Raid on Osama bin Laden
On the night of May 1-2, 2011, United States forces conducted a direct action mission, flying from Afghanistan, to a compound in Abbotabad, Pakistan. Osama bin Laden was killed in the raid and his body, as well as computer storage devices and documents, were taken away. This article deals with the operational aspects and U.S. command authorization of the mission; the legality of the killing of Osama bin Laden is treated separately.
According to President Barack Obama, who personally authorized the raid under Presidential authority, operational control was given to the Central Intelligence Agency, with most of the uniformed force coming from the Joint Special Operations Command of the United States Special Operations Command. The assaulters were United States Navy SEALs.
Command
- See also: Command and control
The operation
Details of the force and tactics remain clouded. The raid was under the control of the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), with military personnel from the Joint Special Operations Command of which the Navy SEALs are assigned. CIA control does present some possible problems under U.S. law. [1]
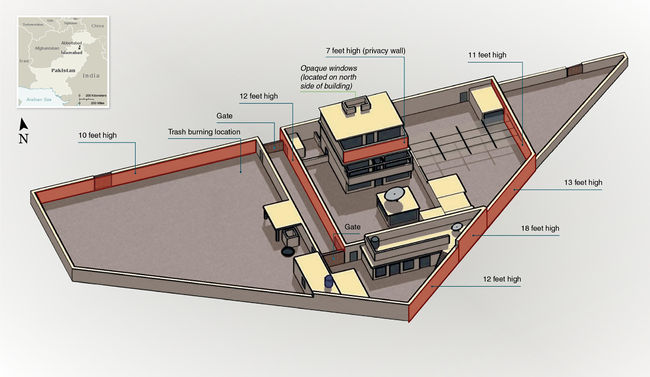
During the raid three of the four compound walls were breached by US Navy SEALs as they entered the compound. Upon entry they killed two al-Qaeda couriers along with an unidentified woman who was caught in the gunfire.[2] One of the helicopters developed mechanical difficulties, was later blown up to protect US assets, and the 25 personnel performed a "surgical raid" to limit collateral damage. One of the couriers killed was named Abu Ahmed al-Kuwaiti who some sources state was killed in the compound along with the unidentified woman with him. The Navy SEALs then entered the first floor of the compound where they killed an unidentified man and bin Laden's son who was using a staircase. The SEALs entered bin Laden's bedroom where they found him along with one of his wives. His wife was shot in the leg after she tried to "rush" the SEALs during the incident. Bin Laden was shot in the chest and head by an unidentified US Navy SEAL.[3]
Infiltration and exfiltration
The assault force flew from Bagram Airfield in Afghanistan, a busy facility from which U.S. Army special operations helicopters frequently fly, and
Helicopters
Aviation Week and Space Technology gave a preliminary report that two H-60 helicopter and two H-47 helicopters were seen flying over the compound. Specifically, the H-60's were the primary assault helicopters, and at least one was heavily modified with previously unknown stealth technology. "it appears to be a significantly modified version of a Sikorsky H-60 Black Hawk, although whether an MH-60K, L or M version is still unknown. The U.S. Army’s 160th Special Operations Aviation Regiment (Airborne), the Night Stalkers, uses all three types of MH-60s."[4] With 25 military personnel in the assault force, operating at a high altitude, the H-60's would have been operating near their maximum weight capability. Air temperature is also important, and Aviation Week quoted the chair of the House Armed Services Committee, Representative Buck McKeon "it was a miscalculation of temperature in and outside the compound. The Black Hawk ran into lift trouble due to a 15F difference inside the courtyard, 'They couldn’t hold the hover.'" The H-47 helicopters carried return fuel, backup assets, and recovered the personnel on the crashed H-60.
While the force attempted to destroy the crashed helicopter, part of the tail broke off on a wall, and was left relatively intact outside the compound wall. Unusual features observed on it, associated with stealth technology, include:[5]
- "The tail plane has a “flat coolie hat” cover over the centre area
- The stabiliser is not flat – it rises each side of the tail approx 15 degrees
- The stabiliser is swept
- The metal surfaces have an infra-red suppression finish similar to some V-22s"
References
- ↑ David Axe (6 May 2011), "Bin Laden killing in legal gray zone", Politico
- ↑ U.S. revises story on bin Laden's raid, offers more details. Retrieved on 2011-05-05.
- ↑ Only single bin Laden defender shot at SEALs. Retrieved on 2011-05-05.
- ↑ Bill Sweetman, Amy Butler (6 May 2011), "Bin Laden Raid Crash Helo Reveals Stealth", Aviation Week and Space Technology
- ↑ "Was Bin Laden casualty a stealth UH-60?", Helihub, 3 May 2011