Deaerator: Difference between revisions
imported>Milton Beychok m (→Oxygen scavengers: Added chemical formulas) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
A '''deaerator''' is a device that is widely used for the removal of air and other dissolved [[gas]]es from the feedwater to steam generating [[boiler]]s. In particular, dissolved [[oxygen]] in boiler feedwaters will cause serious corrosion damage in steam systems by attaching to the walls of metal piping and other metallic equipment and forming [[oxide]]s (rust). It also combines with any dissolved [[carbon dioxide]] to form carbonic acid that causes further corrosion. Most deaerators are designed to remove oxygen down to levels of 7 ppb by weight (0.0005 cm³/L) or less.<ref name=Spirax>[http://www.spiraxsarco.com/resources/steam-engineering-tutorials/the-boiler-house/pressurised-deaerators.asp#head5 Pressurized deaerators]</ref><ref>[http://www.termochimica.com/deaerator.html Deaerator Presentation]</ref> | A '''deaerator''' is a device that is widely used for the removal of air and other dissolved [[gas]]es from the feedwater to [[steam]] generating [[boiler]]s. In particular, dissolved [[oxygen]] in boiler feedwaters will cause serious corrosion damage in steam systems by attaching to the walls of metal piping and other metallic equipment and forming [[oxide]]s (rust). It also combines with any dissolved [[carbon dioxide]] to form [[carbonic acid]] that causes further corrosion. Most deaerators are designed to remove oxygen down to levels of 7 ppb by weight (0.0005 cm³/L) or less.<ref name=Spirax>[http://www.spiraxsarco.com/resources/steam-engineering-tutorials/the-boiler-house/pressurised-deaerators.asp#head5 Pressurized deaerators]</ref><ref>[http://www.termochimica.com/deaerator.html Deaerator Presentation]</ref> | ||
There are two basic types of deaerators, the tray-type and the spray-type:<ref name=Spirax/><ref>[http://www.stork-thermeq.nl/spraytype-deaerator-operating.aspx Spray-type Deaerator Operating Principal]</ref><ref>{{cite book|author=Robert Thurston Kent (Editor in Chief)|title=Kents’ Mechanical Engineers’ Handbook|edition=Eleventh edition (Two volumes)|publisher=John Wiley & Sons (Wiley Engineering Handbook Series)|year=1936|id=}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|author=Babcock & Wilcox Co.|title=Steam: Its Generation and Use|edition=41st edition|year=2005|id=ISBN 0-9634570-0-4}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|author=Thomas C. Elliott, Kao Chen, Robert Swanekamp (coauthors)|title=Standard Handbook of Powerplant Engineering|edition=2nd edition|publisher=McGraw-Hill Professional|year=1997|id=ISBN 0-07-019435-1}}</ref> | There are two basic types of deaerators, the tray-type and the spray-type:<ref name=Spirax/><ref>[http://www.stork-thermeq.nl/spraytype-deaerator-operating.aspx Spray-type Deaerator Operating Principal]</ref><ref>{{cite book|author=Robert Thurston Kent (Editor in Chief)|title=Kents’ Mechanical Engineers’ Handbook|edition=Eleventh edition (Two volumes)|publisher=John Wiley & Sons (Wiley Engineering Handbook Series)|year=1936|id=}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|author=Babcock & Wilcox Co.|title=Steam: Its Generation and Use|edition=41st edition|year=2005|id=ISBN 0-9634570-0-4}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|author=Thomas C. Elliott, Kao Chen, Robert Swanekamp (coauthors)|title=Standard Handbook of Powerplant Engineering|edition=2nd edition|publisher=McGraw-Hill Professional|year=1997|id=ISBN 0-07-019435-1}}</ref> | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
===Tray-type deaerator=== | ===Tray-type deaerator=== | ||
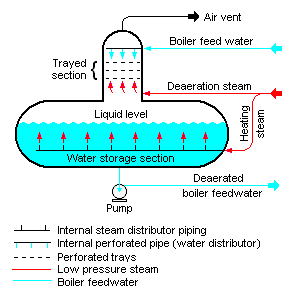
{{Image|Tray-type Deaerator.png|right|296px|Figure 1: A schematic diagram of a typical tray-type deaerator.}} | |||
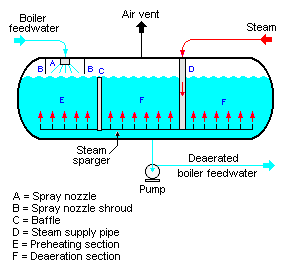
{{Image|Spray-type Deaerator.png|right|287px|Figure 2: A schematic diagram of a typical spray-type deaerator.}} | |||
The typical horizontal tray-type deaerator in Figure 1 has a vertical domed deaeration section mounted above a horizontal boiler feedwater storage vessel. Boiler feedwater enters the vertical | The typical horizontal tray-type deaerator in Figure 1 has a vertical domed deaeration section mounted above a horizontal boiler feedwater storage vessel. Boiler feedwater enters the vertical declaration section above the perforated trays and flows downward through the perforations. Low-pressure deaeration steam enters the below the perforated trays and flows upward through the perforations. Some designs use various types of [[Packed bed|packing]], rather than perforated trays, to provide good contact and mixing between the steam and the boiler feed water. | ||
The steam strips the dissolved gas from the boiler feedwater and exits via the vent at the top of the domed section. Some designs may include a vent condenser to trap and recover any water [[Entrainment (engineering)|entrained]] in the vented gas. The vent line usually includes a valve and just enough steam is allowed to escape with the vented gases to provide a small and visible telltale plume of steam. | The steam strips the dissolved gas from the boiler feedwater and exits via the vent at the top of the domed section. Some designs may include a vent [[Condenser (heat transfer)|condenser]] to trap and recover any water [[Entrainment (engineering)|entrained]] in the vented gas. The vent line usually includes a valve and just enough steam is allowed to escape with the vented gases to provide a small and visible telltale plume of steam. | ||
