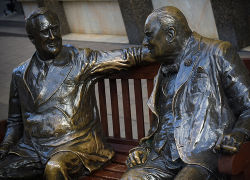Winston Churchill: Difference between revisions
imported>John Leach (British date convention applies: i.e., ddmmccyy with no commas) |
imported>John Leach (this needs to be thoroughly reviewed, then revised and restructured with sub-articles – all based on much better sources) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TOC|right}} | {{TOC|right}} | ||
[[Image:Winstonchurchill.jpg|250px|thumb|left|Winston Churchill]] | [[Image:Winstonchurchill.jpg|250px|thumb|left|Winston Churchill]] | ||
Revision as of 13:22, 7 October 2019
Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 1874 – 24 January 1965) was a leading statesman of the 20th century, best known as the prime minister who led Britain to victory over Nazi Germany in World War II. He was awarded a Nobel Prize in Literature as a military historian for his account of World War II. Knighted in 1953 with the Order of the Garter, he was voted the greatest-ever Briton in a 2002 BBC poll, 100 Greatest Britons.[1]
Churchill was a younger son of an aristocratic family. Educated at Harrow and Sandhurst, he became an officer in the British Army, gaining early fame for his war reporting from the Sudan and the Second Boer War. Entering politics in 1900 as a Conservative, he switched to the Liberal Party in 1906 and soon became a senior figure, and sponsored social reform legislation to end sweatshops and reduce unemployment. During World War I, Churchill was most prominent as civilian head of the Royal Navy (his title was First Lord of the Admiralty), where he planned the failed attack on Turkey in the Gallipoli Campaign. He served in the important roles of Minister of Munitions, 1917-1918 and for War (1918-21). He lost his seat in Parliament in the general election of 1922 but returned in 1924 as a Conservative and became Chancellor of the Exchequer (1924-29). Out of political office in the 1930s, he was a lone voice warning against Hitler and the Nazis, denouncing appeasement and calling for re-armament in preparation for war with Germany.
After the outbreak of the Second World War, Churchill returned to power as the First Lord of the Admiralty. After the resignation of Neville Chamberlain in May 1940, Churchill became Prime Minister in an all-party coalition government with Labour and the Liberals. Churchill was indefatigable in leading the British war effort against Germany; his speeches were an inspiration to the embattled British. He forged a close relationship with American President Franklin D. Roosevelt starting in 1940. Aboard the Royal Navy battleship HMS Prince of Wales, they proclaimed the "Atlantic Charter" in 1941. The U.S. became the "Arsenal of Democracy," sending munitions to Britain starting in 1940. Britain in turn sent munitions to Russia, as Churchill forged a treaty with Stalin. Europe was the centre of his attention, as the Australians complained about his neglect of their interests (and turned to the U.S. for protection). Recalling the death tolls of 1914-1918, Chuurchill was reluctant to invade France, proposing instead invasions of North Africa and Italy (which took place in 1942-43) and the Balkans (which did not happen). He strongly supported the strategic air campaign that bombed enemy cities, railyards and oil refineries. He worked well with Dwight D. Eisenhower, the American general in overall command of the invasion of France that was launched successfully in June 1944. Despite complaints by senior generals and admirals that Churchill interfered too much in military matters, he was successful in balancing the economic, manpower, diplomatic, psychological and military dimensions of the war.
After losing the 1945 general election, Churchill became the Leader of the Opposition. In 1951, despite the obvious frailties of his advanced age, he again became Prime Minister before finally retiring in 1955. His six volume history of the war, shaped the work of most subsequent historians. His state funeral saw one of the largest assemblies of statesmen in the world.
