World War Two in the Pacific
The Pacific War was the part of World War II — and preceding conflicts — that took place in the Pacific Ocean, its islands, and in East Asia, between 1937, and 1945. The most decisive actions took place after the Japan attacked various countries, known as the Allies, in December, 1941, including an attack on United States forces at Pearl Harbor.
Participants
The major Allied participants were the United States and China. The British Commonwealth, including Britain, Australia, New Zealand, and India, and the Netherlands played significant roles. Mexico, DeGaulle's Free French Forces and many other countries also took part, especially forces from other British colonies. The Soviet Union fought two short, undeclared border conflicts with Japan in 1938 and 1939, then remained neutral until August 1945, when it joined the Allies and invaded Manchukuo and Korea.
The Axis states which assisted Japan included the Japanese puppet states of Manchukuo and the Wang Jingwei Government (which controlled most of the population of China). Thailand joined the Axis powers under duress. Japan enlisted many soldiers from its colonies of Korea and Formosa (now called Taiwan). Some German submarines operated in the Indian Ocean.
Conflict between China and Japan
Background
The situation of a weak China unable to resist Japanese demands appeared to be changing toward the end of the 1920s. In 1927, Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek and the National Revolutionary Army of the Kuomintang (KMT) led the Northern Expedition. Chiang was able to defeat the warlords in southern and central China, and was in the process of securing the nominal allegiance of the warlords in northern China. Fearing that the warlord controlling Manchuria, was about to declare his allegiance to Chiang, the Japanese invaded Manchuria in 1931 and set up the puppet state of Manchukuo. The nominal Emperor of this puppet state was better known as Henry Pu Yi of the defunct Qing Dynasty.
Japan's imperialist goals in China were to enhance Japanese prestige as the dominant power in Asia and to have puppet governments in China that would not act against Japanese interests. Japanese actions in Manchuria were roundly criticized and led to Japan's withdrawal from the League of Nations. During the 1930s, China and Japan reached a stalemate with Chiang focusing his efforts at eliminating the Communists, whom he considered to be a more fundamental danger than the Japanese. The influence of Chinese nationalism on opinion both in the political elite and the general population rendered this strategy increasingly untenable.
Meanwhile, in Japan, a policy of assassination by secret societies and the effects of the Great Depression had caused the civilian government to lose control of the military. In addition, the military high command had limited control over the field armies who acted in their own interest, often in contradiction to the overall national interest. Pan-Asianism was used as a justification for expansion. This is perhaps best summarized by the "Amo Doctrine" of 1934, issued by Eiji Amo, head of information department of the Japanese Foreign Ministry. Known as the "Monroe Doctrine of Asia," it announced Japan's intention for European countries to adopt a "hands off" policy in China, thereby negating the Open Door Policy. It stated that Japan was to be the sole leader in security in East Asia, including the task of defeating communism. Economic reason was also a very important factor leading to the invasion of China. During the Great Depression, Japanese exports to American and European markets were severely curtailed, and Japan turned to completely dominating China politically and economically to provide a stable market.
The Second Sino-Japanese War
The "Marco Polo Bridge Incident" in July 7, 1937, started a full-scale war between China and Japan, the "Second Sino-Japanese War". Though the Nationalist and Communist Chinese would cooperate in military campaigns against Japan and sought to create a united national front, Mao Zedong refused to directly submit to the Kuomintang, and the aim of the Communists remained social revolution. In 1939, the Chinese Communist Red Army consisted of 500,000 troops independent of the KMT.
In 1939 Japanese forces tried to push into Siberia, part of the Soviet Union, from Manchuria. They were soundly defeated in the Battle of Halhin Gol by a mixed Soviet and Mongolian force. This stopped Japanese expansion to the North, and Japan and the Soviet Union kept an uneasy peace until 1945.
In addition, throughout the 1930s Japan succeeded in alienating public opinion in the West, particularly the United States and Britain. During the early 1930s, public opinion in the United States had been neutral. However, news reports of the Panay incident caused American public opinion to swing against Japan.
By 1941, Japan had taken control of most major cities, especially along the coast. The KMT had retreated to the interior setting up a provisional capital at Chungking while the Chinese communists remained in control of base areas in Shaanxi. Japanese control of north and central China was somewhat tenuous, in that Japan was usually able to control railroads and the major cities ("points and lines"), but did not have a major military or administrative presence in the vast Chinese countryside. The Japanese found that its aggression against the retreating and regrouping Chinese army was stalled by the mountainous terrain in southwestern China while the Communists organized widespread guerrilla and saboteur activities in eastern and central China behind the Japanese front line.
Japan sponsored several puppet governments, one of which was headed by Wang Jingwei. However, its policies of brutality toward the Chinese population, of not yielding any real power to the governments, and of support to several competing governments failed to make any of them a popular alternative to Chiang's government. Japan was also unwilling to negotiate directly with Chiang, nor was it willing to attempt to create splits in united front against it, by offering concessions that would make it a more attractive alternative than Chiang's government to the former warlords in Chiang's government. Although Japan was deeply mired in a quagmire, Japan's reaction to its situation was to turn to increasingly more brutal and depraved actions in the hope that sheer terror, including massive use of chemical and biological weapons against civilians and use of living civilians for medical and chemical experiments, would break the will of the Chinese population.
War spreads in the East
This, however, only had the effect of turning world public opinion against it. In an effort to discourage Japan's war efforts in China, the United States, Britain, and the Dutch government in exile (still in control of the oil-rich Dutch East Indies) stopped selling oil and steel to Japan. It was known as the "ABCD encirclement" (American-British-Chinese-Dutch) designed to deny Japan of the raw materials needed to continue its war in China. Japan saw this as an act of aggression, as without these resources Japan's military machine would grind to a halt. On December 8, 1941, Japanese forces attacked the British crown colony of Hong Kong, Shanghai, and the Philippines, which was then a United States possession. Japan also used Vichy French bases in French Indochina to invade Thailand, then used the gained Thai territory to launch an assault against Malaya, a British colony.
Simultaneously (on December 7 ), Japanese carrier-based fleet launched a massive air attack on the American air bases and naval fleet at Pearl Harbor, sinking the entire American battleship fleet and giving Japan naval supremacy. Although Japan knew that it could not win a sustained and prolonged war against the United States, it was the Japanese hope that, faced with this sudden and massive defeat, the United States would agree to a negotiated settlement that would allow Japan to have free reign in China. This calculated gamble did not pay off; the United States refused to negotiate. Furthermore, the American losses were less serious than initially thought; the American carriers were out at sea while vital base facilities like the fuel oil storage tanks, whose destruction could have crippled the whole Pacific Fleet's operating capacity by itself, were left untouched.
The United States enters the war
Until the attack on Pearl Harbor, the United States had officially neutral, but in fact was the main supplier of money and munitions to Britain and China, and a major supplier to Soviet Union as wee. The aid went through the Lend-Lease program. Opposition to war in the United States vanished after the attack. On December 11, Nazi Germany declared war on the United States, drawing America into a two-theater war. In 1941, Japan had only a fraction of the manufacturing capacity of the United States, and was therefore perceived as a lesser threat than Germany.
British, Indian and Dutch forces, already drained of personnel and matériel by two years of war with Germany, and heavily committed in the Middle East, North Africa and elsewhere, were unable to provide much more than token resistance to the battle-hardened Japanese. The Allies suffered many disastrous defeats in the first six months of the war. Two major British warships, HMS Repulse and HMS Prince of Wales were sunk by a Japanese air attack off Malaya on December 10, 1941. The government of Thailand surrendered within 24 hours of Japanese invasion and formally allied itself with Japan. Thai military bases were used as a launchpad against Singapore and Malaya. Hong Kong fell on December 25 and U.S. bases on Guam and Wake Island were lost at around the same time.
The Allied governments appointed the British General Sir Archibald Wavell as supreme commander of all "American-British-Dutch-Australian" (ABDA) forces in South East Asia. This gave Wavell nominal control of a huge but thinly-spread force covering an area from Burma to the Dutch East Indies and the Philippines. Other areas, including India, Australia and Hawaii remained under separate local commands.