The deaerated waster flows down into the horizontal storage vessel from where it is pumped to the steam generating boiler system. Low-pressure heating steam, which enters the horizontal vessel through a ''sparger pipe'' in the bottom of the vessel, is provided to keep the stored boiler feedwater warm. External [[Thermal insulation|insulation]] of the vessel is typically provided to minimize heat loss. | The deaerated waster flows down into the horizontal storage vessel from where it is pumped to the steam generating boiler system. Low-pressure heating steam, which enters the horizontal vessel through a ''sparger pipe'' in the bottom of the vessel, is provided to keep the stored boiler feedwater warm. External [[Thermal insulation|insulation]] of the vessel is typically provided to minimize heat loss. | ||
== Spray-type deaerator == | == Spray-type deaerator == | ||
As shown in Figure 2, the typical spray-type deaerator is a horizontal vessel which has a preheating section (E) and a deaeration section (F). The two sections are separated by a baffle(C). Low-pressure steam enters the vessel through a sparger in the bottom of the vessel. | As shown in Figure 2, the typical spray-type deaerator is a horizontal vessel which has a preheating section (E) and a deaeration section (F). The two sections are separated by a baffle(C). Low-pressure steam enters the vessel through a sparger in the bottom of the vessel. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 29: | ||
The boiler feedwater is sprayed into section (E) where it is preheated by the rising steam from the sparger. The purpose of the feedwater spray nozzle (A) and the preheat section is to heat the boiler feedwater to its [[Boiling point#Saturation temperature and pressure|saturation temperature]] to facilitate stripping out the dissolved gases in the following deaeration section. | The boiler feedwater is sprayed into section (E) where it is preheated by the rising steam from the sparger. The purpose of the feedwater spray nozzle (A) and the preheat section is to heat the boiler feedwater to its [[Boiling point#Saturation temperature and pressure|saturation temperature]] to facilitate stripping out the dissolved gases in the following deaeration section. | ||
The preheated feedwater then flows into the | The preheated feedwater then flows into the deaeration section (F), where it is deaerated by the steam rising from the sparger system. The gases stripped out of the water exit via the vent at the top of the vessel. Again, some designs may include a vent condenser to trap and recover any water entrained in the vented gas. Also again, the vent line usually includes a valve and just enough steam is allowed to escape with the vented gases to provide a small and visible telltale plume of steam | ||
The deaerated boiler feedwater is pumped from the bottom of the vessel to the steam generating boiler system. | The deaerated boiler feedwater is pumped from the bottom of the vessel to the steam generating boiler system. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 39: | ||
== Oxygen scavengers == | == Oxygen scavengers == | ||
Oxygen scavenging chemicals are very often added to the deaerated boiler feedwater to remove any last traces of oxygen that were not removed by the deaerator. The most commonly used oxygen scavenger is [[sodium sulfite]] (Na<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>3</sub>). It is very effective and rapidly reacts with traces of oxygen to form [[sodium sulfate]] (Na<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub>). | Oxygen scavenging chemicals are very often added to the deaerated boiler feedwater to remove any last traces of oxygen that were not removed by the deaerator. The most commonly used oxygen scavenger is [[sodium sulfite]] (Na<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>3</sub>). It is very effective and rapidly reacts with traces of oxygen to form [[sodium sulfate]] (Na<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub>) which is non-scaling. | ||
Other scavengers include [[1,3-diaminourea]] (also known as carbohydrazide), [[diethylhydroxylamine]] (DEHA), [[nitriloacetic acid]] (NTA), [[ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid]] (EDTA), and [[hydroquinone]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:00, 5 August 2024
A deaerator is a device that is widely used for the removal of air and other dissolved gases from the feedwater to steam generating boilers. In particular, dissolved oxygen in boiler feedwaters will cause serious corrosion damage in steam systems by attaching to the walls of metal piping and other metallic equipment and forming oxides (rust). It also combines with any dissolved carbon dioxide to form carbonic acid that causes further corrosion. Most deaerators are designed to remove oxygen down to levels of 7 ppb by weight (0.0005 cm³/L) or less.[1][2]
There are two basic types of deaerators, the tray-type and the spray-type:[1][3][4][5][6]
- The tray-type (also called the cascade-type) includes a vertical domed deaeration section mounted on top of a horizontal cylindrical vessel which serves as the deaerated boiler feedwater storage tank.
