Optic chiasm: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Robert Badgett (New page: In anatomy, the '''optic chiasm''' is "the X-shaped structure formed by the meeting of the two optic nerves. At the optic chiasm the fibers from the medial part of each retina ...) |
imported>Bruce M. Tindall mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | |||
In [[anatomy]], the '''optic chiasm''' is "the X-shaped structure formed by the meeting of the two [[optic nerve]]s. At the optic chiasm the fibers from the medial part of each [[retina]] cross to project to the other side of the brain while the lateral retinal fibers continue on the same side. As a result each half of the brain receives information about the contralateral visual field from both eyes."<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref> | In [[anatomy]], the '''optic chiasm''' is "the X-shaped structure formed by the meeting of the two [[optic nerve]]s. At the optic chiasm the fibers from the medial part of each [[retina]] cross to project to the other side of the brain while the lateral retinal fibers continue on the same side. As a result each half of the brain receives information about the contralateral visual field from both eyes."<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref> | ||
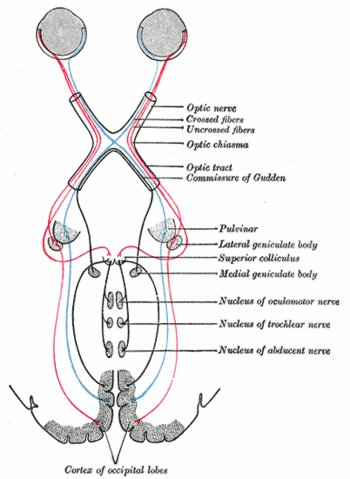
{{Image|Grays-image774.gif|right|350px|Scheme showing central connections of the [[optic nerve]]s and optic tracts.}} | {{Image|Grays-image774.gif|right|350px|Scheme showing central connections of the [[optic nerve]]s and optic tracts.}} | ||
Latest revision as of 17:31, 7 February 2009
In anatomy, the optic chiasm is "the X-shaped structure formed by the meeting of the two optic nerves. At the optic chiasm the fibers from the medial part of each retina cross to project to the other side of the brain while the lateral retinal fibers continue on the same side. As a result each half of the brain receives information about the contralateral visual field from both eyes."[1]

Scheme showing central connections of the optic nerves and optic tracts.
References
- ↑ Anonymous (2024), Optic chiasm (English). Medical Subject Headings. U.S. National Library of Medicine.