Japanese offensives, 1942
January, 1942 saw the invasions of Burma, the Dutch East Indies, New Guinea, the Solomon Islands and the capture of Manila, Kuala Lumpur and Rabaul. After being driven out of Malaya, Allied forces were trapped in the Singapore and surrendered to the Japanese on February 15, 1942; about 130,000[1] Indian, Australian and British troops along with Dutch sailors, became prisoners of war. The pace of conquest was rapid: Bali and Timor also fell in February. The rapid collapse of Allied resistance had left the "ABDA area" split in two.
At the Battle of the Java Sea, in late February and early March, the Japanese Navy inflicted a resounding defeat on the main ABDA naval force, under Admiral Karel Doorman. The Netherlands East Indies campaign subsequently ended with the surrender of Allied forces on Java.
The British, under intense pressure, made a fighting retreat from Rangoon to the Indo-Burmese border. This cut the Burma Road which was the western Allies' supply line to the Chinese National army commanded by Chiang Kai-shek. Cooperation between the Chinese Nationalists and the Communists had waned from its zenith at Battle of Wuhan, and the relationship between the two had gone sour as both attempted to expand their area of operations in occupied territories. Most of the Nationalist guerrilla areas were eventually overtaken by the Communists. On the other hand, some Nationalist units, along with collaborationists, were deployed for blockading the Communists rather than against the Japanese. Further, many of the forces of the Chinese Nationalists were warlords allied to Chiang Kai-Shek, but not directly under his command. "Of the 1,200,000 troops under Chiang's control, only 650,000 were directly controlled by his generals, and another 550,000 controlled by warlords who claimed loyalty to his government; the strongest force was the Szechuan army of 320,000 men. The defeat of this army would do much to end Chiang's power."[1] The Japanese used these divisions to press ahead in their offenses.
Filipino and U.S. forces put up a fierce resistance in the Philippines until May 8, 1942; in all than 80,000 men surrendered.
Meanwhile, Japanese aircraft had all but eliminated Allied air power in South-East Asia and were making attacks on Darwin in northern Australia, beginning with a disproportionately large and psychologically devastating raid on Darwin, February 19. A raid by a powerful Japanese Navy aircraft carrier force into the Indian Ocean resulted in the Battle of Ceylon and sinking of the only British carrier, HMS Hermes in the theatre as well as 2 cruisers and other ships effectively driving the British fleet out of the Indian ocean and paving the way for Japanese conquest of Burma and a drive towards India.
The Allies regroup
In early 1942, the governments of smaller powers began to push for an inter-governmental Asia-Pacific war council, based in Washington. The Pacific War Council was set up in Washington on April 1, 1942, but it never had any direct operational control and any recommendations it made were referred to the U.S.-British Combined Chiefs of Staff, which was also in Washington.
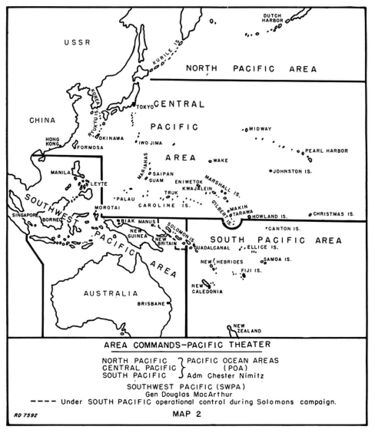
After ABDA became defunct The Americans set up four commands, the Southwest pacific Area, under General Douglas MacArthur in Australia, and three Pacific areas (North, Central and South), all under Admiral Chester Nimitz at Pearl Harbor. The China-Burma-India (CBI) theater was a separate command, involving the British and Chinese, as well as Americans.
Allied resistance, at first symbolic, gradually began to stiffen. Australian and Dutch forces led civilians in a prolonged guerrilla campaign in Portuguese Timor. The Doolittle Raid did minimal damage, but was a huge morale booster for the Allies, especially the United States, and caused repercussions throughout the Japanese military because they were sworn to protect the Japanese emperor and homeland, but did not intercept, down, or damage a single bomber.
Coral Sea and Midway: the turning point
By mid-1942, the Japanese Combined Fleet found itself holding a vast area, even though it lacked the aircraft carriers, aircraft, and aircrew to defend it, and the freighters, tankers, and destroyers necessary to sustain it. Moreover, Fleet doctrine was incompetent to execute the proposed "barrier" defense.[2] Instead, they decided on additional attacks in both the south and central Pacific. While Yamamoto had used the element of surprise at Pearl Harbor, Allied codebreakers now turned the tables. They discovered an attack against Port Moresby, New Guinea was imminent with intent to invade and conquer all of New Guinea. If Port Moresby fell, it would give Japan control of the seas to the immediate north of Australia. Nimitz rushed the carrier Lexington, under Admiral Frank Fletcher, to join Yorktown and a U.S.-Australian task force, with orders to contest the Japanese advance. The resulting Battle of Coral Sea was the first naval battle in which ships involved never sighted each other and aircraft were solely used to attack opposing forces. Although Lexington was sunk and Yorktown seriously damaged, the Japanese lost the aircraft carrier Shōhō, suffered extensive damage to Shōkaku, took heavy losses to the air wing of Zuikaku (both missed the operation against Midway the following month), and saw the Moresby invasion force turn back. Even though losses were almost even, the Japanese attack on Port Moresby was thwarted and their invasion forces turned back, yielding a strategic victory for the allies.
Destruction of U.S. carriers was Yamamoto's main objective and he planned an operation to lure them to a decisive battle. After the Battle of Coral Sea, he had four frontline carriers operational — Sōryū, Kaga, Akagi and Hiryū — and believed Nimitz had a maximum of two: the Enterprise and the Hornet. Saratoga was out of action, undergoing repair after a torpedo attack, and Yorktown sailed after three days' work to repair her flight deck and make essential repairs, with civilian work crews still aboard.
Yamamoto planned to lure Nimitz's carriers into battle, splitting his fleet and thereby gaining a further advantage. A large Japanese force was sent north to attack and invade the Aleutian Islands, off Alaska. The next stage of Yamamoto's plan called for the capture of Midway Atoll, after which it would be turned into a major Japanese airbase. This would give Yamamoto control of the central Pacific, a much better opportunity to destroy Nimitz's remaining carriers, or both. In May, however, Allied codebreakers discovered Midway was the true target. Nagumo was again in tactical command, but was focused on the invasion of Midway; Yamamoto's complex plan had no provision for intervention by Nimitz before the Japanese expected him. Planned surveillance of the U.S. fleet by long range seaplane did not happen (as a result of an abortive identical operation in March), so U.S. carriers were able to proceed to a flanking position on the approaching Japanese fleet without being detected. Nagumo had 272 planes operating from his four carriers, the U.S. 348 (of which 115 were land-based).
As anticipated by American commanders, the Japanese fleet arrived off Midway on June 4 and was spotted by PBY patrol aircraft. By the time the Japanese had launched planes against the island, U.S. Air Force planes had scrambled and were heading for Nagumo's carriers. However, initial U.S. attacks were poorly coordinated, piecemeal, and ineffectual; they failed to score a single hit and half of them were lost. At 09:20 the first carrier aircraft arrived when Hornet's TBD Devastator torpedo bombers attacked; Zero fighters shot down all 15. At 09:35, 15 TBDs from Enterprise skimmed in over the water; 14 were shot down by Zeroes. The carrier aircraft had launched without coordinating their own dive bomber and fighter escort coverage so the torpedo bombers had arrived first, distracted Nagumo's Zeros. When the last of the strike aircraft arrived, the Zeros could not protect his ships against a high-level dive bomber attack. In addition, his four carriers had drifted out of formation, reducing the concentration of their anti-aircraft fire. In his most-criticized error, although Nagumo ordered aircraft armed for shipping attack as a hedge against discovery of American carriers, he changed arming orders twice, based on reports an additional strike was needed against Midway and the sighting of the American task force, wasting time and leaving his hangar decks crowded with refueling and rearming aircraft and ordnance stowed outside the magazines. [3]
When SBD Dauntless dive bombers from Enterprise and Yorktown appeared at 10,000 feet, the Zeroes at sea level were helpless; the dive bombers sank Sōryū, Kaga, and Akagi. Hiryū survived this wave of attacks and launched an attack against the American carriers which caused severe damage to Yorktown (which was later finished off by a Japanese submarine). A second attack from the U.S. carriers a few hours later sank the Hiryū. The battle was over, for Yamamoto's enormous superiority in terms of heavy guns was irrelevant because the U.S. now had air superiority at Midway and could refuse a surface gunfight; his flawed dispositions had made closing to engage after dark on 4 June impossible.[4] Midway was a decisive victory for the U.S. Navy and the end of Japanese offensive aspirations in the Pacific.