Early life
Churchill was born in Blenheim Palace, the palace of the dukes of Marlborough, in Woodstock, Oxfordshire. He was a younger son of the senior branch of the Spencer family, which added the surname "Churchill" to its own in the late 18th century. Churchill was a descendant of the second member of the Churchill family to achieve public prominence, John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough. His father, Lord Randolph Churchill (1849–1895) was a prominent Conservative politician. He married Jennie Jerome (1854–1921), the daughter of American millionaire Leonard Jerome. The parents' marriage faltered, in part because of Lord Randolph's syphilis; Lady Randolph became notorious for her romantic attachments, becoming known as "Lady Jane Snatcher." She liked Winston, but largely ignored him.[2] Churchill rarely spoke with his father, who served as Secretary of state for India, Leader of the House and Chancellor of the Exchequer; he died when Winston was 21. Winston systematically adopted his father's ideas and political positions, and became well known in political circles. He idealized his always-absent mother. "She shone for me like the Evening Star," Churchill later wrote. "I loved her dearly—but at a distance." [3]
He entered Harrow School in 1888 with a track for the Army. Churchill had an independent and rebellious nature; his grades were poor apart from English and history; he avoided team sports but was a fencing champion. His father did not think he was smart enough for Oxford, so he went to the military academy at Sandhurst in 1893. There, he excelled at tactics, fortifications and horsemanship, graduating twentieth out of a class of 130 in 1894; he was commissioned as a Second Lieutenant cavalry officer in the 4th Queen's Own Hussars, where he excelled at polo.
The Army
India
Posted to Bangalore, India, in 1896, he ignored local conditions. His duties were done well before noon; apart from polo he did not socialize with his peers, who considered the slender, short, highly ambitious young man to be pushy, bumptious and not a proper gentleman.[4] Churchill became an intellectual, as he immersed himself in the classics, devouring the works of Adam Smith, Gibbon, Macaulay, Hallam, Lecky, and Darwin. He carefully studied the parliamentary debates of the 1870s to 1890s, adding to them his own imaginary speeches. He never learned Latin or Greek so he fashioned a prose style modeled on the two finest writers among English historians, Gibbon and Macaulay. A book on the evolution of civilization that ridiculed Christianity[5] led to his loss of religious faith; he believed in evolution and the inevitability of progress.
Between 1897 and 1900, with the aid of his mother's lobbying in London, Churchill fought in three imperial wars while doubling as a war correspondent and writing three books. In 1897 he joined three brigades in fighting a Pathan tribe. His lively account of the skirmishes proved he could write for the popular press; he received £5 per column from the Daily Telegraph and soon became the highest paid war correspondent in the world.
In late 1899 Churchill went to South Africa as a war correspondent to cover the Second Boer War; his salary was a remarkable £250 per month plus expenses. Caught in an ambush, Churchill was captured and held in a POW camp in Pretoria; he escaped--an adventure that made him a minor national hero. He rejoined General Redvers Buller's army on its march to relieve Ladysmith and take Pretoria. Churchill was one of the first British troops into Ladysmith and Pretoria. In 1900, he published two books on the Boer war, London to Ladysmith via Pretoria [6] and Ian Hamilton's March [7]
Churchill's mother used her connections with the prince of Wales to get the her son assigned to the force commanded by Lord Kitchener for the reconquest of the Sudan. Churchill arrived just in time to join the cavalry charge at the battle of Omdurman (2 September 1898), in which his regiment galloped by accident into a ravine crammed with armed men. Churchill, who shot and killed at least three of the enemy, was cool, courageous and lucky.[8] The Morning Post ran his stories, and the public snatched up his two-volume The River War: An Account of the Reconquest of the Sudan (1899)[9]. It displayed a remarkably sympathetic history of the Sudanese revolt against Egyptian rule. A speaking tour of Britain, the U.S. and Canada in 1900 netted £10,000, proving the funding he needed for a political-literary career.[10]
Early years in Parliament
Churchill now had a national reputation and plunged into politics. Calling himself as a "Tory democrat" like his father, he stood as a Conservative candidate in Oldham in a by-election. He lost first time but in the 1900 general election, (called "the Khaki election"), he was elected. His maiden speech was a plea for magnanimity toward the Boers (which was granted). He helped form a group of Tory dissidents led by Lord Hugh Cecil called the "Hughligans". Churchill as a military man drew attention when he spoke out against the government's extravagant military expenditure. He opposed the "tariff reform" (high tariff) platform of Liberal Unionist Joseph Chamberlain, who was in coalition with the Conservatives. Churchill stood for free trade and no tariffs. In 1904, disgusted with the Conservatives, he "crossed the floor" to sit as a member of the Liberal Party. He attacked his erstwhile Conservative colleagues relentlessly; they bitterly denounced him as a turncoat. As a Liberal, he continued to campaign for free trade and won the seat of Manchester North West.