- The spray-type consists only of a horizontal (or vertical) cylindrical vessel which serves as both the deaeration section and the boiler feedwater storage tank.
Types of deaerators
There are many different horizontal and vertical designs available from a number of manufacturers, and the actual construction details will vary from one manufacturer to another. Figures 1 and 2 are representative schematic diagrams that depict each of the two major types of deaerators.
Tray-type deaerator
The typical horizontal tray-type deaerator in Figure 1 has a vertical domed deaeration section mounted above a horizontal boiler feedwater storage vessel. Boiler feedwater enters the vertical declaration section above the perforated trays and flows downward through the perforations. Low-pressure deaeration steam enters the below the perforated trays and flows upward through the perforations. Some designs use various types of packing, rather than perforated trays, to provide good contact and mixing between the steam and the boiler feed water.
The steam strips the dissolved gas from the boiler feedwater and exits via the vent at the top of the domed section. Some designs may include a vent condenser to trap and recover any water entrained in the vented gas. The vent line usually includes a valve and just enough steam is allowed to escape with the vented gases to provide a small and visible telltale plume of steam.
The deaerated waster flows down into the horizontal storage vessel from where it is pumped to the steam generating boiler system. Low-pressure heating steam, which enters the horizontal vessel through a sparger pipe in the bottom of the vessel, is provided to keep the stored boiler feedwater warm. External insulation of the vessel is typically provided to minimize heat loss.
Spray-type deaerator
As shown in Figure 2, the typical spray-type deaerator is a horizontal vessel which has a preheating section (E) and a deaeration section (F). The two sections are separated by a baffle(C). Low-pressure steam enters the vessel through a sparger in the bottom of the vessel.
The boiler feedwater is sprayed into section (E) where it is preheated by the rising steam from the sparger. The purpose of the feedwater spray nozzle (A) and the preheat section is to heat the boiler feedwater to its saturation temperature to facilitate stripping out the dissolved gases in the following deaeration section.
The preheated feedwater then flows into the deaeration section (F), where it is deaerated by the steam rising from the sparger system. The gases stripped out of the water exit via the vent at the top of the vessel. Again, some designs may include a vent condenser to trap and recover any water entrained in the vented gas. Also again, the vent line usually includes a valve and just enough steam is allowed to escape with the vented gases to provide a small and visible telltale plume of steam
The deaerated boiler feedwater is pumped from the bottom of the vessel to the steam generating boiler system.
Deaeration steam
The deaerators in the steam generating systems of most thermal power plants use low pressure steam obtained from an extraction point in their steam turbine system. However, the steam generators in many large industrial facilities such as petroleum refineries may use whatever low-pressure steam that is available.
Oxygen scavengers
Oxygen scavenging chemicals are very often added to the deaerated boiler feedwater to remove any last traces of oxygen that were not removed by the deaerator. The most commonly used oxygen scavenger is sodium sulfite (Na2SO3). It is very effective and rapidly reacts with traces of oxygen to form sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) which is non-scaling.
Other scavengers include 1,3-diaminourea (also known as carbohydrazide), diethylhydroxylamine (DEHA), nitriloacetic acid (NTA), ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and hydroquinone.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Pressurized deaerators
- ↑ Deaerator Presentation
- ↑ Spray-type Deaerator Operating Principal
- ↑ Robert Thurston Kent (Editor in Chief) (1936). Kents’ Mechanical Engineers’ Handbook, Eleventh edition (Two volumes). John Wiley & Sons (Wiley Engineering Handbook Series).
- ↑ Babcock & Wilcox Co. (2005). Steam: Its Generation and Use, 41st edition. ISBN 0-9634570-0-4.
- ↑ Thomas C. Elliott, Kao Chen, Robert Swanekamp (coauthors) (1997). Standard Handbook of Powerplant Engineering, 2nd edition. McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 0-07-019435-1.