New Guinea and the Solomons
Japanese land forces continued to advance in the Solomon Islands and New Guinea. From July, 1942, a few Australian militia battalions, many of them very young and untrained, fought a stubborn rearguard action in New Guinea, against a Japanese advance along the Kokoda Track, towards Port Moresby, over the rugged Owen Stanley Ranges. The Militia, worn out and severely depleted by casualties, were relieved in late August by regular troops from the Second Australian Imperial Force, returning from action in the Middle East.
In early September 1942, Japanese Special Naval Landing Forces ("Japanese marines") attacked a strategic Australian Air Force base at Milne Bay, near the eastern tip of New Guinea. They were beaten back by the Australian Army and some U.S. forces, inflicting the first outright defeat on Japanese land forces since 1939.
Guadalcanal
At the same time as major battles raged in New Guinea, Allied forces spotted a Japanese airfield under construction at Guadalcanal. The Allies made an amphibious landing in August to convert it to their use and start to reverse the tide of Japanese conquests. As a result, Japanese and Allied forces both occupied various parts of Guadalcanal. Over the following six months, both sides fed resources into an escalating battle of attrition on the island, at sea, and in the sky, with eventual victory going to the Allies in February 1943. It was a campaign the Japanese could ill afford. A majority of Japanese aircraft from the entire South Pacific area was drained into the Japanese defense of Guadalcanal. The U.S. Air Forces based at Henderson Field became known as the Cactus Air Force (from the codename for the island), and held their own. The Japanese launched a pair of ill-coordinated attacks on U.S. positions around Henderson Field to suffer bloody repulse and then to suffer even worse losses to starvation and disease during the retreat. These offensives were supplied by a series of ill-considered supply runs (called the "Tokyo Express" by the Americans), often also bringing about night battles with the U.S. Navy, expending destroyers IJN could not spare. Japanese troops named Guadalcanal "The Island of Death" as their fortunes declined. The Japanese survivors were evacuated in another series of "Toyoko Express" runs. The final American assaults found empty camps.
Allied advances in New Guinea and the Solomons
By late 1942, the Japanese were also retreating along the Kokoda Track in the highlands of New Guinea. Australian and U.S. counteroffensives culminated in the capture of the key Japanese beachhead in eastern New Guinea, the Buna-Gona area, in early 1943.
In June 1943, the Allies launched Operation Cartwheel, which defined their offensive strategy in the South Pacific. The operation was aimed at isolating the major Japanese forward base, at Rabaul, and cutting its supply and communication lines. This prepared the way for Nimitz's island-hopping campaign towards Japan.
Stalemate in China and South-East Asia
British Commonwealth forces were also counter-attacking in Burma, albeit with limited success.
In August 1943, the western Allies formed a new South East Asia Command (SEAC) to take over strategic responsibilities for Burma and India from the British India Command, under Wavell. In October 1943, Churchill appointed Admiral Lord Louis Mountbatten as Supreme Allied Commander, SEAC. General William Slim was commander of Commonwealth land forces and directed the Burma Campaign. General Joseph Stilwell commanded U.S. forces in the CBI Theater, directed aid to China and assisted in the coordination of Chinese operations.
In November, 1943 U.S. President Roosevelt, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill, and Chinese leader Chiang Kai-Shek met at the Cairo Conference in Egypt, to discuss a strategy to defeat Japan.
Allied offensives, 1943-44
Midway proved to be the last great naval battle for two years. Admiral King complained that the Pacific deserved 30% of Allied resources but was getting only 15%; he used what he had to neutralize the Japanese forward bases at Rabaul and Truk.
The United States used the two years to turn its vast industrial potential into actual ships, planes, and trained aircrew. At the same time, Japan, lacking an adequate industrial base or technological strategy, and lacking a good aircrew training program, fell further and further behind.
Island hopping
In strategic terms the Allies began a long movement across the Pacific, seizing one island base after another. Not every Japanese stronghold had to be captured; some, like Truk, Rabaul and Formosa were neutralized by air attack and bypassed. The goal was to get close to Japan itself, then launch massive strategic air attacks, improve the submarine blockade, and finally (if necessary) execute an invasion.[5]
On 18 October 1943, land-based aircraft bombed Rabaul [6] This was followed, on 5 November, by a carrier raid that rendered Rabaul ineffective. [7] Still, the U.S. continued to harass Rabaul by air, and with a destroyer raid, into 1944.
In November 1943, Marines sustained high casualties when they overwhelmed the 4,500-strong Japanese garrison at Tarawa. This helped the allies to improve the techniques of amphibious warfare, learning from their mistakes and implementing changes such as thorough pre-emptive bombings and bombardment, more careful planning regarding tides and landing craft schedules, and better overall coordination.
Mahanian doctrine called for a decisive naval battle. The Japanese repeatedly sought such a battle, but the U.S. did not. Instead it pushed closer and closer to the Japanese home islands. The Allied advance could only be stopped by a Japanese naval attack, which became increasingly difficult as Japan ran low on fuel, modern planes, trained pilots and major warships.
Intercepting Yamamoto: equivalent to a fleet victory?
On April 13, 1943, American communications intelligence intercepted messages, in a relatively low-level cryptosystem, giving the inspection itinerary of Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto, commanding the Japanese Combined Fleet. There were points along his inspection tour where long-range fighters could intercept and shoot down his aircraft.
The concern was not especially with the idea that this would be an inappropriate assassination. If the interception was successful, it would be a meeting of military warplanes from both sides, and shooting down a senior commander, in uniform, while in a combat theater. [8] One concern was that the Japanese might realize that the U.S. had broken their secure communications, which would cause them to change systems and risk a major source of intelligence. Another would be Yamamoto's successor -- might a more able admiral replace him? [9]
Edwin Layton, the Pacific Command intelligence officer, presented the risks and benefits to Nimitz. Layton, who personally knew Yamamoto, wrote that he said there was "only one Yamamoto."[10] Layton also wrote "it was impossible for me not to feel for Admiral Yamamoto with a certain sense of fondness." Nevertheless, Layton considered that, if Japan lost an immensely admired commander as well as their best strategist, the effect would be equivalent to a major fleet victory. [9] Layton believed that the U.S. could leak a report that Yamamoto's tour had been reported by Australian coastwatchers, and probably make the Japanese, who were generally overconfident about their communications security,[9] believe their cryptosystem was secure. No operations were planned in the short term, so U.S. forces would have time to attack a new cryptosystem if the Japanese did change. Nimitz, after clearing the decision with the Secretary of the Navy and the President, authorized the mission.
On April 18, Yamamoto died when a force of 18 U.S. Army Air Force P-38 Lightning fighters intercepted and shot down the two bombers carrying staff officers, which were escorted by six Japanese fighters.
There was only one Yamamoto, and no one is able to replace him His loss is an unsupportable blow to us — Adm. Mineichi Koga, Yamamoto's successor
.
Recapture of the Aleutians
On 11 May, U.S. Army forces landed on the Japanese-held island of Attu, in the Alaskan Aleutian chain. It was secured after two weeks of hard fighting. An extensive bombardment preceded the 15 August invasion of nearby Kiska, but the Japanese had evacuated Kiska without the U.S. becoming aware of it. [10]
The submarine war
U.S. submarines (with some aid from the British and Dutch), operating from bases in Australia, Hawaii, and Ceylon, played a major role in defeating Japan. Japanese submarines, however, played a minimal role, although they had the best torpedoes of any nation in the Second World War, and quite good submarines. The difference in results is due to the very different doctrines of the sides, which, on the Japanese side, were based on cultural traditions.
Allied doctrine and equipment
Allied submarines concentrated on destroying Japanese logistics, which was a center of gravity for an island nation. The importance of transport shipping was confirmed by the immense effect of German submarines on Britain, with the Battle of the Atlantic being as critical as the Battle of Britain.
Within hours of Pearl Harbor, Roosevelt ordered a new doctrine into effect: unrestricted submarine warfare against Japan. This meant sinking any warship, commercial vessel, or passenger ship in Axis controlled waters, without warning and without help to survivors.[11]
U.S. torpedoes, the standard issue Mark XIV torpedo and its Mark VI exploder were both defective, problems not corrected until September 1943. Worst of all, before the war, an uninformed Customs officer had seized a copy of the Japanese merchant marine code (called the "maru code" in the USN), not knowing U.S. communications intelligence had broken it;[12] Japan promptly changed it, and it was not recovered until 1943.