Ministerial office
Growing prominence
When the Liberals took office, with Henry Campbell-Bannerman as Prime Minister, in December 1905, Churchill became Under-Secretary of State for the Colonies; dealing with the adoption of constitutions for the defeated Boer republics of the Transvaal and Orange River Colony and with the issue of 'Chinese slavery' in South African mines. He also became a prominent spokesman on free trade.
When Herbert Henry Asquith became Prime Minister in 1908, Churchill was promoted to the Cabinet as [[President of the Board of Trade. Working closely with David Lloyd George he helped pass major social welfare legislation, called the "New Liberalism.". Churchill focused on the "Trade Boards Bill," a scheme to end the sweatshops in the garment industry; on labour exchanges, designed to reduce unemployment by making job searches easier; and unemployment insurance for 3 million workers in cyclical industries. He supported Lloyd George's highly controversial "People's Budget" of 1909-10 (with spending increase of 11% and multiple tax increases that especially targeted rich landowners), even as it caused a constitutional crisis with the House of Lords.[11] Churchill denied that war with Germany was a threat and opposed the tripling of the warship budget proposed by the Admiralty.[12] Churchill generally was on the winning side, though he was beaten on the warships.[13]
In 1910, Churchill was promoted to Home Secretary. Regarding a dispute at the Cambrian Colliery mine in Tonypandy, initially, Churchill blocked the use of troops fearing a repeat of the 1887 "bloody Sunday" in Trafalgar Square. Nevertheless, troops were deployed to protect the mines and to avoid riots when thirteen strikers were tried for minor offences, an action that broke the tradition of not involving the military in civil affairs and led to lingering dislike for Churchill in Wales.
First Lord of the Admiralty
In 1911, Churchill became First Lord of the Admiralty, a post he held into World War I. He gave impetus to reform efforts, including development of naval aviation, tanks, and the switch in fuel from coal to oil.
He promoted the development of tanks, hoping they would break through trenches, barbed wire and machine gun fire.
In 1915, Churchill was the chief promoter of the strategy of the Dardanelles Campaign, including the Battle of Gallipoli, which failed miserably. He took much of the blame for the fiasco, and when Prime Minister Asquith formed an all-party coalition government, the Conservatives demanded Churchill's demotion as the price for entry. For several months Churchill served as "Chancellor of the Duchy of Lancaster", before resigning from the government. He rejoined the army, though remaining an MP, and served for several months on the Western Front commanding the 6th Battalion of the Royal Scots Fusiliers.
Return to power
In December 1916, Asquith resigned as Prime Minister and was replaced by David Lloyd George. The time was thought not yet right to risk the Conservatives' wrath by bringing Churchill back into government. However, in July 1917, Churchill was appointed Minister of Munitions, and in January 1919, Secretary of State for War and Secretary of State for Air. He was the main architect of the "Ten Year Rule," but the major preoccupation of his tenure in the War Office was the Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War. Churchill was a staunch advocate of foreign intervention, declaring that Bolshevism must be "strangled in its cradle". He secured, from a divided and loosely organised Cabinet, intensification and prolongation of the British involvement beyond the wishes of any major group in Parliament or the nation — and in the face of the bitter hostility of Labour. In 1920, after the last British forces had been withdrawn, Churchill was instrumental in having arms sent to the Poles when they invaded Ukraine.
He became Secretary of State for the Colonies in 1921 and was a signatory of the Anglo-Irish Treaty of 1921, which established the Irish Free State. Churchill always disliked Éamon de Valera, the Sinn Féin leader. Churchill, to protect British maritime interests engineered the Irish Free State agreement to include three "Treaty Ports" which could be used as Atlantic bases by the Royal Navy.[14]
As Colonial Secretary he advocated the use of poison gas against tribesmen revolting in what was soon to become Iraq. He did however set up a Middle East Department of the Colonial Office and under the instigation of T E Lawrence he supported the claims of Feisal and Abdullah as Kings of Iraq and Jordan respectively,[15]
Career between the wars
Second crossing of the floor
In 1920, as Secretary for War and Air, Churchill had responsibility for using air power to quell the rebellion of Kurds and Arabs in British-occupied Iraq.
