro:Statele Confederate ale Americii ru:Конфедеративные Штаты Америки simple:Confederate States of America sr:Конфедеративне Америчке Државе fi:Etelävaltiot sv:Amerikas konfedererade stater zh:美利堅聯盟國