Thus it was not until 1944 the U.S. Navy learned to use its 150 submarines to maximum effect: effective shipboard radar installed, commanders seen to be lacking in aggression replaced, and faults in torpedoes fixed.
Japanese doctrine and equipment
For the Imperial Japanese Navy, however, submarines, as part of the Japanese warrior tradition of bushido, preferred to attack warships rather than transports. Faced with a convoy, an Allied submarine would try to sink the merchant vessels, while their Japanese counterparts would give first priority to the escorts. This was important in 1942, before Allied warship production came up to capacity. So, while the U.S. had an unusually long supply line between its west coast and frontline areas that was vulnerable to submarine attack, Japan's submarines were instead used for long range reconnaissance and to resupply strongholds which had been cut off, such as Truk and Rabaul.
Supply runs were a lesser drain on Allied resources. The problem of MacArthur's forces trapped in the Philippines led to diversion of boats to "guerrilla submarine" missions. As well, basing in Australia placed boats under Japanese aerial threat while en route to patrol areas, inhibiting effectiveness, and Nimitz relied on submarines for close surveillance of enemy bases. A small number of oversized submarines handled much of the resupply, submarines that were less agile than their sisters attacking escorted convoys.
Requirements of the Japanese Army to supply cut-off garrisons by submarine further reduced the effectiveness of Japanese anti-shipping warfare. [13] In addition, Japan honored its neutrality treaty with the Soviet Union, and ignored U.S. freighters shipping millions of tons of war supplies from San Francisco to Vladivostok.[14]
A small number of Allied submarines--less than 2 percent of the fleet tonnage--strangled Japan by sinking its merchant fleet, intercepting many troop transports, and cutting off nearly all the oil imports that were essential to warfare. By early 1945 the oil tanks were dry.[15]
Results
U.S. submarines alone accounted for 56% of the Japanese merchantmen sunk; most of the rest were hit by planes at the end of the war, or were destroyed by mines. U.S. submariners also claimed 28% of Japanese warships destroyed.[16] Furthermore they played important reconnaissance roles, as at the battles of the Philippine Sea and Leyte Gulf, when they gave accurate and timely warning of the approach of the Japanese fleet. Submarines operated from secure bases in Fremantle, Australia; Pearl Harbor; Trincomalee, Ceylon; and later Guam. These had to be protected by surface fleets and aircraft.
Fortunately, Japanese convoy protection was "shiftless beyond description"[17] and convoys were poorly organized and defended compared to Allied ones, a product of flawed IJN doctrine and training, errors concealed by American faults as much as Japanese overconfidence. The number of U.S. submarines on patrol at any one time increased from 13 in 1942, to 18 in 1943, to 43 in late 1944. Half of their kills came in 1944, when over 200 subs were operating.[16] By 1945, patrols had decreased because so few targets dared to move on the high seas. In all, Allied submarines destroyed 1,200 merchant ships. Most were small cargo carriers, but 124 were tankers bringing desperately needed oil from the East Indies. Another 320 were passenger ships and troop transports. At critical stages of the Guadalcanal, Saipan, and Leyte campaigns, thousands of Japanese troops were killed before they could be landed. Over 200 warships were sunk, ranging from many auxiliaries and destroyers to eight carriers and one battleship.
The cost
Underwater warfare was especially dangerous; of the 16,000 Americans who went out on patrol, 3,500 (22%) never returned, the highest casualty rate of any American force in World War II.[18] The Japanese losses were even worse.
Japanese counteroffensives in China, 1944
In mid-1944, Japan launched a massive invasion across China, under the code name Operation Ichigo. These attacks, the biggest in several years, gained much ground for Japan before they were stopped in Guangxi.
The beginning of the end in the Pacific, 1944
Saipan and Philippine Sea:
On June 15, 1944, 535 ships began landing 128,000 U.S. Army and Marine personnel on on the island of Saipan. The Allied objective was the creation of airfields — within B-29 range of Tokyo. The ability to plan and execute such a complex operation in the space of 90 days was indicative of Allied logistical superiority.
It was imperative for Japanese commanders to hold Saipan. The only way to do this was to destroy the U.S. 5th Fleet, which had 15 big carriers and 956 planes, 28 battleships and cruisers, and 69 destroyers. Vice Admiral Jisaburo Ozawa attacked with nine-tenths of Japan's fighting fleet, which included nine carriers with 473 planes, 18 battleships and cruisers, and 28 destroyers. Ozawa's pilots were outnumbered 2-1 and their aircraft were becoming obsolete. The Japanese had substantial AA guns, but lacked proximity fuzes and good radar. With the odds stacked against him, Ozawa devised an appropriate strategy. His planes had greater range because they were not weighed down with protective armor; they could attack at about 480 km (300 mi), and could search a radius of 900 km (560 mi). U.S. Navy Hellcat fighters could only attack within 200 miles, and only search within a 325 mile radius. Ozawa planned to use this advantage by positioning his fleet 300 miles out. The Japanese planes would hit the U.S. carriers, land at Guam to refuel, then hit the enemy again, when returning to their carriers. Ozawa also counted on about 500 ground-based planes at Guam and other islands.
Admiral Raymond A. Spruance was in overall command of the 5th Fleet. The Japanese plan would have failed if the much larger U.S. fleet had closed on Ozawa and attacked aggressively; Ozawa had the correct insight that the unaggressive Spruance would not attack. U.S. Admiral Marc Mitscher, in tactical command of Task Force 58, with its 15 carriers, was aggressive but Spruance vetoed Mitscher's plan to hunt down Ozawa because Spruance's personal doctrine made it his first priority to protect the soldiers landing on Saipan.
The forces converged in the largest sea battle of World War II up to that point. Over the previous month American destroyers had destroyed 17 of the 25 submarines Ozawa had sent ahead. Repeated U.S. raids destroyed the Japanese land-based planes. Ozawa's main attack lacked coordination, with the Japanese planes arriving at their targets in a staggered sequence. Following a directive from Nimitz, the U.S. carriers all had combat information centers, which interpreted the flow of radar data instantaneously and radioed interception orders to the Hellcats. The result was later dubbed the Great Marianas Turkey Shoot. The few attackers to reach the U.S. fleet encountered massive AA fire with proximity fuzes. Only one American warship was slightly damaged.
On the second day U.S. reconnaissance planes finally located Ozawa's fleet, 275 miles away and submarines sank two Japanese carriers. Mitscher launched 230 torpedo planes and dive bombers. He then discovered that the enemy was actually another 60 miles further off, out of aircraft range. Mitscher decided that this chance to destroy the Japanese fleet was worth the risk of aircraft losses. Overall, the U.S. lost 130 planes and 76 aircrew. However, Japan lost 450 planes, three carriers and 445 pilots. The Imperial Japanese Navy's carrier force was effectively destroyed.
Leyte Gulf 1944
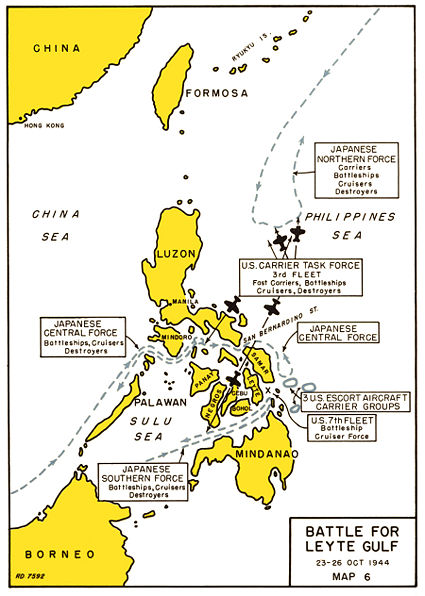
The Battle of Leyte Gulf, October 23-26, 1944, was the largest naval battle in history. It involved coordinated Japanese attacks designed to hit the hundreds of thousands of American soldiers who had just landed at Leyte Gulf, and their supply ships. Severe communications failures on both sides characterized the battle, which ended in a total American victory and the end of Japanese sea power.