With the 1922 election looming, Churchill's Liberal Party was internally split. He lost badly, and lost again (as a Liberal) in 1923 and as an independent in a by-election. Running in 1924 as a "Constitutionalist" with Conservative backing, he was elected to represent Epping. In 1925, he formally rejoined the Conservative Party, commenting wryly that "Anyone can rat [change parties], but it takes a certain ingenuity to re-rat."
Chancellor of the Exchequer
He was appointed Chancellor of the Exchequer in 1924 under Stanley Baldwin and oversaw Britain's disastrous return to the Gold Standard, which resulted in deflation, unemployment, and the miners' strike that led to the General Strike of 1926. This decision prompted the economist John Maynard Keynes to write The Economic Consequences of Mr. Churchill, arguing that the return to the gold standard at the pre-war parity in 1925 (£1=$4.86) would lead to a world depression. [16] During the "General Strike of 1926", Churchill helped break the strike arguing that "either the country will break the General Strike, or the General Strike will break the country."
Political isolation
The Conservative government was defeated in the 1929 General Election. In the next two years, Churchill became estranged from the Conservative leadership over the issues of protective tariffs and Indian Home Rule, which he bitterly opposed. When Ramsay MacDonald formed the National Government in 1931, Churchill was not invited to join the Cabinet. He was now at the low point in his career, in a period known as "the wilderness years".
He spent much of the next few years concentrating on his writing, including Marlborough: His Life and Times — a biography of his ancestor and A History of the English Speaking Peoples (which was not published until after World War II). When struck by a taxi he wrote an article about the experience. He supported himself largely by his writing and lectures and was one of the best paid writers of his time.
His military experience in India led him to vigorously oppose the granting of independence to India. He denigrated the Indian leader Mahatma Gandhi, as "a half-naked fakir."[17] He helped found the India Defence League a group dedicated to the preservation of British power in India. He warned of widespread unemployment in Britain and civil strife in India should independence be granted to India.[18]
Churchill was always an indefatigable advocate and actor of Anglo-American cooperation, with the constant argument that this policy was in the best interest of Britain. His mother was an American, and he made 16 trips to the U.S., at first for lectures and book promotions. He summed up his sense of two kindred nations in his 4-colume History of the English Speaking Peoples, written mostly in the 1930s, but lamented they had failed to cooperate stop the rise of Hitler. He made the theme of the first volume of his World War II history, "How the English-speaking Peoples through their Unwisdom, Carelessness and Good Nature allowed the Wicked to Rearm."[19]
By the mid 1930s Churchill started warning against Adolf Hitler and the dangers of Germany's rearmament. Churchill was a fierce critic of Neville Chamberlain's appeasement of Hitler, leading the wing of the Conservative Party that opposed the Munich Agreement which Chamberlain famously declared to mean "peace in our time". He was also an outspoken supporter of King Edward VIII during the Abdication Crisis, leading to some speculation that he might be appointed Prime Minister if the King refused to take Baldwin's advice and consequently the government resigned. However, this did not happen, and Churchill found himself politically isolated and bruised for some time after this.
Role as wartime Prime Minister
"Winston is back"
After the outbreak of World War II Churchill was appointed First Lord of the Admiralty and a member of the 5-man War Cabinet. The Navy sent out the signal: "Winston is back." In this job, he proved to be one of the highest-profile ministers during the so-called "Phony War", when the only noticeable action was at sea. Churchill advocated dangerous policies, including sending a battle fleet into the Baltic, and mining the Norwegian harbors through which Swedish iron ore was shipped to Germany. The Norwegian intervention was attempted but was upstaged by the Germans, who forced the British to retreat from Norway.
