DDT
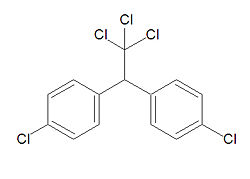
DDT, abbreviated from Dichloro-diphenyl-trichloroethane, but correctly called by its IUPAC name 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane is an organochlorine pesticide that is very effective at killing mosquitoes and was used effectively in the fight against malaria.[1]
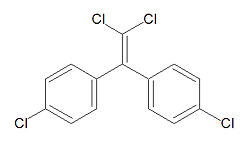
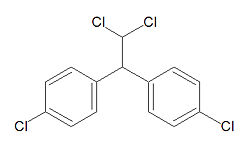
The campaign against DDT was started by Rachel Carson with her book Silent Spring. While DDT itself is safe, DDT breaks down into DDE(dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene) and DDD(dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane).[2] DDE has been classified as a possible carcinogen by the EPA.[3]
DDT was banned in 1972 by the Environmental Protection Agency under Administrator William Ruckelshaus, but it is still used in some countries.[4]
Legacy
The use of DDT along the Saint Lawrence River valley continues to have an impact the river's Beluga whales, though the chemical has long been banned. [5]
References
- ↑ http://www.aaenvironment.com/DDT.htm
- ↑ http://www.eco-usa.net/toxics/ddt.shtml
- ↑ http://www.epa.gov/ttn/atw/hlthef/dde.html
- ↑ http://www.aaenvironment.com/DDT.htm
- ↑ Pollution stunts Canada's beluga whales, Agence France Presse, 2007-09-02. Retrieved on 2008-02-06.