Japan was heavily outgunned, so it designed a trick that would neutralize American strength. Sho-1 called for using the remaining Japanese carriers as a decoy, knowing they would all be destroyed, to pull the main American battle fleet, the Third Fleet, north away from the real action. Then two other Japanese fleets would attack Leyte from the center and the south.[19] The plan almost worked, but the Japanese had poor radios and the different units were not in touch; the Japanese Army knew what was happening but it never talked to the Navy and did not help out.
The Americans had a divided command. The small Seventh Fleet, under Vice Admiral Thomas Kincaid, had no fast battleships or big carriers. It had six small escort carriers and several old battleships that had been restored after being sunk at Pearl Harbor. Kincaid reported to MacArthur, and had the mission of defending the landing force. Admiral William Halsey commanded the powerful Third Fleet. He reported to Nimitz (at Pearl Harbor) and thought his mission was to destroy Japanese sea power. Halsey and Kincaid seldom communicated directly, but they did read each other's coded messages and assumed they knew what the other was doing.
Halsey's Third Fleet had numerous task forces including one, Task Force 34, (TF34) comprising four battleships two heavy cruisers, three light cruisers, and two squadrons of destroyers. TF 34 was a contingency force designed to protect San Bernardino Strait; but it was only to form on Halsey's orders, and Halsey never gave the order. Halsey, like the Japanese, was a fervent follower of theorist Alfred Thayer Mahan, who preached victory in great battles; Halsey's main goal was a decisive naval victory over the main Japanese fleet and he did not want to divide his forces by leaving TF 34 behind.
Center: Battle of the Sibuyan Sea
Vice Admiral Kurita's "Center Force" consisted of five battleships, 12 cruisers and 13 destroyers. As they passed Palawan Island after midnight on October 23, the force was spotted and U.S. submarines sank two cruisers. On October 24, as Kurita's force entered the Sibuyan Sea, elements of Halsey's fleet launched 260 planes, which scored hits on several ships. A second wave of planes scored many direct hits on the big battleship Musashi, which sank after being hit by a third wave. Kurita retreated, but in the evening turned around to head for San Bernardino Strait.
Halsey knew Kurita had been defeated and was retreating. Halsey did not notice that Kurita soon turned around and headed back to the San Bernardino Strait. (he ignored vague reports to the contrary.) Halsey did not form TF 34 at this time and he decided to leave the San Bernardino Strait unguarded--everything was pulled out to chase the decoys; not so much as a picket destroyer was left. Meanwhile Kincaid assumed mistakenly that TF 34 was operational, as did Nimitz. [20]
South: Battle of Surigao Strait
Assuming that TF 34 was protecting Leyte from the north, Kincaid now made the blunder of sending his main force south to intercept the third Japanese fleet at Surigao Strait. Nishimura's force consisted of two battleships, one cruiser and four destroyers. It force ran into a trap set by the Seventh Fleet Support Force. Rear Admiral Jesse Oldendorf had six battleships, four heavy cruisers, four light cruisers, 29 destroyers and 39 PT boats. To pass the strait and reach the landings, Nishimura had to run the gauntlet. At about 03:00 the Japanese battleship Fuso and three destroyers were hit by torpedoes and Fuso broke in two. At 03:50 the American battleships opened fire using radar fire control that allowed them to hit targets from a much greater distance than the Japanese. The battleship Yamashiro sank under 16-inch (406 mm) shells and only one of Nishimura's seven ships survived.
North: Battle of Cape Engaño
Ozawa's "Northern Force" had four aircraft carriers, two obsolete battleships partly converted to carriers, three cruisers and nine destroyers. The carriers had only 108 planes. The force was not spotted by the Allies until 16:40 on October 24. Halsey saw an opportunity to destroy Japan's main naval strength. His Third Fleet had nine large carriers, eight light carriers, six battleships, 17 cruisers, 63 destroyers and 1,000 modern planes. Halsey set out in pursuit of Ozawa just after midnight, ignoring confusing reports that perhaps Kurita had turned back towards San Bernardino Strait. On the morning of October 25, Ozawa launched 75 planes, just to be sure Halsey knew where he was. Most were shot down by American fighter patrols. By 08:00 American fighters had destroyed the screen of Japanese fighters and were hitting ships. By evening, they had sunk the carriers Zuikaku, Zuiho, and Chiyoda and hit the fourth carrier, Chitose which soon sank.
Center: Action off Samar
Kurita secretly passed through the San Bernardino Strait at 03:00 on 25 October and headed along the coast of Samar. The only thing standing in his path was three small units of the Seventh Fleet, commanded by Rear Admiral Clifton "Ziggy" Sprague. His "Task Unit 77.4.3" (Taffy 1, 2 and 3) used radio call sign "Taffy Three". Sprague had six small, slow escort carriers, with a total of more than 500 planes, three destroyers and four small destroyer escorts. Sprague was astonished to see Kurita's battleships coming full speed at him at 06:45. Both Halsey's main force and Oldendorf's battleships were now out of range, for the Japanese ruse had succeeded. The 178,000 soldiers on the beaches and on board the transports were helpless.
As his small, slow escort carriers stood little chance against a battleship, Sprague directed the carriers of Taffy 3 to turn and flee eastward, hoping that bad visibility would reduce the accuracy of Japanese gunfire; he sent his destroyers in to divert the Japanese battleships with torpedo attacks that gained ten precious minutes. Three American ships were sunk but they had bought enough time for the Taffy groups to launch planes. Taffy 3 turned south, with shells scoring hits on some of its carriers, and sinking one of them. The superior speed of the Japanese force allowed it to draw closer and fire on the other two Taffy groups. Sprague sent planes with no bombs or torpedoes to make dummy runs to further distracted the battleships.
During this fight, Kinkaid sent repeated pleas for help--one of them unencrypted --calling for TF 34 to support his ships, against the major Japanese surface units. Halsey, still racing north, ignored the pleas. At that point, Nimitz at Pearl Harbor, who believed TF 34 was operational, sent Halsey his own message.
At the time, U.S. communications procedures called for prefixing (after the address header) and suffixing nonsense text to the actual message, and then encrypting the entire message as a unit. The nonsense text was not supposed to have any relationship to the message, and was to be separated by doubled letters from the real text. In this case, Nimitz's actual message was:
WHERE IS TASK FORCE 34As the ensign in the communications center later said [9] that he put down the first phrases that "popped into his head". The prefix, TURKEY TROTS TO WATER indeed was meaningless, but the suffix THE WHOLE WORLD WONDERS is from a poem about the Charge of the Light Brigade. The message sent, therefore, read:
FROM: CINCPAC
TO: COMTHIRDFLEET
TURKEY TROTS TO WATER RR
WHERE IS TASK FORCE 34 RR
THE WORLD WONDERS
The receiving communications officer clearly recognized the nonsense prefix and deleted it, but the suffix was sufficiently pertinent that he decided it was part of the message. What Halsey actually saw, therefore, was:
FROM: CINCPAC
TO: COMTHIRDFLEET
WHERE IS TASK FORCE 34 THE WORLD WONDERS
While a violation in communications procedure, unknown to Halsey, caused the "message" to read as it did, he took it as a personal insult. He recalled, "I was as stunned as if I had been struck in the face." It was a humiliation for Halsey who turned around his force to assist Kinkaid.[21]
Suddenly the Japanese made a momentous mistake. Kurita mistook the small Taffy carriers for large fleet carriers and thought he faced the whole Third Fleet that was far stronger, so he did not realize he faced only a much weaker force that he could have crushed. At 09:20 Kurita, only two hours from his destination and with victory over the helpless soldiers almost in his grasp, suddenly disobeyed his orders and turned back, racing north at top speed. He later gave many reasons, none very clear. Japanese communications were so poor he did not know the decoy plan had worked; he greatly exaggerated the threat to his force. American destroyer attacks had broken the Japanese formations, shattering tactical control, and two of Kurita's heavy cruisers had been sunk, and the threat of massive attacks was on Kurita's mind, he later said. Kurita retreated through the San Bernardino Strait, where he did encounter Halsey racing south.[22] The Japanese land based Kamikaze planes now showed up to attack Sprague, sinking one small carrier, but it was too little, too uncoordinated and too late. (It was the first use of the Kamikaze tactic.) Sprague had lost five of his thirteen ships and 105 planes, but was the hero of the victory.
Aftermath
The battle secured the beachheads of MacArthur's forces on Leyte against attack from the sea, permanently ended Japanese naval power and opened the way for an invasion of Okinawa in June 1945.