On 10 May 1940, (hours before the German invasion of France), it became clear that following repeated failures, the nation had lost confidence in Chamberlain's prosecution of the war and so Chamberlain resigned. The only alternative to Churchill was Lord Halifax, the foreign minister, who did not want the job and who favoured peace negotiations with a much stronger Germany. Churchill did want it and won the approval of Labour and the Liberals, who agreed with him that Britain must fight on.
When the Germans moved west in May 1940 there were 144 Allied divisions on the Western Front: 104 were French, 22 Belgian, 10 British, and eight Dutch. The British had not yet mobilized their manpower and hurriedly retreated when the French army was split in half and crumbled. At the end of May 250,000 British troops and 100,000 French were withdrawn through Dunkirk, leaving all their equipment and arms behind. The Allies had been decisively defeated. France signed an armistice making the new regime, called "Vichy France," in effect an ally of the Germans, albeit neutral. Churchill, fearing the Germans would acquire the French fleet, destroyed the main units at Oran on July 3. At the same time the "special relationship" with Roosevelt started paying off as the first major shipments of weapons arrived from the U.S., including 500,000 rifles and 80,000 machine guns. In September the unofficial American ally gave Churchill 50 destroyers to help hunt U-boats.[20]
Battle of Britain
The Battle of Britain began in August, as German light and medium bombers attacked British airfields, and U-boats attacked shipping. The first critical "secret weapon" of the war, radar, now went into operation, allowing the Royal Air Force (RAF) to parry the attacks. When Churchill ordered the bombing of Berlin, the Germans fell into the trap by retaliating with a "Blitz" of air raids against London and other cities. Attacking civilians instead of the RAF was a fatal mistake for the Luftwaffe, as the RAF replaced its losses and the Luftwaffe grew weaker and eventually abandoned the air attack.
While its details had to stay secret at the time, and even after the war, in his history of the war, Churchill paid tribute to the electronic intelligence and electronic countermeasures that defeated the German navigation systems used to guide their bombers at night: the "Wizard War", or the "Battle of the Beams".
"During the human struggle between the British and the German Air Forces, between pilot and pilot, between AAA batteries and aircraft, between ruthless bombing and fortitude of the British people, another conflict was going on, step by step, month by month. This was a secret war, whose battles were lost or won unknown to the public, and only with difficulty comprehended, even now, to those outside the small scientific circles concerned. Unless British science had proven superior to German, and unless its strange, sinister resources had been brought to bear in the struggle for survival, we might well have been defeated, and defeated, destroyed." — Winston Churchill[21]
Fears of an invasion across the English Channel faded – the risk was small as long as the Royal Navy controlled the seas.
As American munitions poured in, the British credit of $6.5 billion evaporated; Roosevelt solved that crisis in spring 1941 with "Lend Lease," whereby $50 billion in munitions and supplies were given to the Allies, primarily Britain, in 1941-45.
Churchill's rejected the Halifax proposal to negotiate when Germany had the upper hand. Churchill rallied public opinion and kept democracy alive in Britain. The long-term goal was to turn Britain into the platform for the supply of Soviet Russia and the liberation of Western Europe.
Churchill created and took the additional position of Minister of Defence. He immediately put his friend and confidant, the industrialist and newspaper baron Lord Beaverbrook, in charge of aircraft production. It was Beaverbrook's business acumen that allowed Britain to quickly gear up aircraft production and engineering that by 1942 gave the Allies a better air force than the Luftwaffe.
Churchill's speeches proved a profound inspiration to the embattled British. His first speech as Prime Minister said
"I have nothing to offer but blood, toil, tears, and sweat" speech. Later he pledged, "We shall defend our island, whatever the cost may be, we shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight on the landing grounds, we shall fight in the fields and in the streets, we shall fight in the hills; we shall never surrender." "Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves that, if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, 'This was their finest hour.' "
At the height of the Battle of Britain, his bracing survey of the situation included the memorable line "Never in the field of human conflict was so much owed by so many to so few."On 10 November 1942 Churchill perceptively concluded:
"This is not the end. It is not even the beginning of the end. But it is, perhaps, the end of the beginning."