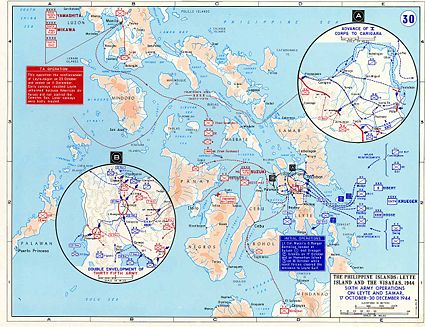
The Philippines, 1944-45

On 20 October 1944, the U.S. Sixth Army, supported by naval and air bombardment, landed on the favorable eastern shore of Leyte, one of the three large Philippine Islands, north of Mindanao. The U.S. Sixth Army continued its advance from the east, as the Japanese rushed reinforcements to the Ormoc Bay area on the western side of the island. While the Sixth Army was reinforced successfully, the U.S. Fifth Air Force was able to devastate the Japanese attempts to resupply. In torrential rains and over difficult terrain, the advance continued across Leyte and the neighboring island of Samar to the north. On 7 December 1944, U.S. Army units landed at Ormoc Bay and, after a major land and air battle, cut off the Japanese ability to reinforce and supply Leyte. Although fierce fighting continued on Leyte for months, the U.S. Army was in control.
On 15 December 1944, landings against minimal resistance were made on the southern beaches of the island of Mindoro, a key location in the planned Lingayen Gulf operations, in support of major landings scheduled on Luzon. On 9 January 1945, on the south shore of Lingayen Gulf on the western coast of Luzon, General Krueger's Sixth Army landed his first units. Almost 175,000 men followed across the twenty-mile beachhead within a few days. With heavy air support, Army units pushed inland, taking Clark Field, 40 miles northwest of Manila, in the last week of January.
Two more major landings followed, one to cut off the Bataan Peninsula, and another, that included a parachute drop, south of Manila. Pincers closed on the city and, on 3 February 1945, elements of the 1st Cavalry Division pushed into the northern outskirts of Manila and the 8th Cavalry passed through the northern suburbs and into the city itself.
As the advance on Manila continued from the north and the south, the Bataan Peninsula was rapidly secured. On 16 February, paratroopers and amphibious units assaulted Corregidor, and resistance ended there on 27 February.
In all, ten U.S. divisions and five independent regiments battled on Luzon, making it the largest campaign of the Pacific war, involving more troops than the United States had used in North Africa, Italy, or southern France.
Palawan Island, between Borneo and Mindoro, the fifth largest and western-most Philippine Island, was invaded on 28 February, with landings of the Eighth Army at Puerto Princesa. The Japanese put up little direct defense of Palawan, but cleaning up pockets of Japanese resistance lasted until late April, as the Japanese used their common tactic of withdrawing into the mountain jungles, disbursed as small units. Throughout the Philippines, U.S. forces were aided by Filipino guerrillas to find and dispatch the holdouts.
The U.S. Eighth Army then moved on to its first landing on Mindanao (17 April), the last of the major Philippine Islands to be taken. Mindanao was followed by invasion and occupation of Panay, Cebu, Negros and several islands in the Sulu Archipelago. These islands provided bases for the U.S. Fifth and Thirteenth Air Forces to attack targets throughout the Philippines and the South China Sea.
The final stages of the war
Allied offensives in Burma, 1944-45
The British launched a series of offensive operations back into Burma during late 1944 and the first half of 1945. Command of the British formations on the front was rearranged in November 1944; the 11th Army Group was replaced with Allied Land Forces South East Asia.
The Japanese Burma Area Army withdrew the 15th Army behind the Irrawaddy River (Operation BAN). 28th Army was to continue to defend the Arakan and lower Irrawaddy valley (Operation KAN), while 33rd Army would attempt to prevent the completion of the new Ledo Road between India and China by defending Bhamo and Lashio, and mounting guerrilla raids (Operation DAN).
In Arakan, as the monsoon ended, the British Commonwealth XV Corps resumed its advance on Akyab Island for the third year in succession. This time the Japanese were numerically far weaker, and had already lost the most favorable defensive positions. The Indian 25th Infantry Division advanced on Foul Point and Rathedaung at the end of the Mayu Peninsula, while the West African 81st Division and West African 82nd Division converged on Myohaung at the mouth of the Kaladan River. The Japanese evacuated Akyab Island on December 31, 1944. It was occupied by XV Corps without resistance two days later.
Following the incursion into western Burma, XV Corps operations were halted in order to transfer transport aircraft to support U.S. Fourteenth Army. With the coastal area secured the Allies were free to build sea-supplied airbases on the two offshore islands, Ramree Island and Cheduba. Cheduba, the smaller of the two islands, had no Japanese garrison, but the clearing of the small but typically tenacious Japanese garrison on Ramree took about six weeks
NCAC's operations were limited from late 1944 onwards by the need for Chinese troops on the main front in China. The American and British commanders attacked the Chinese leadership's decision to focus their limited resources on the defensive of Chinese cities rather than the defeat of the Japanese in Burma. In spite of these limitations, General Sultan was still able to resume his advance against the Japanese 33rd Army.
On his right, the British 36th Infantry Division, brought in to replace the Chindits, made contact with the Indian 19th Infantry Division near Indaw on December 10, 1944, and Fourteenth Army and NCAC now had a continuous front. Meanwhile, three Chinese divisions and a US Force known as the "Mars Brigade" (which had replaced Merrill's Marauders) advanced slowly from Myitkyina to Bhamo. The Japanese resisted for several weeks, but Bhamo fell on December 15.
Sultan's forces made contact with Chiang's Yunnan armies on January 21, 1945, and the Ledo road could finally be completed, although it was not yet secure. The Ledo road by this point in the war was also of uncertain value. It would not be completed soon enough to change the overall military situation in China. Chiang, to the annoyance of the British and Americans, ordered Sultan to halt his advance at Lashio, which was captured on March 7. In April, OSS Detachment 101 took over control of American forces from the NCAC, which had withdrawn to China, while the 36th Division withdrew to India.
Fourteenth Army made the main thrust into central Burma. It had IV Corps and XXXIII Corps under its command, with six infantry divisions, two armoured brigades and three independent infantry brigades. Logistics were the primary problem the advance faced. A carefully designed system involving large amounts of supply by air was introduced as well endless construction projects designed to improve the land route from India into Burma.
When it was realised that the Japanese had fallen back behind the Irrawaddy River, the plan was modified. Initially both corps had been attacking into the Shwebo Plain between the Chindwin and Irrawaddy rivers. Now, only XXXIII Corps would continue this attack, while IV Corps changed its axis of advance to the Gangaw Valley west of the Chindwin, aiming to cross the Irrawaddy close to Pakokku and then capture the main Japanese line of communication centre of Meiktila. Diversionary measures (such as dummy radio traffic) would persuade the Japanese that both corps were aimed at Mandalay.
The plan was completely successful. Allied air superiority and the thin Japanese presence on the ground meant that the Japanese were unaware of the strength of the force moving on Pakokku. During January and February, XXXIII Corps seized crossings over the Irrawaddy River near Mandalay. There was heavy fighting, which attracted Japanese reserves and fixed their attention. Late in February, Indian 7th Division, leading IV Corps, seized crossings at Nyaungu, near Pakokku. Indian 17th Division and 255th Indian Armoured brigade followed them across and struck for Meiktila.
While the Japanese were distracted by events at Meiktila, XXXIII Corps had renewed its attack on Mandalay. It fell to Indian 19th Division on March 20, though the Japanese held the former citadel of Fort Dufferin for another week. The battle was extremely costly in that much of the historically and culturally significant portions of Mandalay, including the old royal palace were burned to the ground. With the fall of Mandalay (and of Maymyo to its east), communications to the Japanese front in the north of Burma were cut. The Japanese 15th Army was completely scattered, leaving only small detachments and parties of stragglers making their way east.
The Allied armies continued their southward drive towards Rangoon, with the goal of capturing the vital port before the monsoon season cut the overland supply routes. IV Corps made the main attack, down the "Railway Valley" by striking at the delaying position held by the remnants of Japanese 33rd Army at Pyawbwe. The Indian 17th Division and 255th Armoured Brigade were initially halted by a strong defensive position behind a dry chaung, but a flanking move by tanks and mechanized infantry struck the Japanese from the rear and shattered them. Following the route of the 33rd Army, organized resistance along the route to Rangoon all but ceased.
A general uprising delayed the Japanese 15th Division long enough for the Allied forces to reach the city of Toungoo, only 136 miles from Rangoon. The Indian 17th Division reached Pegu, 40 miles north of Rangoon by April 25th. Kimura had formed the various service troops, naval personnel and even Japanese civilians in Rangoon into the Japanese 105 Independent Mixed Brigade. This scratch formation used buried aircraft bombs, anti-aircraft guns and suicide attacks with pole charges to delay the British advance, holding the British off until April 30, and covered the evacuation of the Rangoon area.
General Slim feared that the Japanese would defend Rangoon to the last man through the monsoon, which would put Fouteenth Army in a disastrous supply situation. His lines of communication by land were impossibly long, and the troops relied on supplies ferried by aircraft to airfields close behind the leading troops. Heavy rain would make these airfields unusable, and curtail flying. However, Kimura had ordered Rangoon to be evacuated, starting on April 22. Many troops were evacuated by sea, although British submarines claimed several ships. Kimura's own HQ left by land. The Japanese 105 Independent Mixed Brigade, by holding Pegu, covered this evacuation.
On May 1, a Gurkha parachute battalion was dropped on Elephant Point, and cleared Japanese rearguards from the mouth of the Rangoon River. The Indian 26th Infantry Division landed the next day and took over Rangoon, which had seen an orgy of looting and lawlessness similar to the last days of the British in the city in 1942. Following the capture of Rangoon, there were still Japanese forces to take care of in Burma, but it was largely a mopping up operation.
The liberation of Borneo
The Borneo Campaign of 1945 was the last major Allied campaign in the South West Pacific Area. In a series of amphibious assaults between May 1 and July 21, the Australian I Corps, under General Leslie Morshead, attacked Japanese forces occupying the island. Allied naval and air forces, centred on the U.S. 7th Fleet under Admiral Thomas Kinkaid, the Australian First Tactical Air Force and the U.S. Thirteenth Air Force also played important roles in the campaign.
The campaign opened with a landing on the small island of Tarakan on May 1. This was followed on June 1 by simultaneous assaults in the north west, on the island of Labuan and the coast of Brunei. A week later the Australians attacked Japanese positions in North Borneo. The attention of the Allies then switched back to the central east coast, with the last major amphibious assault of World War II, at Balikpapan on July 1.
Although the campaign was criticised in Australia at the time, and in subsequent years, as pointless or a "waste" of the lives of soldiers, it did achieve a number of objectives, such as increasing the isolation of significant Japanese forces occupying the main part of the Dutch East Indies, capturing major oil supplies and freeing Allied prisoners of war, who were being held in deteriorating conditions.
Iwo Jima
Okinawa
- see Okinawa, battle of
- see Kamikaze
Landings in the Japanese home islands
Hard-fought battles on the Iwo Jima and Okinawa resulted in horrific casualties on both sides, but finally produced a Japanese retreat. Faced with the loss of most of their experienced pilots, the Japanese increased their use of Kamikaze tactics in an attempt to create unacceptably high casualties for the Allies, who were now joined by the British fleet. Upwards of a third of the U.S. fleet was hit, and the U.S. Navy recommended against an invasion of Japan in 1945. It proposed to force a Japanese surrender through a total naval blockade and air raids.
Towards the end of the war as the role of strategic bombing became more important, a new command for the U.S. Strategic Air Forces in the Pacific was created to oversee all U.S. strategic bombing in the hemisphere, under Air Force General Curtis LeMay. Japanese industrial production plunged as nearly half of the built-up areas of 64 cities were destroyed by B-29 firebombing raids. On March 9-10, 1945 alone, about 100,000 people were killed in a fire storm caused by an attack on Tokyo. In addition, LeMay also oversaw Operation Starvation which the interior waterways of Japan were extensively mined by air which seriously disrupted the enemy's logistical operations.
The atomic bomb
In August of 1945 the U.S. attacked two cities with nuclear weapons; on August 6 , Hiroshima was destroyed with a single atomic bomb, as was Nagasaki on August 9. More than 200,000 people died as a direct result of these two bombings, but policy makers argued that even more lives were saved because Japan quickly ended the war.[23]
In February, 1945, Stalin agreed with Roosevelt to enter the Pacific conflict. He promised to act 90 days after the war ended in Europe and did so exactly on schedule on August 9, by launching Operation August Storm. A battle-hardened, one million-strong Soviet force, transferred from Europe attacked Japanese forces in Manchuria and quickly defeated their Kwantung Army.
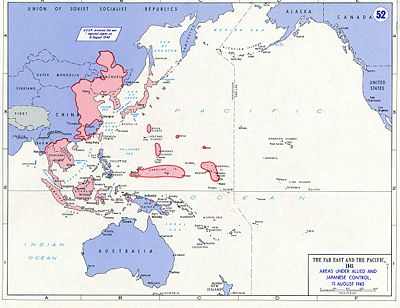
Imperial Japan surrendered on August 15, "V-J Day". The formal surrender was signed on September 2, 1945, on an American battleship in Tokyo Bay. The surrender was accepted by General Douglas MacArthur as Supreme Allied Commander, with representatives of each Allied nation..
A separate surrender ceremony between Japan and China was held in Nanking on September 9, 1945.
Following this period, MacArthur went to Tokyo to oversee the postwar development of the country. This period in Japanese history is known as the occupation.
Timeline
Second Sino-Japanese war
- 7 July 1937 – 9 September 1945
Japanese conquest of Southeast Asia and Pacific
- 1941-12-07 (12-08 Japan Standard Time|Asian Time) Attack on Pearl Harbor
- 1941-12-08 Japanese Invasion of Thailand
- 1941-12-08 – 1941-12-25 Battle of Hong Kong
- 1941-12-08 – 1942-01-31 Battle of Malaya
- 1941-12-10 Sinking of Prince of Wales and Repulse|Sinking of HMS Prince of Wales (1939)|HMS Prince of Wales and HMS Repulse (1916)|HMS Repulse
- 1941-12-11 – 1941-12-24 Wake Island#World War II|Battle of Wake Island
- 1941-12-16 – 1942-04-01 Borneo campaign (1942)
- 1941-12-22 – 1942-05-06 Battle of the Philippines (1941-42)|Battle of the Philippines
- 1942-01-01 – 1945-10-25 Transport of POWs via Hell Ships
- 1942-01-11 – 1942-01-12 Battle of Tarakan (1942)|Battle of Tarakan
- 1942-01-23 Battle of Rabaul (1942)
- 1942-01-24 Naval Battle of Balikpapan
- 1942-01-25 Thailand declares war on the Allies
- 1942-01-30 – 1942-02-03 Battle of Ambon
- 1942-01-30 – 1942-02-15 Battle of Singapore
- 1942-02-04 Battle of Makassar Strait
- 1942-02-14 – 1942-02-15 Battle of Palembang
- 1942-02-19 Air raids on Darwin, February 19, 1942|Air raids on Darwin, Australia
- 1942-02-19 – 1942-02-20 Battle of Badung Strait
- 1942-02-19 – 1943-02-10 Battle of Timor (1942-43)
- 1942-02-27 – 1942-03-01 Battle of the Java Sea
- 1942-03-01 Battle of Sunda Strait
- 1942-03-01 – 1942-03-09 Battle of Java (1942)|Battle of Java
- 1942-03-31 – 1942-04-10 Indian Ocean raid
- 1942-04-09 Bataan Death March begins
- 1942-04-18 Doolittle Raid
- 1942-05-03 invasion of Tulagi (May 1942)|Japanese invasion of Tulagi
- 1942-05-04 – 1942-05-08 Battle of the Coral Sea