"Rhetorical power," wrote Churchill, "is neither wholly bestowed, nor wholly acquired, but cultivated."
Relations with the United States
Churchill had 12 strategic conferences with Roosevelt which covered the Atlantic Charter, the "Europe First" strategy, the "Declaration by the United Nations" and other war policies. Churchill initiated the Special Operations Executive (SOE) under Hugh Dalton's Ministry of Economic Warfare, which ran subversive and partisan operations in occupied Europe with notable success. He created the Commandos, setting the pattern for most of the world's current Special Forces.
Churchill's health suffered, as shown by a mild heart attack he suffered in December 1941 at the White House and also in December 1943 when he contracted pneumonia. Despite this, he travelled over 100,000 miles throughout the war to meet other national leaders.
Postwar plans
Churchill was party to treaties that would redraw post-World War II European and Asian boundaries. These were discussed as early as 1943. Proposals for European boundaries and settlements were officially agreed to by Harry S. Truman, Churchill, and Stalin at Potsdam. At the second Quebec Conference in 1944 he drafted and together with U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt signed a toned down version of the original Morgenthau Plan, where they pledged to convert Germany after its unconditional surrender "into a country primarily agricultural and pastoral in its character."[22]
Relations with the Soviet Union
The settlement concerning the borders of Poland, that is, the Curzon line (boundary between Poland and the Soviet Union) and the Oder-Neisse line (between Germany and Poland) upset the Polish government in exile in London. Churchill was convinced that the only way to alleviate tensions between the two populations was the transfer of people, to match the national borders.
After World War II
Although the importance of Churchill's role in World War II was undeniable, his domestic positions were unpopular. he had many enemies in his own country. His expressed contempt for a number of popular ideas, in particular public health care and expanded schooling. better education for the majority of the population, hurt his standing. During the opening broadcast of the election campaign Churchill astonished many of his admirers by warning that a Labour government would introduce into Britain "some form of Gestapo, no doubt humanely administered in the first instance". Churchill had been genuinely worried during the war by the inroads of state bureaucracy into civil liberty, and was clearly influenced by Friedrich Hayek's anti-totalitarian tract, The Road to Serfdom (1944). Churchill and his party were surprised by a landslide defeat in the 1945 election. British voters believed that the man who had led the nation so well in war was not the best man to lead it in peace. It was a reaction not against Churchill personally, but against the Conservative Party's record in the 1930s under Baldwin and Chamberlain.
Out of power, Churchill was an early supporter of the pan-Europeanism that eventually led to the formation of the European Common Market and later the European Union (for which one of the three main buildings of the European Parliament is named in his honour).
Churchill pushed the U.S. into realization that Soviet Communism was an aggressive threat. In a major speech in Missouri, on 5 March 1946, he declared:
- From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an Iron Curtain has descended across the continent. Behind that line lie all the capitals of the ancient states of Central and Eastern Europe. Warsaw, Berlin, Prague, Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade, Bucharest and Sofia, all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must call the Soviet sphere.
His history of World War II, appearing in 6 large volumes (1948-1953), was a publishing sensation and best-seller in many countries; it was translated into 18 languages. It solidified his identification with the war, and his interpretation of what happened. When it was written, however, the critical ULTRA program of communications intelligence was highly classified, and his writings sometimes need to be re-evaluated given the reality that he knew the Germans' secret thoughts.
Second term
After Labour's defeat in the General Election of 1951, Churchill again became Prime Minister, serving until his resignation in 1955. He renewed the "special relationship" between Britain and the United States, and engaged himself in the formation of the post-war order. On racial questions, Churchill was still a late Victorian. He tried in vain to manoeuvre the cabinet into restricting West Indian immigration. "Keep England White" was a good slogan, he told the cabinet in January 1955.[23]
A series of foreign policy crises were partly the result of the continued decline of British military and imperial prestige and power. Being a strong proponent of Britain as an international power, Churchill would often meet such moments with direct action. Trying to retain what he could of the Empire, he once stated that, "I will not preside over a dismemberment."