- 1942-05-31 – 1942-06-08 Attack on Sydney Harbour|Attacks on Sydney Harbour area, Australia
- 1942-06-04 – 1942-06-06 Battle of Midway
Pacific War campaigns
Burma Campaign: 1941-12-16 – 1945-08-15
New Guinea campaign
- 1942-01-23 – Battle of Rabaul
- 1942-03-07 – Operation Mo (Japanese invasion of New Guinea)
- 1942-05-04 – 1942-05-08 Battle of the Coral Sea
- 1942-07-01 – 1943-01-31 Kokoda Track Campaign
- 1942-08-25 – 1942-09-05 Battle of Milne Bay
- 1942-11-19 – 1942-01-23 Battle of Buna-Gona
- 1943-01-28 – 1943-01-30 Battle of Wau
- 1943-03-02 – 1943-03-04 Battle of the Bismarck Sea
- 1943-06-29 – 1943-09-16 Battle of Lae
- 1943-06-30 – 1944-03-25 Operation Cartwheel
- 1943-09-19 – 1944-04-24 Finisterre Range campaign
- 1943-09-22 – 1944-01-15 Huon Peninsula campaign
- 1943-11-01 – 1943-11-11 Attack on Rabaul
- 1943-12-15 – 1945-08-15 New Britain campaign
- 1944-02-29 – 1944-03-25 Admiralty Islands campaign
- 1944-04-22 – 1945-08-15 Western New Guinea campaign
Aleutian Islands campaign
- 1942-06-07 – 1943-08-15 Battle of Kiska
Guadalcanal campaign
- 1942-08-07 – 1943-02-09 Battle of Guadalcanal
- 1942-08-09 Battle of Savo Island
- 1942-08-24 – 1942-08-25 Battle of the Eastern Solomons
- 1942-10-11 – 1942-10-12 Battle of Cape Esperance
- 1942-10-25 – 1942-10-27 Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands
- 1942-11-13 – 1942-11-15 Naval Battle of Guadalcanal
- 1942-11-30 Battle of Tassafaronga
Solomon Islands campaign
- 1943-01-29 – 1943-01-30 Battle of Rennell Island
- 1943-03-06 Battle of Blackett Strait
- 1943-06-10 – 1943-08-25 Battle of New Georgia
- 1943-07-06 Battle of Kula Gulf
- 1943-07-12 – 1943-07-13 Battle of Kolombangara
- 1943-08-06 – 1943-08-07 Battle of Vella Gulf
- 1943-08-17 – 1943-08-18 Battle off Horaniu
- 1943-10-07 Battle of Vella Lavella
- 1943-11-01 – 1945-08-21 Battle of Bougainville
- 1943-11-01 – 1943-11-02 Battle of Empress Augusta Bay
- 1943-11-26 Battle of Cape St. George
Gilbert Islands campaign
- 1943-11-20 – 1943-11-23 Battle of Tarawa
- 1943-11-20 – 1943-11-24 Battle of Makin
Marshall Islands campaign
- 1944-01-31 – 1944-02-07 Battle of Kwajalein
- 1944-02-16 – 1944-02-17 Operation Hailstone (attack on Truk)
- 1944-02-16 – 1944-02-23 Battle of Eniwetok
Mariana Islands campaign
- 1944-06-15 – 1944-07-09 Battle of Saipan
- 1944-06-19 – 1944-06-20 Battle of the Philippine Sea
- 1944-07-21 – 1944-08-10 Battle of Guam
- 1944-07-24 – 1944-08-01 Battle of Tinian
Palau Islands campaign
- 1944-09-15 – 1944-11-25 Battle of Peleliu
- 1944-09-17 – 1944-09-30 Battle of Angaur
Philippines campaign
- 1944-10-20 – 1944-12-10 Battle of Leyte
- 1944-10-24 – 1944-10-25 Battle of Leyte Gulf
- 1944-11-11 – 1944-12-21 Battle of Ormoc Bay
- 1944-12-15 – 1945-07-04 Battle of Luzon
- 1945-01-09 Invasion of Lingayen Gulf
- 1945-02-27 – 1945-07-04 Southern Philippines campaign
Ryukyu Islands campaign
- 1945-02-16 – 1945-03-26 Battle of Iwo Jima
- 1945-04-01 – 1945-06-21 Battle of Okinawa
- 1945-04-07 Operation Ten-Go
Borneo campaign
- 1945-05-01 – 1945-05-25 Battle of Tarakan
- 1945-06-10 – 1945-06-15 Battle of Brunei
- 1945-06-10 – 1945-06-22 Battle of Labuan
- 1945-06-17 – 1945-08-15 Battle of North Borneo
- 1945-07-07 – 1945-07-21 Battle of Balikpapan (1945)|Battle of Balikpapan
Japan campaign
- 1944-45 Bombings of Japanese cities
- 194-45 Mining Inland Sea
- 1945-07-22 Battle of Tokyo Bay
- 1945-08-06 – 1945-08-09 Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
notes
- ↑ Edwin P. Hoyt, Japan's War (1986) pp. 262-263.
- ↑ Parillo, Japanese Merchant Marine; Peattie & Evans, Kaigun.
- ↑ Willmott, Barrier and the Javelin; however see Dallas Woodbury Isom, "The Battle of Midway." Naval War College Review, (2000), Vol. 53, Issue 3 in EBSCO, regarding the exact timing.
- ↑ Willmott, Barrier and the Javelin.
- ↑ The technique of amphibious landings to seize forward bases in preparation for a great fleet battle was propounded in 1921 by U.S. Marine MAJ Earl H. Ellism Advanced Base Operations in Micronesia (1921) [http://www.ibiblio.org/hyperwar/USMC/ref/AdvBaseOps/index.html#contents online
- ↑ Cleaver, Thomas McKelvey (August 2004), "Raid on Rabaul: B-25 gunships terrorize Japanese shipping", Flight Journal
- ↑ Carrier Raid on Rabaul (November 5, 1943)
- ↑ Grant, Rebecca (March 2006), "Magic and Lightning", Air Force Magazine 89 (3)
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 Kahn, David (1996). The Codebreakers - The Story of Secret Writing. Scribners. ISBN 0684831309.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Layton, Edwin T.; Roger Pineau & John Costello (1985), And I Was There, William Morris
- ↑ The U.S. thereby reversed its opposition to unrestricted submarine warfare. After the war, when moralistic doubts about Hiroshima and other raids on civilian targets were loudly voiced, no one ever criticized Roosevelt's submarine policy. The top German admirals, Erich Raeder and Karl Dönitz, were charged at the Nuremberg War Crimes Trials of violating international law through unrestricted submarine warfare; they were acquitted after proving British merchantmen were legitimate military targets under the rules in force at the time.
- ↑ Ladislas Farago, Broken Seal.
- ↑ Clay Blair, Silent Victory: The U. S. Submarine War Against Japan (1975) and Theodore Roscoe, United States Submarine Operations in World War II (1949).
- ↑ Carl Boyd, "The Japanese Submarine Force and the Legacy of Strategic and Operational Doctrine Developed Between the World Wars," in Larry Addington ed. Selected Papers from the Citadel Conference on War and Diplomacy: 1978 (1979) 27–40; Clark G. Reynolds, Command of the Sea: The History and Strategy of Maritime Empires (1974) 512.
- ↑ Submariners systematically avoided publicity, in order to encourage enemy overconfidence. Japan thought its defensive techniques sank 468 American subs; the true figure was only 42. (Ten others went down in accidents, the Atlantic Ocean, or as the result of friendly fire.) Submarines also rescued hundreds of downed fliers, most famously George H. W. Bush.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Larry Kimmett and Margaret Regis, U.S. Submarines in World War II
- ↑ Chihaya Masataka, in Pearl Harbor Papers, p.323. Chihaya went on to note, when IJN belatedly improved its ASW methods, the Sub Force responded by increasing Japanese loses.
- ↑ Roscoe, op. cit.
- ↑ For the relative strengths of the fleets see Vincent P. O'Hara, The U.S. Navy Against the Axis: Surface Combat, 1941-1945 (2007) pp 261-2
- ↑ C. Vann Woodward, The Battle of Leyte Gulf, (1947), p. 74, 80-81
- ↑ Halsey complained, "I turned my back on the opportunity I had dreamed of since my days as a cadet. For me, one of the biggest battles of the war was off." William F. Halsey with J. Bryan, Admiral Halsey's Story (1947) pp. 220-1
- ↑ Woodward, The Battle for Leyte Gulf 200-6 for interviews with Kurita and his senior staff; David Sears, The Last Epic Naval Battle: Voices from Leyte Gulf (2005) p. 150
- ↑ Precise figures are not available, but the firebombing together with the nuclear bombing between March and August 1945 may have killed more than one million Japanese civilians. Official estimates from the United States Strategic Bombing Survey put the figures at 330,000 people killed, 476,000 injured, 8.5 million people made homeless and 2.5 million buildings destroyed.