Quelling rebellions in Kenya and Malaya
In 1952, the Mau Mau rebellion led to a crisis in Kenya; Churchill sent in British troops to deal with the rebellion. As both sides increased the ferocity of their attacks, the country moved to full-scale civil war. In 1953, the Lari massacre, perpetrated by Mau-Mau insurgents against Kikuyu loyal to the British, damaged the rebels' prestige. Churchill's strategy was to use a military stick combined with implementing many of the concessions that Attlee's government had blocked in 1951. He ordered an increased military presence that implemented Operation Anvil in 1954; it broke the back of the rebellion in the city of Nairobi. Operation Hammer, in turn, was designed to root out rebels in the countryside. Churchill ordered peace talks opened, but these collapsed shortly after his leaving office.
In Malaya, a rebellion based on Communist and Chinese elements, had been in progress since 1948. Once again, Churchill's government inherited a crisis, and once again Churchill chose to use direct military action against those in rebellion while attempting to build an alliance with those who were not. He stepped up the implementation of a "hearts and minds" campaign and approved the creation of fortified villages, a tactic that would become a recurring part of Western military strategy in South-east Asia, but was less successful in the American Vietnam War.
The "Malayan Emergency" was a more direct case of a guerrilla movement, centred in the Chinese community and backed by the Soviet Union. As such, Britain's policy of direct confrontation and military victory had a great deal more support than in Iran or in Kenya. At the highpoint of the conflict, over 35,500 British troops were stationed in Malaya. As the rebellion lost ground, it began to lose favour with the local population. While the rebellion was slowly being defeated, it was equally clear that colonial rule from Britain was no longer plausible. In 1953, plans were drawn up for independence for Singapore and the other crown colonies in the region. The first elections were held in 1955, just days before Churchill's own resignation.
Family and personal life
On 12 September 1908, Churchill married Clementine Hozier, granddaughter of the 7th Earl of Airlie. They had five children: Diana; Randolph; Sarah; Marigold]] (1918–21); and Mary. Churchill's son Randolph and his grandsons Parliament. When not in London, Churchill usually lived at his beloved Chartwell House in Kent, two miles south of Westerham. He and his wife bought the house in 1922 and lived there until his death in 1965. During his Chartwell stays, he enjoyed writing as well as painting, bricklaying, and admiring the estate's famous black swans.
As a painter he was prolific, with over 570 paintings and two sculptures; he received a Diploma from the Royal Academy of London. Like many politicians of his age, Churchill was a member of several English gentlemen's clubs; he spent relatively little time in each of these, and preferred to conduct any lunchtime or dinner meetings at the Savoy Grill or the Ritz hotel, or else in the Members' Dining Room of the House of Commons when meeting other MPs.
Churchill's fondness for alcohol is well-documented. He consumed alcoholic drinks on a near-daily basis for long periods in his life, often before, after, and during meals. He is not generally considered by historians to have been an alcoholic.
- For much of his life, Churchill battled with depression (or perhaps a sub-type of manic-depression), which he called his black dog.[24]
- On becoming First Lord of the Admiralty, he immediately became close to Nelson, the resident black cat, who joined him at conferences, and moved with him to 10 Downing Street.[25]
- Churchill was recognised for his trademark cigar, suit with bow tie and his red hair, (which became sandy as he grew older).
Last days
Aware that he was slowing down both physically and mentally; he suffered a stroke in June 1953, when he was 78. Churchill retired as Prime Minister in 1955 and was succeeded by Anthony Eden, who had long been his ambitious protégé (three years earlier, Eden had married Churchill's niece). Churchill declined a dukedom to stay in the House, sometimes voting in parliamentary divisions, but never again speaking there. In 1959, he became Father of the House, the MP with the longest continuous service. Churchill spent most of his retirement at Chartwell House in Kent.
Churchill's final years were melancholy. He never resolved the love–hate relationship between himself and his son. Sarah was descending into alcoholism and Diana committed suicide in the autumn of 1964. Churchill himself suffered a number of minor strokes. It was a figure ravaged by age and sorrow who appeared at the window of his London home, 28 Hyde Park Gate, to greet the photographers on his ninetieth birthday in November 1964.
On 15 January 1965, Churchill suffered another stroke — a severe cerebral thrombosis; he died at his home nine days later, at age 90. His body lay in state for three days and a state funeral service was held at St Paul's Cathedral. This was the first state funeral for a non-royal family member since 1914, and no other of its kind has been held since. He was buried in the family plot at St Martin's Church, Bladon, near Woodstock, not far from his birthplace at Blenheim. Churchill's estate was probated at £304,044.
Churchill as historian
Churchill wrote Lord Randolph Churchill, a two-volume biography of his father which was published in 1906 and received much critical acclaim. Some historians suggest Churchill used the book in part to vindicate his own career and in particular to justify crossing the floor.[26] Later, he wrote Marlborough: His Life and Times[27][28], a biography of an earlier ancestor.
Churchill, himself the son of a British father and American mother, was a staunch advocate of the role of "the Dominions" in the Empire, and of the "special relationship" between the US and the UK. He had close personal and working relationships with a number of leaders of other English-speaking countries, notably Franklin Roosevelt of the US and Jan Smuts in South Africa. His four-volume History of the English-Speaking Peoples reflects this attitude.
His The World Crisis (six volumes, 1923–31) was a broad-scale history of the First World War, with Churchill never far offstage. His greatest work was The Second World War (six volumes, 1948–53), using secret papers not available to other for many years; he did not reveal the prime secret of breaking the German codes (which was revealed in the early 1970s). Churchill's highly detailed narrative structured much of the historiography for the first decade or two after the war, especially in his analysis and denunciation of the appeasement policy of the late 1930s.[29]
Notes
- ↑ Poll of the 100 Greatest Britons.
- ↑ . H. L. Le May, "Churchill, Jeanette (Lady Randolph Churchill) (1854–1921)", Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, 2004; online
- ↑ Jenkins, p. 8
- ↑ In 1902 the intellectual Beatrice Webb found him "egotistical, bumptious, shallow-minded and reactionary, but with a certain personal magnetism, great pluck and some originality, not of intellect but of character. More of the American speculator than the English aristocrat." Jenkins, p. 148
- ↑ Winwood Reade Martyrdom of Man (1872)
- ↑ London to Ladysmith via Pretoria online at [1]
- ↑ Ian Hamilton's March online at [2].
- ↑ Over 30,000 Sudanese were killed, compared with 28 British soldiers.
- ↑ online at [3]
- ↑ Churchill met Theodore Roosevelt; they resembled each other in many ways but never became friends.
- ↑ Jenkins, 157-66; Bruce K. Murray, "The Politics of the 'People's Budget'" The Historical Journal, Vol. 16, No. 3 (Sep., 1973), pp. 555-570 in JSTOR
- ↑ Jenkins 154-56
- ↑ Jenkins, ch 8
- ↑ In 1938 the bases were returned to Éire and were not available in World War II.
- ↑ James p172
- ↑ James p206
- ↑ Jenkins (2001) p. 436
- ↑ James p 257-60
- ↑ Gilbert (2005)
- ↑ In the "destroyer deal", the Americans received leases of naval and air bases on islands from Trinidad to Newfoundland.
- ↑ Churchill, Winston (2005). The Second World War, Volume 2: Their Finest Hour. Penguin Books Ltd. ISBN 0141441739.
- ↑ Michael R. Beschloss, (2002) The Conquerors’’ p. 131
- ↑ Hennessy, p. 205
- ↑ Black Dog, PBS.
- ↑ Michael Korda, Margaret Korda (2005), Cat People, HarperCollins, ISBN 0060756632, p. 12
- ↑ James, Churchill a study in failure p34-35
- ↑ Churchill, Winston. Marlborough: His Life and Times, Bk. 1, vols. i & ii. University of Chicago Press, (2002). ISBN 0-226-10633-0
- ↑ Churchill, Winston. Marlborough: His Life and Times, Bk. 2, vols. iii & iv. University of Chicago Press, (2002). ISBN 0-226-10635-7
- ↑ See Reynolds (2001) and Reynolds (2005)